At its core, a vacuum furnace provides unparalleled control over the heat-treating process. By removing the atmosphere, it eliminates variables like oxygen and other reactive gases, resulting in superior purity, precise temperature uniformity, and highly repeatable outcomes that are often impossible to achieve with conventional atmosphere furnaces.
The fundamental advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just what it does, but what it removes. By creating a controlled vacuum, it eliminates the unpredictable and contaminating effects of air, giving you complete command over the material's final properties.

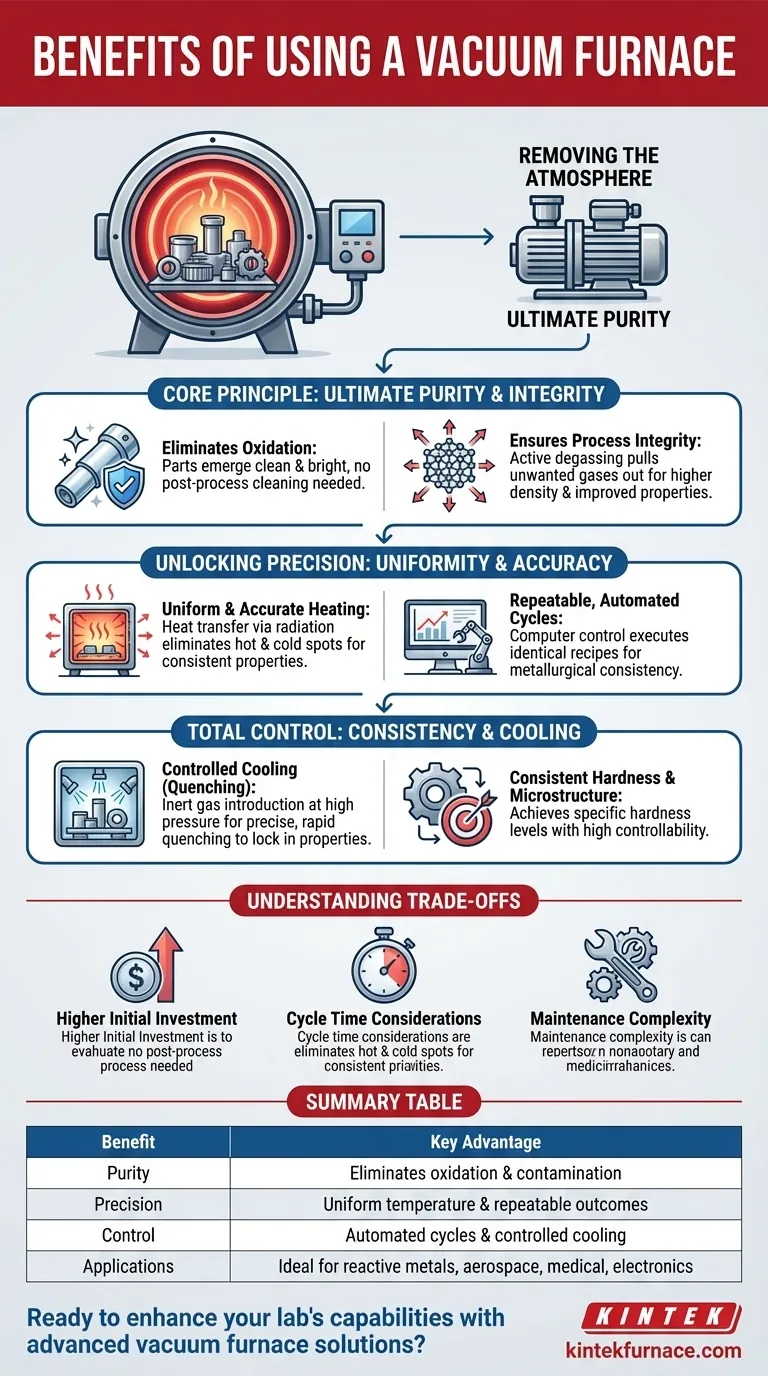
The Core Principle: Removing the Atmosphere
The primary function that drives all other benefits is the creation of a vacuum. Removing the air from the heating chamber fundamentally changes the heat-treating environment.
Achieving Ultimate Purity
By evacuating reactive gases like oxygen, the risk of oxidation is completely eliminated. This means parts emerge from the furnace clean and bright, with no need for post-process cleaning.
This prevents the formation of unwanted surface layers, ensuring the integrity and purity of the base material remains unchanged. This is critical for reactive metals like titanium and for high-purity applications.
Ensuring Process Integrity
A vacuum environment can actively pull unwanted gases out of the material itself, a process known as degassing. This results in a final product with higher density and improved mechanical properties.
Without an atmosphere to interfere, you have precise control over the chemical composition of the material from start to finish, preventing unintended reactions like nitridation or hydrogenation.
Unlocking Precision from Start to Finish
A vacuum furnace is a closed, highly controlled system. This enables a level of precision and automation that directly translates to quality and consistency.
Uniform and Accurate Heating
In a vacuum, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation. This method promotes exceptionally uniform temperature distribution across the entire workload, eliminating the hot and cold spots common in convection-based furnaces.
This uniformity ensures that every part of a component, whether thick or thin, receives the exact same thermal treatment, leading to consistent hardness and microstructure.
Repeatable, Automated Cycles
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled. Once a specific heating and cooling profile (a "recipe") is perfected, it can be saved and executed identically time and time again.
This automation removes operator guesswork and guarantees metallurgical repeatability, a non-negotiable requirement for critical components in the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
The control extends to the cooling phase. After heating, an inert gas like nitrogen or argon can be introduced at high pressure to quench the material at a precise, rapid rate.
This controlled cooling is essential for locking in the desired metallurgical properties and achieving specific hardness levels, a process that is far more controllable than quenching in oil or water.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated machines with complex pumping systems, seals, and controls. This results in a significantly higher upfront cost compared to standard atmosphere furnaces.
Cycle Time Considerations
The process of pulling a deep vacuum can add time to the beginning of each cycle. For high-volume, low-margin parts where speed is the only priority, this can be a drawback.
Maintenance Complexity
The high-performance components, particularly the vacuum pumps and chamber seals, require specialized and diligent maintenance to ensure leak-free operation and peak performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on the requirements of your material and the desired outcome of your process.
- If your primary focus is material purity and a bright surface finish: A vacuum furnace is essential for preventing oxidation and contamination.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for critical components: The precise computer control of a vacuum furnace provides unmatched consistency for aerospace or medical parts.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals like titanium: The inert vacuum environment is non-negotiable to protect material integrity.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume processing of non-critical parts: A simpler and less expensive atmosphere furnace may be the more economical choice.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is an investment in control, quality, and consistency.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Purity | Eliminates oxidation and contamination for clean, bright parts |
| Precision | Ensures uniform temperature distribution and repeatable outcomes |
| Control | Allows automated cycles and controlled cooling for specific properties |
| Applications | Ideal for reactive metals, aerospace, medical, and electronics |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced vacuum furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can deliver precise, reliable heat treatment for your critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















