In short, graphite heating elements offer exceptional longevity and high performance due to a unique combination of physical properties. Their longevity stems from high-temperature stability and chemical inertness, while their performance is driven by fast heating rates and the ability to provide highly uniform temperatures.
In the demanding environment of high-temperature applications, material failure is a constant risk. Graphite’s core advantage lies in its rare ability to combine extreme heat resistance and chemical stability with efficient, uniform heat delivery, making it a uniquely reliable choice.
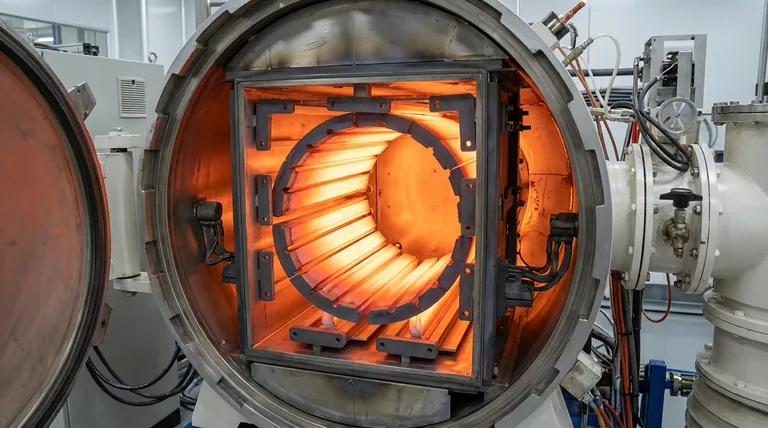
The Foundation of Graphite's Longevity
The long service life of a graphite element is not accidental; it is a direct result of its fundamental material characteristics. These properties ensure it withstands the harsh conditions of high-heat processes.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Graphite is a highly non-reactive material, especially in vacuum or inert gas atmospheres. This means it does not easily degrade from chemical reactions with materials inside the furnace, preserving its integrity over countless cycles.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This allows it to endure rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking or failing, a common point of failure for more brittle ceramic materials.
High-Temperature Structural Stability
With an extremely high melting point (sublimating around 3652°C) and low vapor pressure, graphite maintains its solid structure and strength at temperatures where most metals would melt or vaporize. This ensures its physical integrity in extreme heat.
Driving High Performance
Beyond simply lasting a long time, graphite elements are engineered to deliver precise and efficient heating, which is critical for process control and product quality.
Rapid Heating and Fast Ramp Rates
Graphite's good electrical conductivity allows it to convert electricity into heat very efficiently. This translates to fast "ramp rates," enabling the furnace to reach its target temperature quickly and reducing overall cycle times.
Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
The isostatic properties of modern graphite allow it to be machined with incredible precision. This means heating elements can be manufactured to be perfectly homogeneous, ensuring they deliver exceptionally uniform heat across the entire work zone.
Unmatched Design Flexibility
Graphite can be machined from large, solid blocks into virtually any size or shape. This allows for the creation of custom-designed elements that are perfectly optimized for a specific furnace or application, something not possible with many other materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Its primary benefits are tied to a specific operating environment, and understanding its main limitation is critical for success.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The remarkable longevity and performance of graphite are almost exclusively realized in a vacuum or an inert gas environment. Its properties degrade rapidly when this condition is not met.
The Threat of Oxidation
Graphite's primary vulnerability is oxygen. At high temperatures (typically above 450°C), graphite will react with oxygen and rapidly burn away, or oxidize. Operating a graphite furnace in an air atmosphere will destroy the elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a heating element requires matching its properties to your process goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and process purity: Graphite is the superior choice for high-temperature vacuum or inert gas applications due to its stability and non-reactive nature.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: Graphite's fast ramp rates and excellent thermal conductivity will help minimize cycle times and improve efficiency.
- If your application must run in an open-air atmosphere: You must use an alternative, such as a metallic alloy (like Kanthal) or a ceramic element (like molybdenum disilicide), as graphite is unsuitable.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct operational requirements of graphite empowers you to leverage its unparalleled performance where it truly excels.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Graphite Heating Element Advantage |
|---|---|
| Longevity | Exceptional high-temperature stability, chemical inertness, and superior thermal shock resistance. |
| Performance | Fast ramp rates, high thermal efficiency, and excellent temperature uniformity across the work zone. |
| Ideal Environment | Vacuum or inert gas atmospheres; oxidizes rapidly in air above 450°C. |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable, high-performance heating solutions?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our expertise in graphite element technology, combined with our deep customization capabilities for products like Tube Furnaces and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, ensures your application achieves peak efficiency and longevity.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory's performance.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability



















