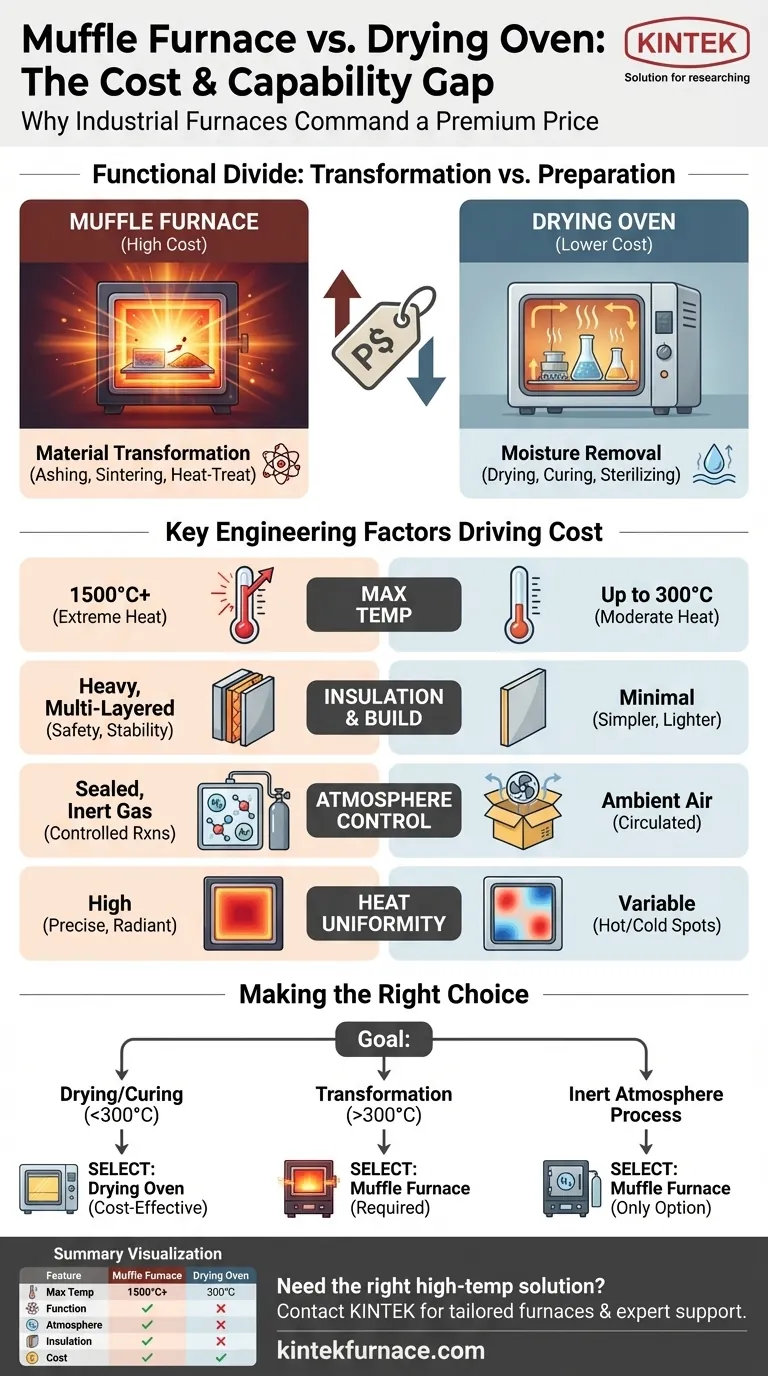
In short, industrial muffle furnaces are significantly more expensive than drying ovens. This price difference is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of the furnace's advanced engineering, which enables it to perform high-temperature material transformations, a capability that drying ovens are not designed for. The cost reflects fundamental differences in temperature range, construction, and atmospheric control.
The core reason for the cost gap is function: a drying oven removes moisture, while a muffle furnace fundamentally alters the chemical or physical properties of a material. This requires a furnace to safely achieve extreme temperatures and control its internal atmosphere, demanding far more sophisticated engineering and materials.
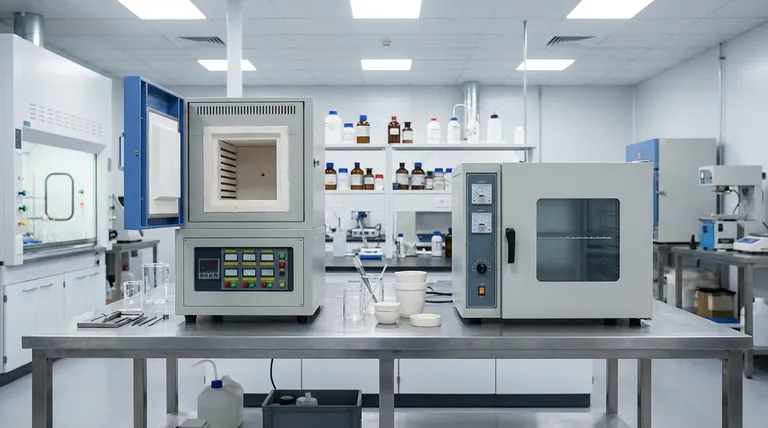

The Functional Divide: Preparation vs. Transformation
The most critical distinction between these two pieces of equipment is their intended purpose. Understanding this will clarify why their costs are in different leagues.
Muffle Furnace: High-Temperature Transformation
A muffle furnace is designed for processes that require intense heat to change a material. This includes applications like ashing, annealing, heat-treating metals, and sintering ceramics.
These processes occur in a sealed chamber, isolated from the heating elements, to ensure a clean and controlled environment.
Drying Oven: Low-Temperature Moisture Removal
A drying oven has a much simpler task: to remove moisture from samples at relatively low temperatures. Common uses include drying glassware, curing coatings, or sterilizing equipment.
They work by circulating heated air over the items and venting the resulting moist air, a process that is fundamentally different from the sealed, static heating of a furnace.
Key Engineering Factors Driving the Cost
The higher price of a muffle furnace is a direct consequence of the engineering required to achieve its advanced capabilities.
Maximum Operating Temperature
A standard industrial drying oven typically operates at temperatures up to 300°C (572°F).
A muffle furnace, by contrast, is built to reach temperatures of 1500°C (2732°F) or higher. Achieving these extreme temperatures requires more powerful heating elements, robust power delivery systems, and advanced temperature controllers, all of which add significant cost.
Insulation and Construction
To safely contain extreme heat, a muffle furnace is constructed with heavy, multi-layered insulation. This ensures temperature stability, protects the operator, and maintains energy efficiency at high temperatures.
Drying ovens operate at much lower temperatures and therefore require only minimal insulation, resulting in a simpler, lighter, and less expensive build.
Atmosphere Control
Muffle furnaces are designed with sealed chambers that allow for atmosphere control. This means the air can be replaced with an inert or reducing gas (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation and facilitate specific chemical reactions.
Drying ovens are not sealed and operate by circulating ambient air. They lack the gaskets, seals, and gas-handling ports necessary for atmosphere control, simplifying their design and lowering their cost.
Heat Uniformity
The sealed, insulated chamber of a muffle furnace provides highly uniform heat distribution through radiation and natural convection. This is critical for processes where every part of the sample must be at the same temperature.
Forced-air drying ovens can sometimes create hot and cold spots due to airflow patterns, resulting in less precise temperature uniformity across the chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong equipment based on price alone leads to wasted resources and failed processes.
The Cost of Unused Capability
Purchasing a muffle furnace for a task that only requires a drying oven means you are paying a premium for temperature and atmosphere control capabilities you will never use.
Operational Inefficiency
Using a high-power muffle furnace for a simple, low-temperature drying task is extremely inefficient. It consumes significantly more energy and often takes longer to heat up and cool down than a purpose-built oven.
The Dangers of Misapplication
Attempting to use a drying oven for a high-temperature furnace application is not only ineffective but also dangerous. The oven lacks the insulation and safety features to handle such heat, creating a risk of equipment failure and fire.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based entirely on the temperature and atmospheric requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or low-temperature curing (below 300°C): A drying oven is the correct and most cost-effective tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing, heat-treating, sintering, or any process requiring temperatures above 300°C: You must use a muffle furnace, as an oven is physically incapable of performing these tasks.
- If your process requires an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation: A muffle furnace is your only option, as a drying oven cannot control its internal atmosphere.
Ultimately, selecting the right equipment is about matching the tool's capability to your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Max Temperature | 1500°C or higher | Up to 300°C |
| Primary Function | Material transformation (e.g., ashing, sintering) | Moisture removal (e.g., drying, sterilizing) |
| Atmosphere Control | Yes (sealed, inert gases) | No (ambient air) |
| Insulation | Heavy, multi-layered | Minimal |
| Heat Uniformity | High (uniform distribution) | Variable (potential hot/cold spots) |
| Relative Cost | High | Low |
Need the right furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















