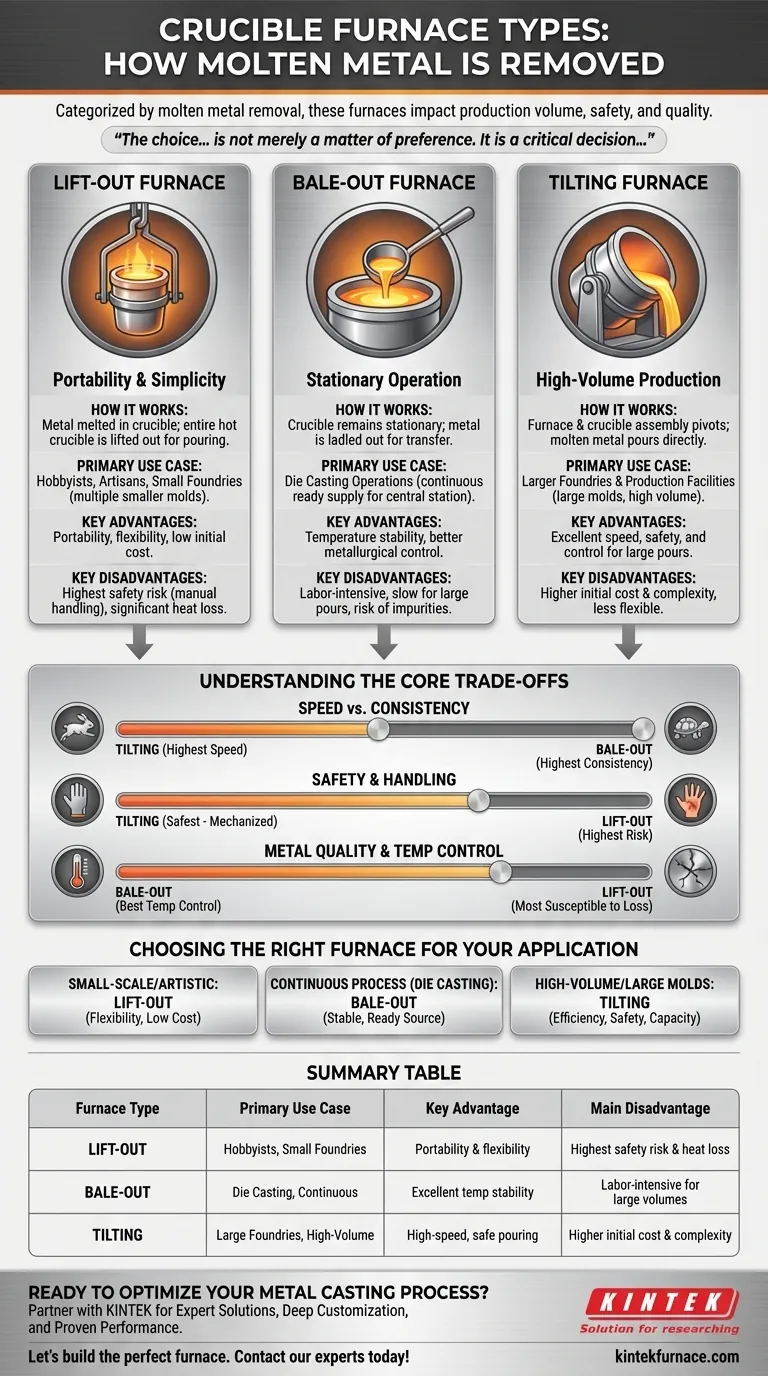
In metal casting operations, crucible furnaces are categorized into three distinct types based on how molten metal is removed from the crucible. These are the lift-out furnace, where the entire crucible is removed for pouring; the bale-out furnace, where metal is ladled out from a stationary crucible; and the tilting furnace, where the entire furnace assembly pivots to pour the metal directly. Each design serves a different operational scale and purpose.
The choice between a lift-out, bale-out, or tilting furnace is not merely a matter of preference. It is a critical decision that directly impacts production volume, operational safety, energy efficiency, and the quality of the final casting.

The Lift-Out Furnace: Portability and Simplicity
The lift-out design is the most basic type of crucible furnace, often favored in small-scale operations.
How It Works
In this setup, the metal is melted within a crucible that sits inside the furnace. Once the metal reaches the desired temperature, the furnace lid is opened, and the entire crucible—glowing hot and full of molten metal—is lifted out using special tongs. It is then carried to the mold for pouring.
Primary Use Case
Lift-out furnaces are the standard for hobbyists, artisans, and small foundries that require direct pouring into multiple, smaller molds. Their flexibility is a key advantage.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit is portability. A single furnace can serve numerous molds located away from the furnace area. They are also relatively simple and have a lower initial cost.
Key Disadvantages
This method poses the highest safety risk due to the need to manually carry a crucible of molten metal. It also results in significant heat loss as the crucible is removed from the heat source, which can affect metal quality if the pouring process is slow.
The Bale-Out Furnace: Stationary Operation
Bale-out furnaces are designed for applications where a continuous, ready supply of molten metal is needed at a central station.
How It Works
The crucible remains stationary inside the furnace, which constantly maintains the metal at the target temperature. Workers use a hand ladle to "bale out" or scoop molten metal from the crucible and transfer it to nearby molds.
Primary Use Case
This design is ideal for die casting operations where casting machines are arranged around the furnace. It provides a consistent reservoir of molten metal for repeated, smaller pours.
Key Advantages
The main advantage is temperature stability, as the crucible never leaves the furnace. This leads to better metallurgical control. It is also safer than the lift-out method, as only a small ladle of metal is moved at a time.
Key Disadvantages
The process is labor-intensive and slow for pouring large castings. There is also a risk of introducing impurities or dross into the ladle with each scoop if not done carefully.
The Tilting Furnace: High-Volume Production
Tilting furnaces represent a solution for pouring large quantities of metal quickly and safely.
How It Works
The entire furnace and crucible assembly are mounted on a pivot. A mechanical or hydraulic system is used to tilt the furnace, pouring the molten metal directly from a spout into a large ladle or mold.
Primary Use Case
These furnaces are the workhorses of larger foundries and production facilities that need to pour large molds or transfer significant volumes of metal efficiently.
Key Advantages
Tilting furnaces offer excellent speed, safety, and control for large-volume pours. The mechanical tilting mechanism minimizes manual handling and associated risks.
Key Disadvantages
They have a higher initial cost and complexity compared to the other types. Their stationary nature also means they are less flexible for serving widely dispersed molds.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace requires balancing the relationship between volume, safety, and operational efficiency.
Speed vs. Consistency
A tilting furnace offers the highest speed for large-volume pours. A bale-out furnace offers the highest consistency for a continuous process. A lift-out furnace is the most flexible but generally the slowest for overall throughput due to handling time.
Safety and Handling
The lift-out method involves the highest risk, requiring operators to carry the entire volume of molten metal. The bale-out method reduces this risk to a single ladle's worth. The tilting furnace is inherently the safest, as it mechanizes the pouring of large volumes and minimizes operator exposure.
Metal Quality and Temperature Control
The bale-out furnace provides the best temperature control, as the metal bath remains heated. The lift-out furnace is most susceptible to rapid temperature loss during transfer, which can lead to premature solidification and casting defects. The tilting furnace offers a good balance, minimizing transfer time for large pours.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your specific production requirements.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting or artistic work: The flexibility and low cost of a lift-out furnace make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is supplying a continuous process like die casting: The bale-out furnace provides the stable, ready source of molten metal necessary for consistent production.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and pouring large molds: The tilting furnace offers the unmatched efficiency, safety, and capacity required for industrial-scale work.
Understanding these fundamental differences ensures you select a furnace that aligns with your production goals, safety standards, and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Main Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lift-Out | Hobbyists, small foundries, multiple small molds | Portability and flexibility | Highest safety risk and heat loss |
| Bale-Out | Die casting, continuous process operations | Excellent temperature stability and control | Labor-intensive for large volumes |
| Tilting | Large foundries, high-volume production | High-speed, safe pouring of large quantities | Higher initial cost and complexity |
Ready to Optimize Your Metal Casting Process?
Choosing the right furnace is critical for your production volume, safety, and final product quality. At KINTEK, we understand that every operation has unique requirements.
Why Partner with KINTEK?
- Expert Solutions: Whether you need the flexibility of a lift-out furnace, the consistency of a bale-out system, or the high-volume capacity of a tilting furnace, we have the right solution.
- Deep Customization: Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we tailor our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions—including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces—to precisely meet your experimental and production needs.
- Proven Performance: Our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems are trusted by diverse laboratories and foundries worldwide for their reliability and precision.
Let's build the perfect furnace for your application. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can enhance your operational efficiency and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials are rotary tube furnaces typically constructed from? Choose the Right Tube for Your Process
- What optional features enhance the processing capabilities of rotary tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Customizations
- What are the advantages of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Material Processing
- In what environments are rotary tube furnaces considered indispensable? Essential for Uniform Thermal Processing
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in the carbon activation process? Achieve Uniform, High-Porosity Activated Carbon



















