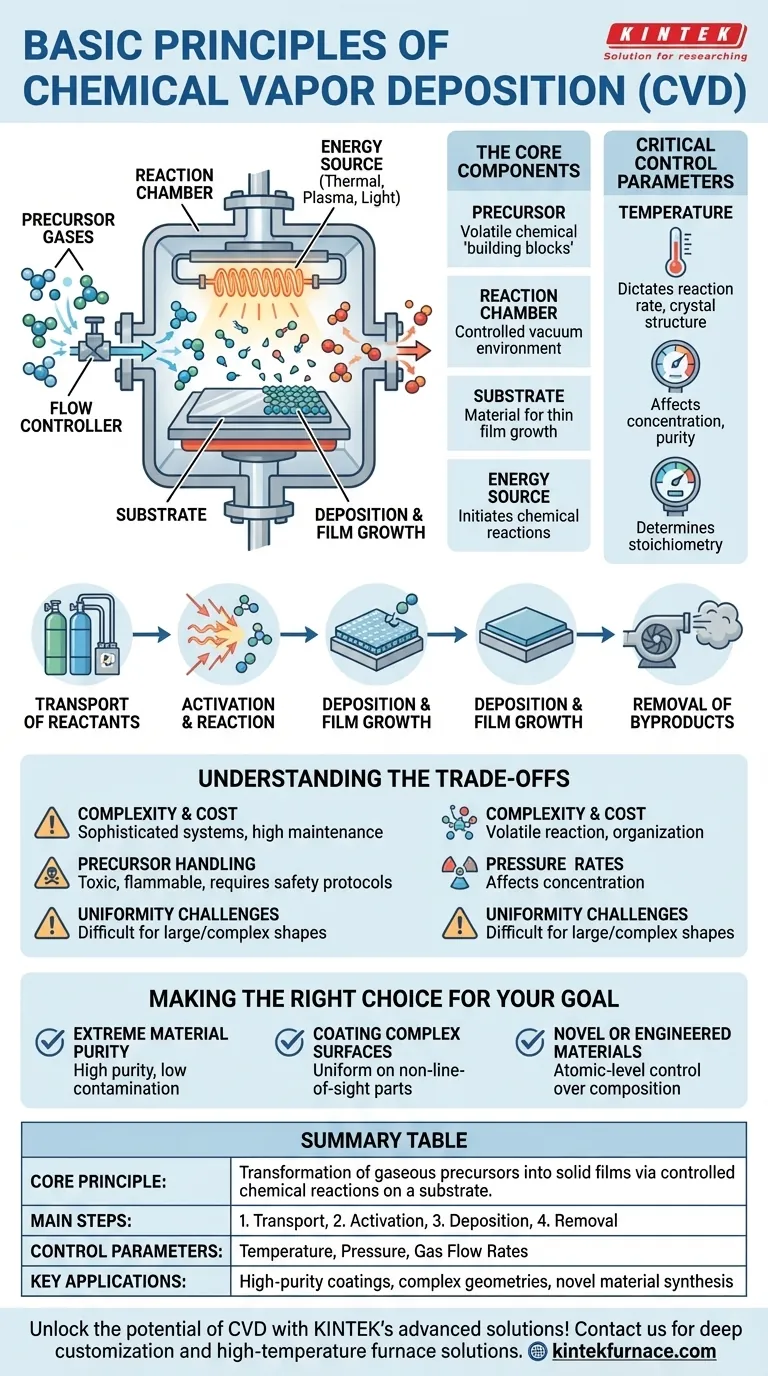
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a synthesis process for creating high-purity solid materials, typically as thin films. It works by introducing volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber where they are energized, causing them to react or decompose and deposit a new solid material onto a substrate surface. The entire process relies on precise control over conditions like temperature, pressure, and gas flow to build the desired material layer by layer.
The fundamental principle of CVD is the transformation of chemical precursors from a gaseous state into a solid film through a controlled chemical reaction on a substrate's surface. It is not merely a coating technique; it is a method for synthesizing new materials with specific, engineered properties.

The Core Components of a CVD Process
To understand the CVD principle, it helps to break the system down into its essential components. Each part plays a critical role in the final outcome.
The Precursor Gases
Precursors are the chemical "building blocks" of the final film. They are volatile compounds, meaning they can be easily turned into a gas, and contain the specific elements you want to deposit.
The Reaction Chamber
This is the controlled environment, typically held under a vacuum, where the entire deposition process takes place. It isolates the reaction from outside contaminants.
The Substrate
The substrate is the material or workpiece onto which the thin film is grown. The process conditions are optimized for deposition on this surface.
The Energy Source
Energy is required to initiate the chemical reactions. This energy can be supplied in several forms, such as high heat (Thermal CVD), plasma (Plasma-Enhanced CVD), or light (Photo-assisted CVD).
The Step-by-Step Deposition Mechanism
The CVD process can be understood as a sequence of well-defined physical and chemical steps that must be carefully managed.
Step 1: Transport of Reactants
Precursor gases, often mixed with carrier gases like nitrogen or argon, are introduced into the reaction chamber at precisely controlled flow rates.
Step 2: Activation and Reaction
Once inside the chamber, the supplied energy (e.g., heat) "activates" the precursor molecules. This causes them to decompose or react with other gases, forming the solid material in vapor form and other gaseous byproducts.
Step 3: Deposition and Film Growth
The newly formed solid species travel to the substrate, adsorb onto its surface, and begin to form a continuous layer. This film grows over time as more material is deposited.
Step 4: Removal of Byproducts
The gaseous byproducts generated during the chemical reaction are continuously pumped out of the chamber, ensuring the reaction proceeds efficiently and byproducts do not contaminate the film.
The Critical Control Parameters
The power of CVD lies in its precise tunability. Adjusting key parameters allows for the engineering of films with a wide range of properties, from hardness to electrical conductivity.
Temperature
Temperature is arguably the most critical parameter. It directly dictates the rate of the chemical reactions and significantly influences the film's crystal structure, density, and stress.
Pressure
The chamber pressure affects the concentration of reactant gases and the mean free path of the molecules. Lower pressures often lead to higher purity and better uniformity.
Gas Flow Rates
The flow rate of each precursor gas, and their ratio to one another, determines the stoichiometry (chemical composition) of the final film. This allows for the creation of complex compound materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not without its challenges. Understanding its limitations is key to its successful implementation.
Complexity and Cost
CVD systems are sophisticated and can be expensive to acquire and maintain, especially those that operate at very high temperatures or use ultra-high vacuum.
Precursor Handling
Many chemical precursors used in CVD are highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates strict safety protocols and specialized handling equipment.
Uniformity Challenges
Achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness and composition across a large or complex-shaped substrate can be difficult and often requires significant process optimization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use CVD is driven by the desired properties of the final material.
- If your primary focus is extreme material purity: CVD is an ideal choice because it starts with purified gases, leading to films with exceptionally low levels of contamination.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight surfaces: The gas-phase nature of CVD allows it to deposit uniform coatings on intricate internal and external geometries.
- If your primary focus is creating novel or engineered materials: CVD provides the atomic-level control over composition and structure needed to synthesize advanced alloys, ceramics, and semiconductors.
Ultimately, mastering CVD is about harnessing controlled chemical reactions to build materials from the ground up, making it a foundational technology in modern engineering and science.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Transformation of gaseous precursors into solid films via controlled chemical reactions on a substrate. |
| Main Steps | 1. Reactant transport 2. Activation and reaction 3. Deposition and growth 4. Byproduct removal |
| Control Parameters | Temperature, pressure, gas flow rates |
| Key Applications | High-purity coatings, complex geometries, novel material synthesis |
Unlock the potential of CVD for your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, all with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your material synthesis and drive innovation in your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















