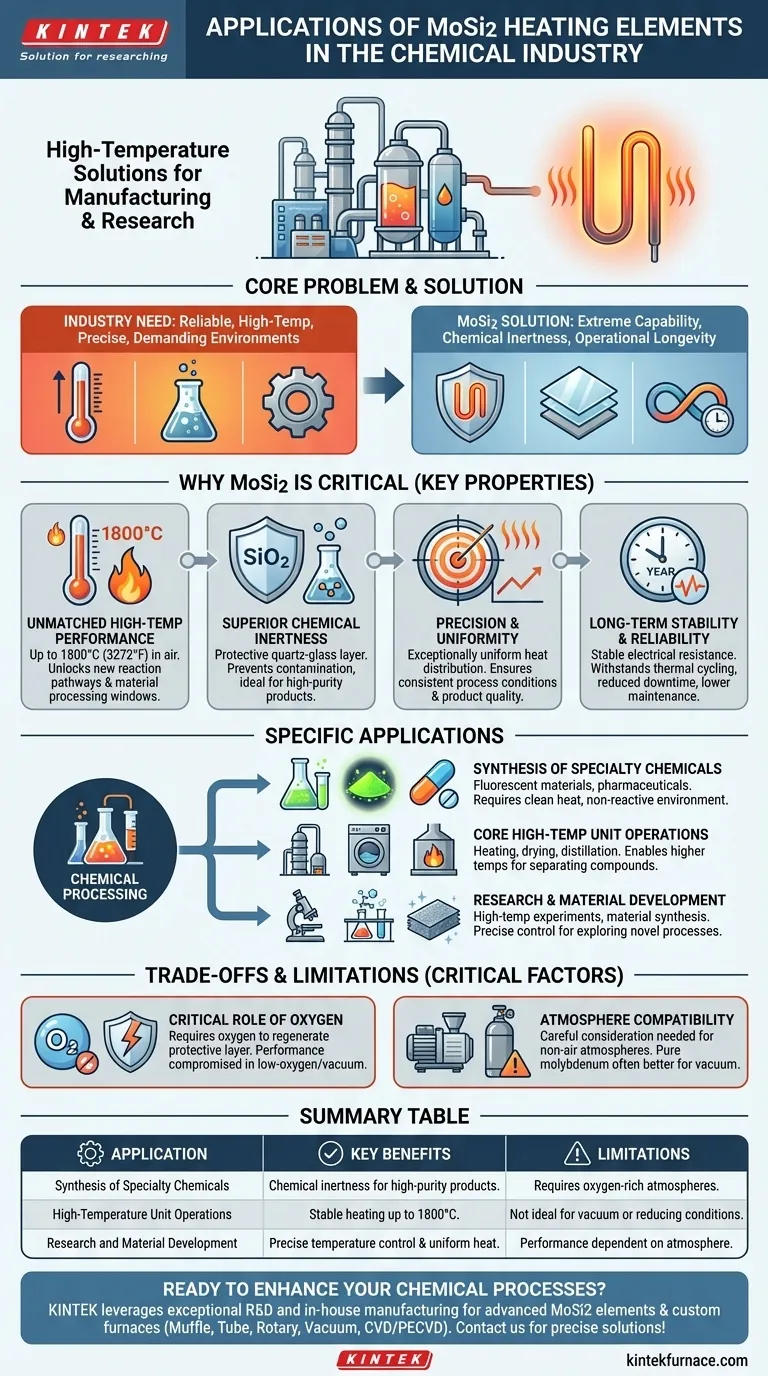
In the chemical industry, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are employed for a range of high-temperature processes essential for both manufacturing and research. They are specifically used in the synthesis of specialized products like fluorescent materials and medicines, and for core unit operations including high-temperature heating, drying, and distillation where conventional heaters cannot perform.
The chemical industry's need for reliable, high-temperature heating in precise and often demanding environments is the core problem. MoSi2 elements solve this by offering a unique combination of extreme temperature capability, chemical inertness, and operational longevity that is difficult to match.

Why MoSi2 Is a Critical Tool for Chemical Processing
MoSi2 elements are not just another heating option; their specific material properties make them uniquely suited for the challenges of modern chemical production and research. Understanding these properties reveals why they are a preferred choice for high-stakes applications.
Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
MoSi2 elements can operate stably in air at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). This capability unlocks chemical reaction pathways and material processing windows that are simply inaccessible with most other electric heating technologies.
Superior Chemical Inertness
The surface of a MoSi2 element forms a protective quartz-glass (SiO2) layer when heated. This layer makes the element highly resistant to oxidation and chemically inert, preventing it from reacting with or contaminating the chemical products being processed. This is critical for producing high-purity medicines and materials.
Precision and Uniformity
These elements provide exceptionally uniform heat distribution within a furnace or reactor. This prevents hotspots and ensures consistent process conditions, which is vital for achieving predictable reaction yields and consistent product quality in sensitive chemical syntheses.
Long-Term Stability and Reliability
MoSi2 elements do not suffer from the same aging effects as many metallic elements, meaning their electrical resistance remains stable over thousands of hours of operation. They can also withstand rapid thermal cycling without degradation, leading to reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and highly repeatable process results.
Specific Applications in the Chemical Industry
The properties of MoSi2 translate directly into several key application areas, ranging from bulk processing to cutting-edge research.
Synthesis of Specialty Chemicals
The manufacture of products like fluorescent materials and certain pharmaceuticals often requires high temperatures and a sterile, non-reactive environment. MoSi2's ability to provide clean heat without contamination makes it ideal for these demanding synthesis processes.
Core High-Temperature Unit Operations
Standard chemical engineering processes like heating, drying, and distillation are elevated by MoSi2 elements. They enable these operations to be carried out at much higher temperatures, which can be necessary for separating compounds with very high boiling points or for rapidly drying thermally stable materials.
Research and Material Development
In laboratory and R&D settings, MoSi2 heaters are invaluable for high-temperature experiments and material synthesis. Their precise temperature control and wide operating range allow researchers to explore novel chemical processes and create new materials under extreme conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, MoSi2 elements are not a universal solution. Their optimal performance is dependent on specific operating conditions, and understanding these limitations is key to their successful implementation.
The Critical Role of Oxygen
The protective silica (SiO2) layer that gives MoSi2 its chemical resistance must be able to regenerate. This process requires the presence of oxygen. In low-oxygen, reducing, or vacuum atmospheres, this protective layer cannot reform if damaged, forcing a reduction in the maximum operating temperature to prevent element failure.
Atmosphere Compatibility
While excellent in air, MoSi2 elements require careful consideration for other atmospheres. For moderate-temperature processes in a hard vacuum, pure molybdenum elements are often a better choice. The suitability of MoSi2 must always be evaluated against the specific chemical atmosphere of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires matching the technology's strengths to your primary process goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature production in air: MoSi2 elements are an exceptional choice, offering unmatched stability, longevity, and clean heating up to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis or R&D: The chemical inertness and precise, uniform heating of MoSi2 ensure product quality and repeatable experimental results.
- If your primary focus is processing in a vacuum or reducing atmosphere: You must carefully evaluate the operating temperature and atmosphere, as MoSi2's performance is compromised without sufficient oxygen.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental properties of MoSi2 empowers you to leverage its power for the right application.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Synthesis of Specialty Chemicals | Chemical inertness for high-purity products like pharmaceuticals and fluorescent materials |
| High-Temperature Unit Operations | Stable heating up to 1800°C for drying, distillation, and heating processes |
| Research and Material Development | Precise temperature control and uniform heat for consistent experimental results |
| Limitations | Requires oxygen-rich atmospheres; not ideal for vacuum or reducing conditions |
Ready to enhance your chemical processes with reliable high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced MoSi2 heating elements and custom furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, boosting efficiency and product purity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your chemical industry applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















