In short, coatings created by Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) are known for being exceptionally dense, thin, and multi-functional. These nano-scale films provide a comprehensive protective barrier, offering robust environmental resistance, specialized optical properties, and broad material compatibility that traditional methods struggle to match.
PECVD's core advantage lies in its ability to produce highly uniform, high-performance protective films at low temperatures. This versatility allows it to coat a wide range of materials, including sensitive electronics and polymers, with customized properties for protection, optics, and more.
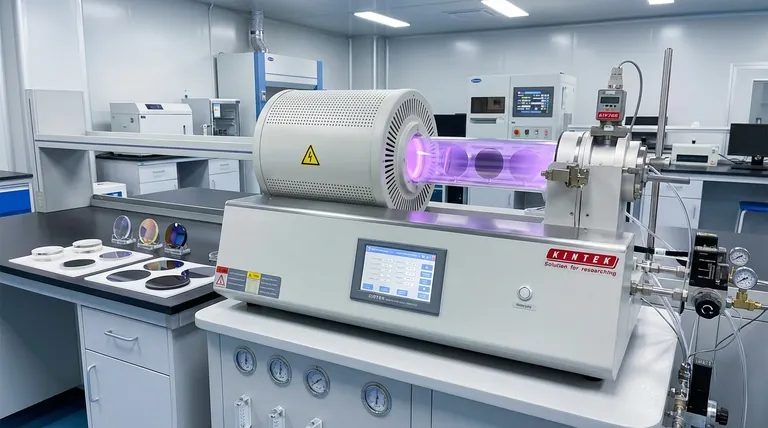

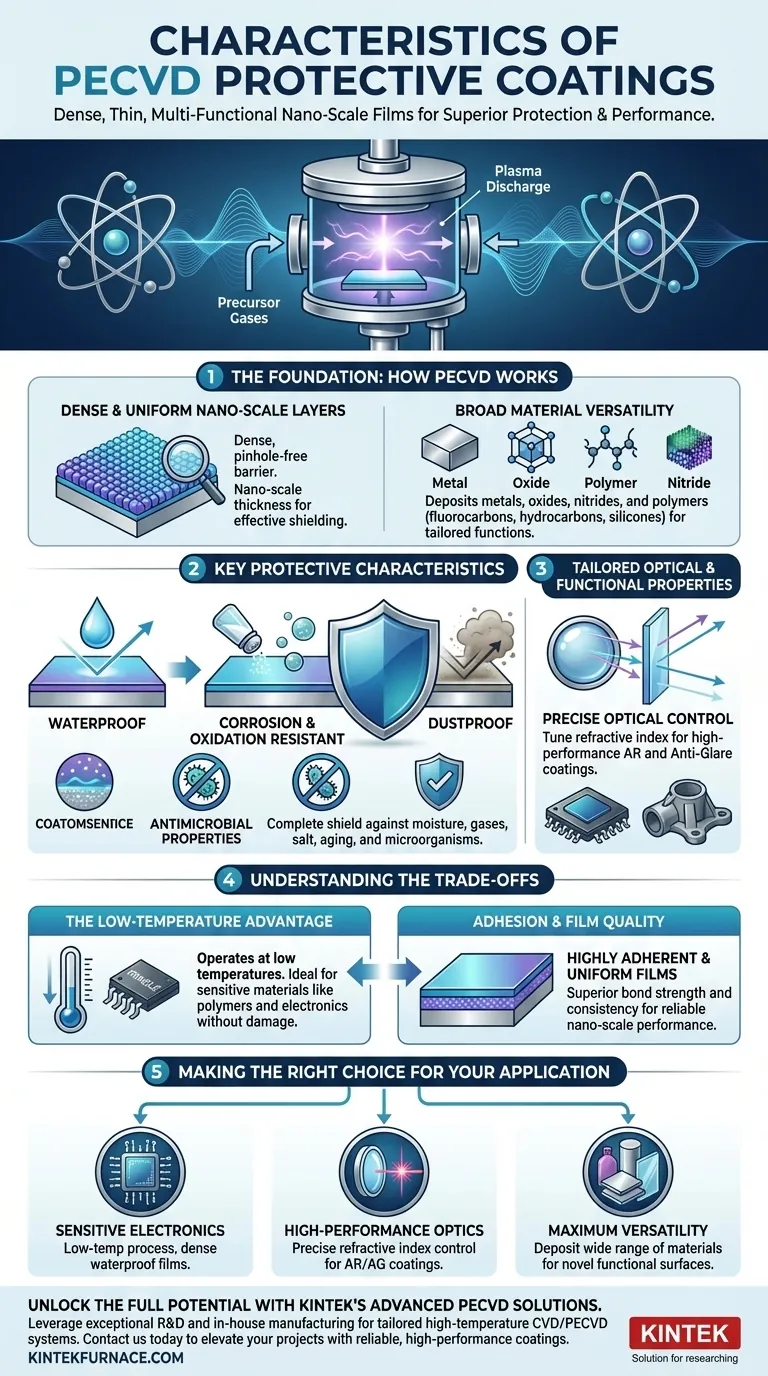
The Foundation: How PECVD Creates Superior Films
PECVD is not just another coating method; it is a precision tool for engineering materials at the atomic level. The use of plasma is the key differentiator that enables its unique capabilities.
Dense and Uniform Nano-scale Layers
The primary physical characteristic of a PECVD coating is its dense, pinhole-free structure at a nano-scale thickness. This creates a highly effective and uniform barrier, preventing the ingress of moisture, gases, or other contaminants.
This uniformity stands in contrast to some traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes, which can suffer from particle contamination and inconsistent film thickness.
Broad Material Versatility
PECVD is exceptionally flexible in the types of materials it can deposit. This allows for tailoring the coating's function to the specific need of the application.
The process can be used to create films from metals, oxides, and nitrides. It is also uniquely capable of depositing polymers like fluorocarbons, hydrocarbons, and silicones, which opens up a vast range of functional possibilities.
Key Protective Characteristics
The dense, uniform nature of PECVD films translates directly into a suite of powerful protective properties. These characteristics shield the underlying substrate from a wide variety of environmental threats.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance
PECVD coatings form a complete shield against common causes of degradation. They are known for exceptional hydrophobicity (water repellency), making them inherently waterproof.
This protection extends to resistance against salt spray, corrosion, oxidation, and general aging, preserving the integrity and appearance of the coated product over time. Many are also inherently dustproof.
Antimicrobial Properties
For medical devices or high-touch surfaces, specific PECVD films can be engineered to possess antimicrobial properties. This helps to inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms on the surface of the product.
Tailored Optical and Functional Properties
Beyond simple protection, PECVD is a powerful tool for manipulating light and enhancing the optical performance of components.
Precise Optical Control
By carefully managing plasma parameters like pressure, temperature, and gas flow, engineers can precisely tune the refractive index of the deposited film.
This control is critical for creating high-performance anti-reflective (AR) and anti-glare coatings. These are used in everything from consumer sunglasses to scientific instruments like photometers and optical data storage systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, choosing PECVD requires understanding its context. Its primary advantage over conventional, thermally-driven CVD is its ability to operate at much lower temperatures.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Traditional CVD often requires very high temperatures to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This limits its use to materials that can withstand extreme heat, such as metals and ceramics.
PECVD uses energy from the plasma—not just heat—to activate the precursor gases. This low-temperature operation is why PECVD can coat temperature-sensitive materials like polymers, plastics, and complex electronics without damaging them.
Adhesion and Film Quality
While traditional CVD films can be quite adherent, the process can result in poor uniformity. PECVD improves on this by creating films that are both highly adherent and exceptionally uniform, which is critical for reliable performance in nano-scale applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PECVD is a strategic decision based on the specific performance you need to achieve and the material you need to protect.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive electronics or polymers: PECVD is the superior choice due to its low-temperature process and ability to create dense, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant films.
- If your primary focus is high-performance optics: PECVD offers the precise control over refractive index needed to engineer specialized anti-reflective or anti-glare coatings for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is maximum versatility: PECVD's capacity to deposit a wide range of materials—from oxides to silicones—makes it an ideal platform for research and developing novel functional surfaces.
Ultimately, leveraging PECVD allows you to move beyond simple protection and begin engineering the exact surface properties your product requires.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Film Density | Dense, pinhole-free nano-scale layers for effective barrier protection |
| Uniformity | Highly uniform thickness, preventing inconsistencies and contamination |
| Material Versatility | Deposits metals, oxides, nitrides, and polymers like silicones and hydrocarbons |
| Environmental Resistance | Waterproof, corrosion-resistant, and dustproof with antimicrobial options |
| Optical Properties | Tunable refractive index for anti-reflective and anti-glare coatings |
| Low-Temperature Operation | Coats sensitive materials (e.g., polymers, electronics) without damage |
| Adhesion | Highly adherent films ensuring reliable performance in applications |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced PECVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise coatings for your unique experimental needs, enhancing protection, optics, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can elevate your projects with reliable, high-performance coatings!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What are gas barrier films, and how is PECVD involved in their creation? Discover Advanced Packaging Solutions
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the main advantages of PECVD tube furnaces compared to CVD tube furnaces? Lower Temp, Faster Deposition, and More
- What is the difference between PVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Coating Technology



















