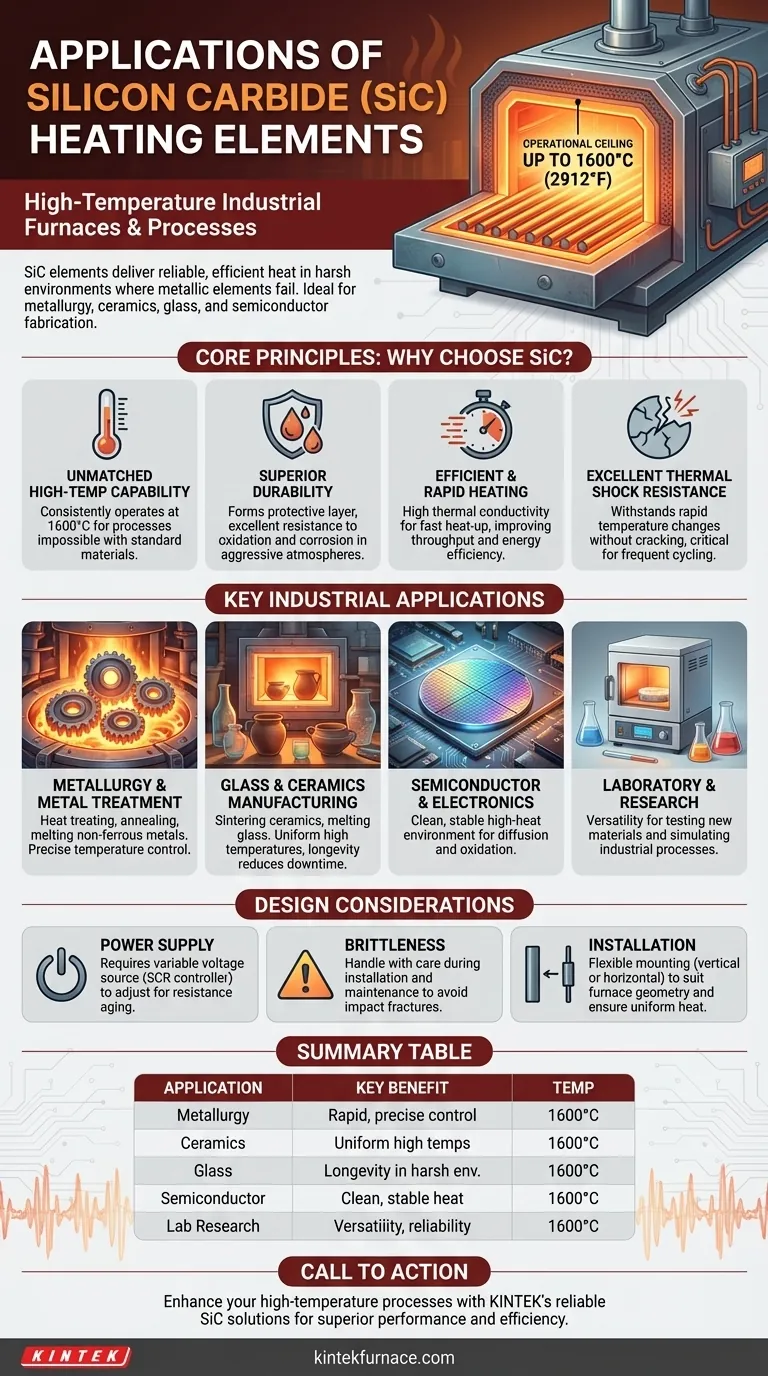
In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are used in high-temperature industrial furnaces and processes where traditional metallic elements cannot survive. Their primary applications are found in metallurgy, ceramics manufacturing, glass production, and semiconductor fabrication, where furnace temperatures can reach up to 1600°C (2912°F).
The decision to use Silicon Carbide is not just about reaching a high temperature; it is about achieving that heat reliably and efficiently in harsh industrial environments. SiC's unique resistance to oxidation and thermal shock makes it the definitive choice for processes where element failure is not an option.

The Core Principle: Why Choose Silicon Carbide?
Understanding the applications of SiC elements requires looking beyond a list of industries. The choice is driven by a unique combination of material properties that solve critical challenges in high-temperature process heating.
Unmatched High-Temperature Capability
Silicon Carbide elements can operate consistently at temperatures far exceeding the limits of traditional metallic heating elements. Their operational ceiling of 1600°C (2912°F) allows for processes like metal melting, ceramic sintering, and glass forming that are otherwise impossible with standard materials.
Superior Durability in Harsh Atmospheres
Industrial furnaces are often chemically aggressive environments. SiC elements naturally form a protective surface layer that provides excellent resistance to oxidation and chemical corrosion, ensuring a long and predictable service life even under punishing conditions.
Efficient and Rapid Heating
A key advantage of SiC is its high thermal conductivity. This allows the elements to transfer heat to the furnace chamber quickly and efficiently. The result is faster furnace heat-up times, which improves process throughput and energy efficiency.
Excellent Resistance to Thermal Shock
Unlike many brittle ceramics, SiC elements exhibit remarkable resistance to thermal shock. This means they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or failing, which is critical for industrial processes that involve frequent cycling.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The physical properties of SiC directly translate to its use in several key industries where precision and reliability at high temperatures are paramount.
Metallurgy and Metal Treatment
In metallurgy, SiC elements are essential for furnaces used in heat treating, annealing, forging, and melting non-ferrous metals. Their rapid heating capability allows for precise control over the material's crystalline structure.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing
The production of glass and advanced ceramics requires extremely high and uniform temperatures. SiC elements are used in kilns for firing and sintering ceramics and in furnaces for melting and annealing glass, where their longevity reduces costly downtime.
Semiconductor and Electronics Production
Manufacturing semiconductors involves numerous high-temperature processes. SiC elements provide the clean, stable, and high-heat environment necessary for processes like diffusion and oxidation on silicon wafers.
Laboratory and Research Furnaces
In research and development, versatility is key. The high-temperature range and reliability of SiC make it ideal for laboratory furnaces used to test new materials and simulate various industrial processes on a smaller scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, SiC elements are not a simple drop-in replacement for other heaters. Their unique properties demand specific system design considerations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
The Critical Power Supply Requirement
SiC elements age as they are used, meaning their electrical resistance gradually increases over time. To maintain consistent power output (and therefore temperature), a properly designed power supply is non-negotiable. This typically involves a variable voltage source, like an SCR controller, that can adjust the voltage upward as the element resistance increases.
Physical Brittleness
Despite their resistance to thermal shock, SiC elements are still ceramic and can be brittle. Care must be taken during installation and maintenance to avoid mechanical impact that could cause them to fracture.
Installation and Orientation
SiC elements are available in various shapes, such as straight rods or U-type spirals. This provides design flexibility, allowing for either vertical or horizontal mounting to best suit the furnace's geometry and ensure uniform heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating element is a crucial engineering decision. Your specific process requirements will determine if SiC is the right solution.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (above 1200°C) and process speed: SiC is the superior choice due to its high-temperature stability and rapid heating capabilities.
- If your primary focus is operating in a chemically aggressive or oxidizing atmosphere: SiC's inherent resistance to oxidation and chemical attack provides a significantly longer and more reliable service life.
- If your primary focus is minimizing maintenance and downtime in a critical process: The proven longevity of properly implemented SiC elements makes them a more dependable long-term solution than metallic alternatives.
Ultimately, choosing Silicon Carbide is an investment in process stability, enabling you to achieve temperatures and performance that other materials simply cannot deliver.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Rapid heating and precise control | Up to 1600°C |
| Ceramics Manufacturing | Uniform high temperatures for sintering | Up to 1600°C |
| Glass Production | Longevity in harsh environments | Up to 1600°C |
| Semiconductor Fabrication | Clean, stable heat for wafer processing | Up to 1600°C |
| Laboratory Research | Versatility and reliability for material testing | Up to 1600°C |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable heating solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our Silicon Carbide heating elements can deliver superior performance and efficiency for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















