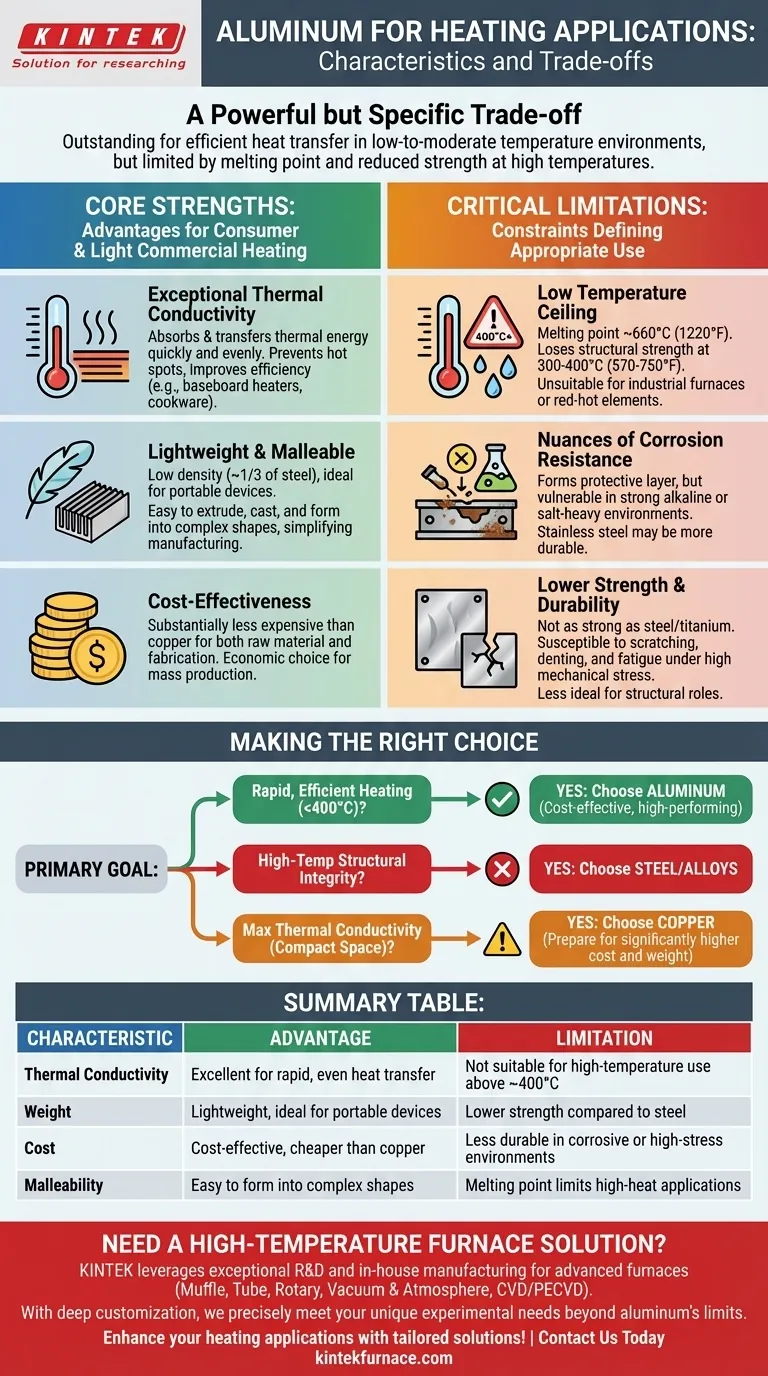
For heating applications, aluminum is defined by a powerful but specific trade-off. It is an outstanding choice for its excellent thermal conductivity, low cost, and light weight, making it highly efficient at transferring heat in many common devices. However, its use is strictly limited by a relatively low melting point and reduced strength at elevated temperatures compared to metals like steel.
Aluminum is the go-to material for cost-effective, rapid, and efficient heat transfer in low-to-moderate temperature environments. Its primary limitation is a non-negotiable temperature ceiling, making it unsuitable for high-heat industrial processes or applications requiring structural strength under intense thermal load.

The Core Strengths of Aluminum in Heating
To understand where aluminum fits, we must first examine its primary advantages. These characteristics make it a default choice for a huge range of consumer and light commercial heating products.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum's ability to conduct heat is one of its most valuable traits. It absorbs and transfers thermal energy very quickly and evenly.
This means that heating elements made with aluminum heat up fast and distribute that heat effectively across a surface, preventing hot spots and improving overall efficiency. This is why it is used extensively in baseboard heaters and cookware.
Lightweight and Malleable
Aluminum has a density roughly one-third that of steel. This low weight makes it ideal for portable heaters or applications where minimizing structural load is a design goal.
Furthermore, it is a soft and malleable metal, making it easy to extrude, cast, and form into complex shapes like the fins on a heat sink. This simplifies manufacturing and can significantly lower production costs.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other highly conductive metals like copper, aluminum is substantially less expensive. This cost advantage applies to both the raw material and the fabrication process.
For mass-produced goods, choosing aluminum allows manufacturers to deliver excellent thermal performance at a competitive price point, making it the economic backbone of many heating-related industries.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
The decision to use aluminum hinges on accepting its limitations. These are not minor points; they are hard physical constraints that define its appropriate use cases.
The Low Temperature Ceiling
This is aluminum's most significant drawback for heating applications. While its melting point is around 660°C (1220°F), it begins to lose a significant amount of its structural strength at temperatures as low as 300-400°C (570-750°F).
For this reason, aluminum is completely unsuitable for applications involving very high temperatures, such as industrial furnaces, engine components exposed to combustion, or high-performance electric heating elements that glow red-hot.
Nuances of Corrosion Resistance
Pure aluminum naturally forms a passive, protective layer of aluminum oxide on its surface. This layer provides excellent corrosion resistance in neutral pH environments.
However, this protective layer can be attacked and broken down by strong alkaline solutions or certain salt-heavy environments. In these specific corrosive conditions, other materials like stainless steel may be a more durable choice.
Lower Strength and Durability
Compared to steel or titanium, aluminum is not a particularly strong or hard metal. It is more susceptible to scratching, denting, and fatigue under high mechanical stress.
When a heating component must also serve a structural role and endure physical impact or high pressure, steel is often the superior choice, even if it means sacrificing some thermal efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning your primary goal with the material's core characteristics.
- If your primary focus is rapid, efficient heating below 400°C (750°F): Aluminum is almost always the most cost-effective and high-performing choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity: You must look to materials like steel, stainless steel, or nickel alloys.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum thermal conductivity in a compact space: Copper is technically superior to aluminum, but you must be prepared for its significantly higher cost and weight.
Ultimately, understanding aluminum's balance of thermal efficiency and temperature sensitivity empowers you to select the right material for the task.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent for rapid, even heat transfer | Not suitable for high-temperature use above ~400°C |
| Weight | Lightweight, ideal for portable devices | Lower strength compared to steel |
| Cost | Cost-effective, cheaper than copper | Less durable in corrosive or high-stress environments |
| Malleability | Easy to form into complex shapes | Melting point limits high-heat applications |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization, we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring reliable performance beyond aluminum's limits. Contact us today to enhance your heating applications with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















