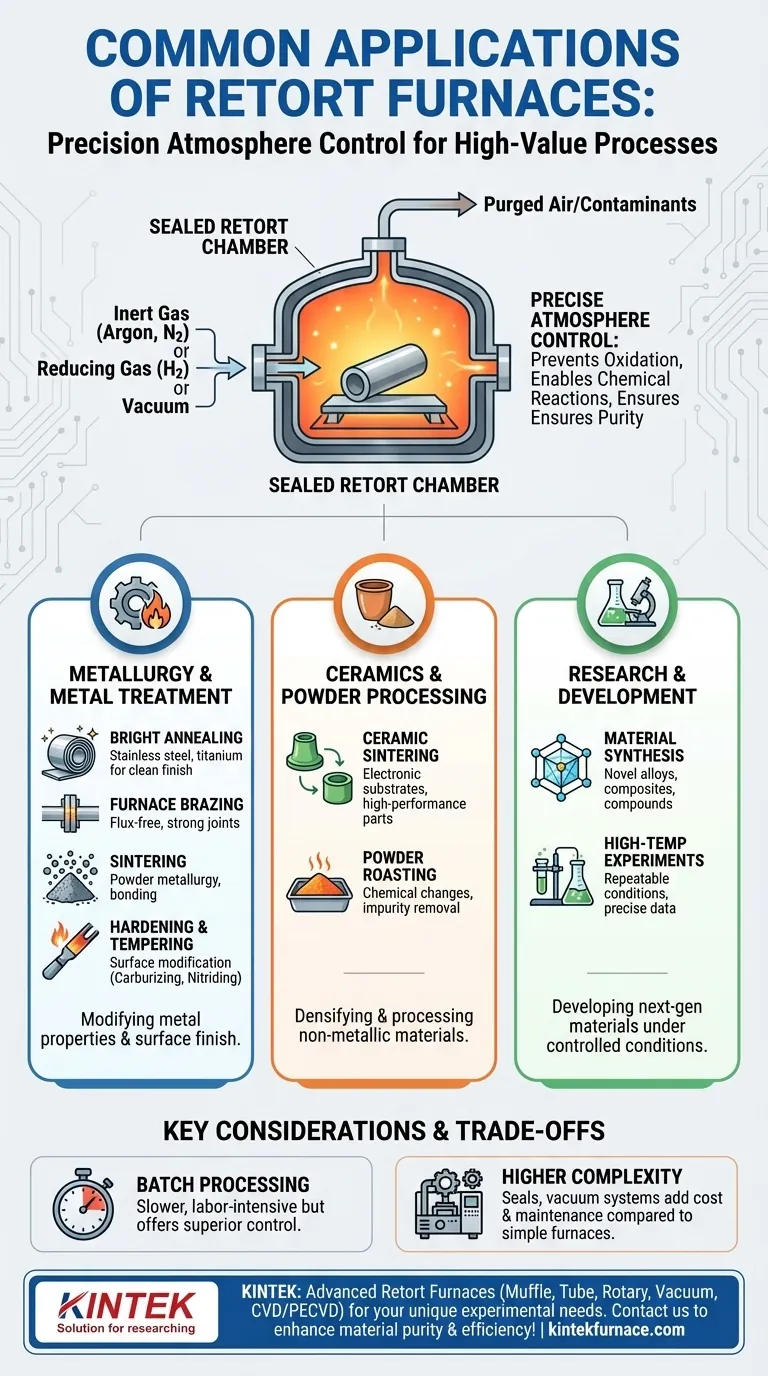
At their core, retort furnaces are used for high-temperature processes that require precise control over the atmospheric environment. Their common applications include the bright annealing of stainless steel, heat treating sensitive metals like titanium, furnace brazing, and the sintering of powdered metals and ceramics. These processes span industries from metallurgy and electronics to advanced materials research.
The defining feature of a retort furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its use of a sealed inner chamber—the "retort"—to isolate the material from the external atmosphere. This isolation is the key to preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and ensuring product purity.

The Core Principle: Why a Sealed Retort is Critical
A standard furnace heats materials in the surrounding air. A retort furnace adds a crucial layer: a sealed vessel, typically made of high-temperature alloy or ceramic, that contains the workpiece. This design provides fundamental advantages.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many heat treatment processes fail if the material reacts with oxygen at high temperatures. The retort solves this by allowing the air to be purged and replaced with a specific atmosphere.
This is essential for bright annealing, where the goal is to soften a metal like stainless steel without creating a dull, oxidized surface layer. By using an inert gas like argon or a reducing atmosphere like hydrogen, the metal retains its bright, clean finish.
Enabling Controlled Chemical Reactions
Beyond preventing reactions, a retort can introduce specific gases to intentionally alter a material's surface.
Processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen) rely on a sealed chamber to contain the reactive gases. This allows for the precise hardening of a metal's surface while leaving the core ductile.
Ensuring Purity for Advanced Materials
In industries like electronics or research and development, even trace amounts of contamination can ruin a product.
When sintering advanced ceramics or growing crystals, a retort furnace can operate under a high vacuum or be filled with ultra-pure gas. This ensures the final material has the exact chemical composition and structural properties required.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to control the atmosphere makes retort furnaces indispensable for specific, high-value tasks in several key sectors.
Metallurgy and Metal Treatment
This is the most common field for retort furnaces. They are used to precisely modify the properties of metals and alloys.
- Annealing: Used to soften metals and relieve internal stresses. It is critical for reactive metals like titanium and for achieving the mirror-like finish in bright annealing.
- Brazing: Components are joined using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base parts. Performing this in a retort with an inert atmosphere or vacuum eliminates the need for corrosive fluxes and produces a stronger, cleaner joint.
- Sintering: This process fuses metallic powders together to form solid parts, a field known as powder metallurgy. A controlled atmosphere is essential to prevent the fine powders from oxidizing and to ensure proper bonding.
- Hardening & Tempering: These processes modify the strength and toughness of steel and other alloys. While possible in other furnaces, a retort offers superior control for high-specification parts.
Ceramics and Powder Processing
The principles that apply to metals are equally important for non-metallic materials.
- Ceramic Sintering: Just like with metal powders, ceramic powders are heated in a controlled environment to densify and form a strong, solid part. This is fundamental to producing everything from electronic substrates to high-performance ceramic components.
- Powder Roasting: Powders are heated to induce chemical changes, drive off volatiles, or remove impurities before a final processing step. The retort ensures the process is clean and predictable.
Research and Development
For scientists and engineers creating the next generation of materials, the retort furnace is a vital laboratory tool.
- Material Synthesis: The precise control over temperature and atmosphere allows researchers to conduct high-temperature experiments and synthesize novel alloys, composites, and chemical compounds under repeatable conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, retort furnaces are not the universal solution for all heating applications. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Most traditional retort furnaces are batch processors. You load a batch of parts, seal the chamber, run the cycle, cool it down, and unload. This can be slower and more labor-intensive than continuous furnaces (like mesh belt furnaces) used for high-volume production.
Size and Capacity Constraints
The retort vessel itself imposes a physical limit on the size and volume of the parts that can be processed. Very large or unusually shaped components may not fit, requiring different types of furnaces.
Higher Cost and Complexity
The systems required for sealing the chamber, creating a vacuum, and controlling the process gas add significant cost and complexity compared to a simple air-atmosphere furnace. Maintenance of seals and vacuum systems is also a critical consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on the requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is surface quality and preventing oxidation: A retort furnace is the definitive choice for processes like bright annealing, high-purity brazing, or heat treating titanium.
- If your primary focus is modifying material chemistry: A retort furnace provides the sealed environment necessary for introducing reactive gases in processes like carburizing or nitriding.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, simple heat treatment where surface oxidation is acceptable or manageable: A more economical continuous or batch furnace without a retort may be the better solution.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize atmospheric control above all else to achieve specific, high-value material properties.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Industries | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bright Annealing | Metallurgy | Prevents oxidation, maintains surface finish |
| Sintering | Powder Metallurgy, Ceramics | Ensures purity, enables bonding |
| Brazing | Electronics, Manufacturing | Produces clean, strong joints without fluxes |
| Carburizing/Nitriding | Automotive, Aerospace | Hardens surfaces with precise gas control |
Ready to elevate your high-temperature processes with tailored furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced retort furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs—whether you're in metallurgy, ceramics, or R&D. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material purity and process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















