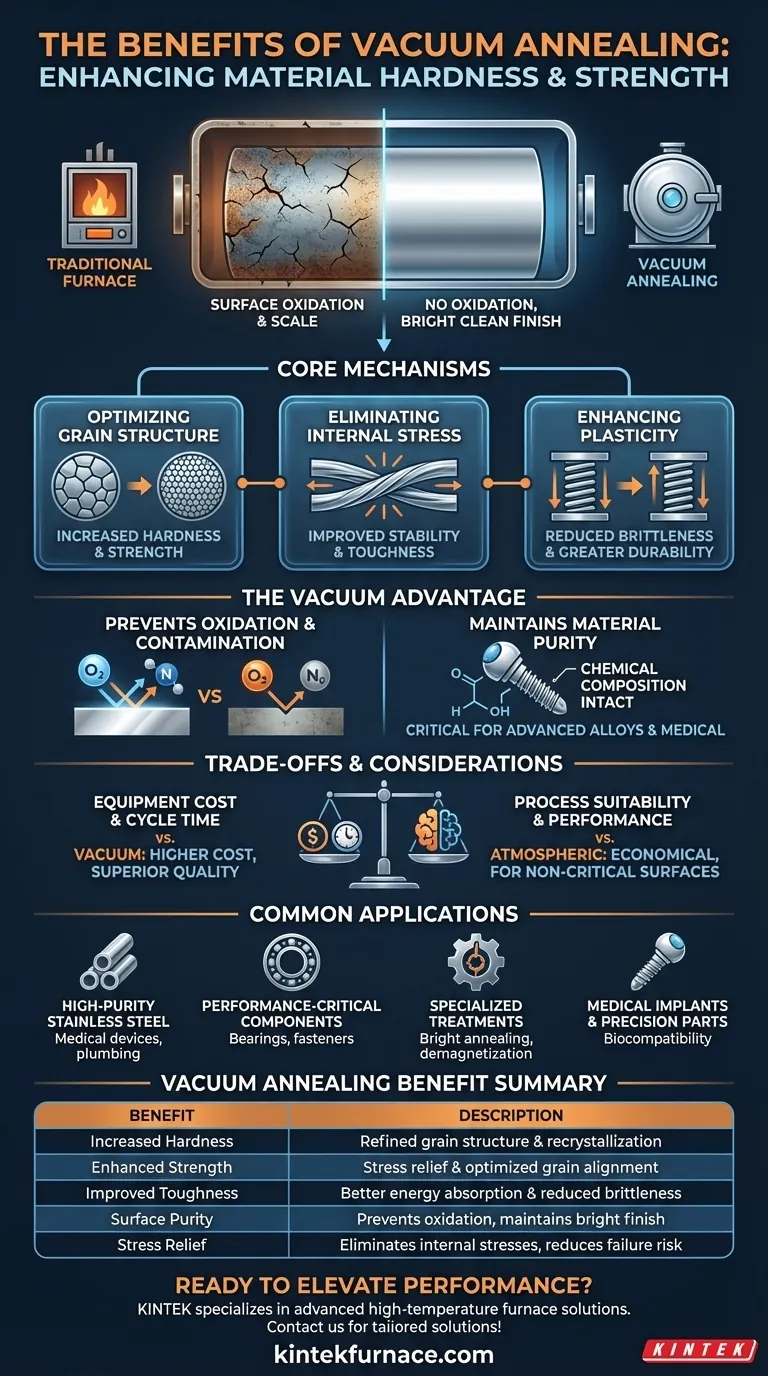
At its core, vacuum annealing enhances material hardness and strength by enabling a highly controlled recrystallization of the material's internal grain structure. By performing this heat treatment in a high vacuum, the process eliminates surface reactions like oxidation, which preserves the material's integrity and allows for the full potential of its mechanical properties to be realized without compromise.
Heat treatment often involves a trade-off between improving internal properties and damaging the material's surface. Vacuum annealing resolves this conflict by creating an ultra-pure environment where materials can be strengthened and relieved of internal stress without suffering from surface oxidation or contamination.
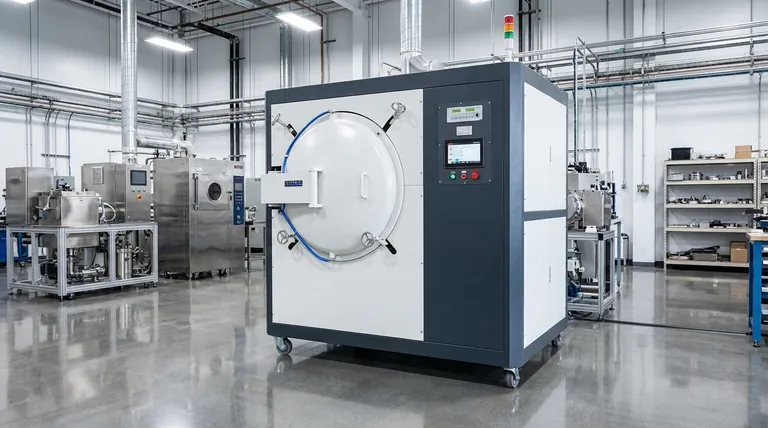

The Core Mechanisms: How Vacuum Annealing Refines Materials
Optimizing Grain Structure
Vacuum annealing allows a material's atomic structure to reorganize at an elevated temperature. This process, known as recrystallization, refines the grain structure.
A more uniform and optimized grain structure directly correlates to increased hardness and strength, making the material more robust for high-pressure or high-stress applications.
Eliminating Internal Stress
Manufacturing processes like forming, machining, or welding introduce significant residual stress into a material. This locked-in stress can lead to premature failure, distortion, or cracking.
Annealing provides the thermal energy needed for atoms to shift into lower-energy, more stable positions, effectively relieving these internal stresses and improving the material's long-term stability and toughness.
Enhancing Plasticity and Toughness
While increasing hardness, vacuum annealing also improves a material's ability to deform without fracturing (plasticity) and its ability to absorb energy (toughness).
By creating a more perfect and stress-free crystal structure, the process reduces brittleness, resulting in a more durable and reliable final component.
The Unique Advantage of the Vacuum Environment
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The defining benefit of using a vacuum is the removal of reactive gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen.
In a traditional furnace, high temperatures cause these gases to react with the material's surface, forming a brittle, discolored oxide layer (scale). A vacuum environment prevents this entirely, resulting in a bright, clean surface finish straight out of the furnace.
Maintaining Material Purity
For advanced alloys, medical implants, and precision components, maintaining the exact chemical composition is critical.
By preventing surface reactions, vacuum annealing ensures the material's purity remains unchanged. This is essential for applications where corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, or specific electrical properties are required.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Equipment Cost and Cycle Time
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts.
The process of pulling a high vacuum and carefully controlling the cooling cycle can also be slower, which may impact high-volume production throughput.
Process Suitability
Vacuum annealing is not a universal necessity. For raw materials or components that will undergo significant subsequent machining, a less expensive atmospheric process may be sufficient.
The key is to determine if the application can tolerate the surface oxidation that standard annealing produces. If it can be easily machined or cleaned off without issue, the expense of a vacuum process may not be justified.
Common Applications Driven by Performance
High-Purity Stainless Steel Products
Vacuum annealing is ideal for components where a clean, bright finish is part of the final specification. This includes medical devices, plumbing fixtures, watch components, and deep-drawn parts.
Performance-Critical Components
For parts like bearings, cutting tools, and high-strength fasteners, mechanical performance is paramount. The combination of stress relief and grain refinement in a contamination-free environment helps maximize hardness, strength, and fatigue life.
Specialized Treatments
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace also makes it suitable for other specialized thermal processes, such as bright annealing, demagnetization, and solid-solution treatments for specific stainless steel grades.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding the distinct advantages of the vacuum environment, you can make a more informed decision for your specific material and application.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and purity: Vacuum annealing is the superior choice to produce a bright, clean component that requires no post-process cleaning, especially for medical or food-grade applications.
- If your primary focus is maximizing mechanical performance: The combination of stress relief and grain refinement in a vacuum provides a clean path to enhanced hardness, strength, and toughness without introducing surface defects.
- If your primary focus is cost for non-critical surfaces: Traditional atmospheric annealing is more economical for components where surface oxidation is acceptable or will be removed by a later machining operation.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum annealing is a decision to invest in the highest possible material integrity, both inside and out.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Hardness | Achieved through refined grain structure and recrystallization in a vacuum environment. |
| Enhanced Strength | Results from stress relief and optimized internal grain alignment without surface damage. |
| Improved Toughness | Enables better energy absorption and reduced brittleness for durable components. |
| Surface Purity | Prevents oxidation and contamination, maintaining bright finish and material integrity. |
| Stress Relief | Eliminates internal stresses from manufacturing, reducing risk of failure and distortion. |
Ready to elevate your material performance with precision heat treatment? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance hardness, strength, and purity for your applications in industries like medical devices, performance components, and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















