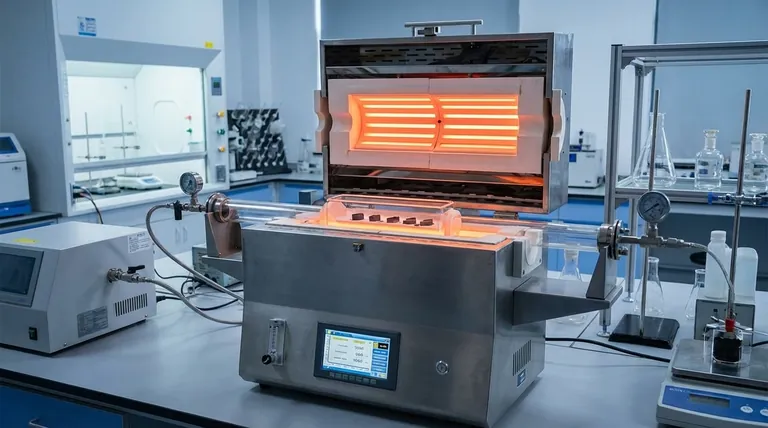
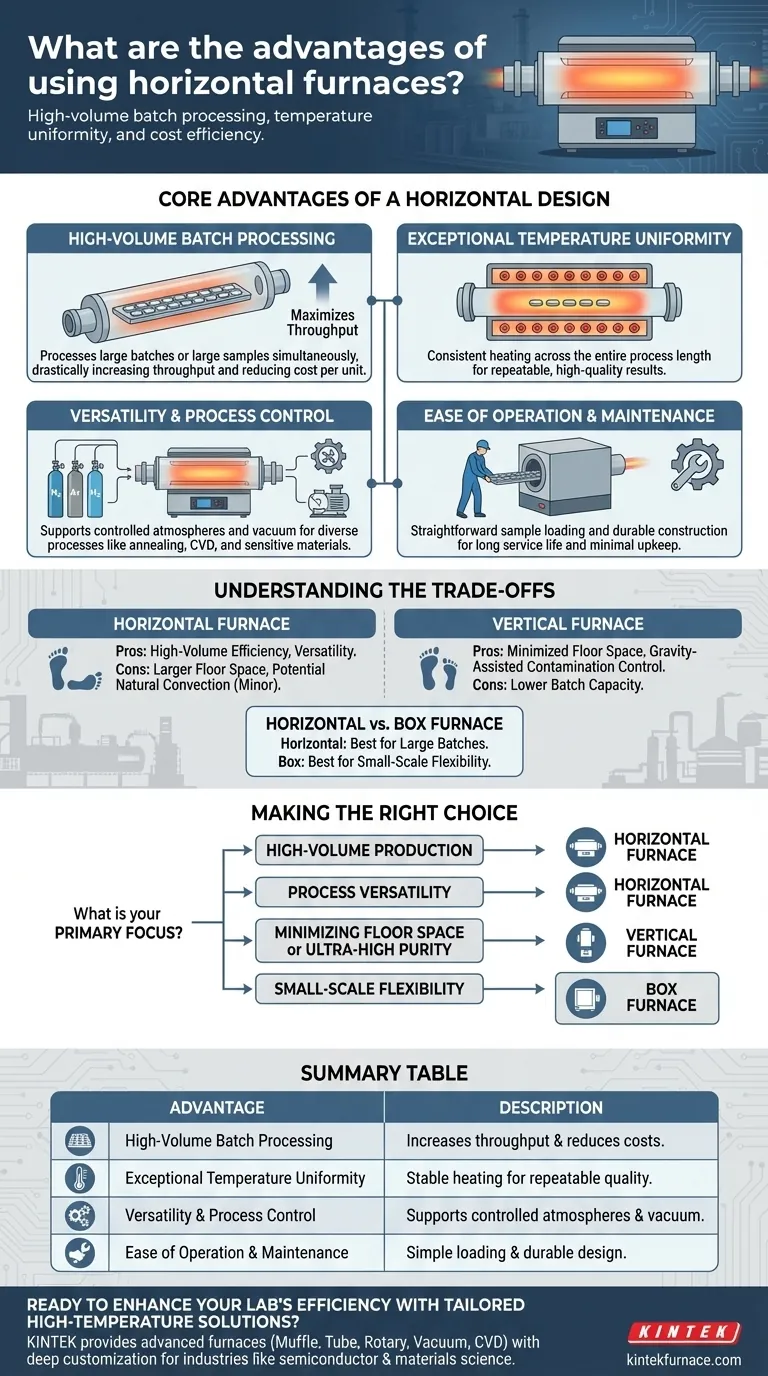
At their core, horizontal furnaces are prized for their ability to process large batches of material with exceptional temperature uniformity and at a lower cost per unit. Their design makes them a versatile and high-performance workhorse for a wide range of industrial and laboratory applications, from semiconductor manufacturing to materials science research.
The primary advantage of a horizontal furnace is economic efficiency at scale. By processing many samples simultaneously in a uniform and controlled environment, it maximizes throughput and minimizes operational costs for batch production.

The Core Advantages of a Horizontal Design
The benefits of a horizontal furnace stem directly from its orientation and typical tube-based construction. This design inherently favors certain operational strengths.
High-Volume Batch Processing
The elongated chamber of a horizontal tube furnace provides a large working volume. This allows you to process significantly larger individual samples or, more commonly, a high quantity of smaller samples at the same time.
This capacity for large-batch processing is a key driver of its cost-effectiveness, as it drastically increases throughput compared to processing samples one by one.
Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
Heating elements typically surround the process tube along its length. This configuration provides excellent heat distribution and creates a highly stable and uniform temperature zone within the furnace.
Consistent heating across all samples is critical for achieving repeatable, high-quality results in processes like annealing, diffusion, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Versatility and Process Control
Horizontal furnaces are not limited to a single function. Their design is adaptable to numerous thermal processes, making them a highly versatile asset.
Many models support controlled atmosphere capabilities. By integrating optional gas delivery systems, you can perform heating under specific conditions, such as in an inert (nitrogen, argon) or reducing atmosphere. This is essential for preventing oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions.
Furthermore, these systems can be configured as vacuum furnaces, providing an extremely low-contamination environment for sensitive materials.
Ease of Operation and Maintenance
Compared to some alternatives, horizontal furnaces offer straightforward sample loading and unloading. Materials are typically placed in a "boat" and pushed into the center of the tube.
They are also valued for their durability and robust construction, often designed for a long service life with minimal maintenance requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the horizontal furnace is not the optimal solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Furnaces
The most significant trade-off is floor space. A horizontal furnace requires a larger physical footprint than a vertical furnace of similar capacity, which can be a major consideration in a cleanroom or crowded lab.
Vertical furnaces also use gravity to their advantage, which can help minimize particle contamination in ultra-high-purity applications like semiconductor wafer fabrication. Particles are less likely to fall from the chamber ceiling onto the product below.
Throughput vs. Small-Scale Flexibility
The strength of a horizontal furnace is in large batches. For low-volume production or R&D environments that require frequent process changes on just a few samples, a smaller, less expensive box furnace may be more practical and cost-effective.
Natural Convection
In a horizontal tube, natural convection can create slight temperature variations between the top and bottom of the tube. While modern designs minimize this, applications demanding the absolute highest level of thermal precision might favor a vertical furnace, where heat naturally rises along the axis of the samples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right equipment, you must align its advantages with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: The horizontal furnace is the industry standard for maximizing throughput and achieving a low cost-per-sample.
- If your primary focus is process versatility: The ability to handle different sample sizes and implement controlled atmospheres makes the horizontal tube furnace a highly adaptable choice.
- If your primary focus is minimizing floor space: A vertical furnace offers a much smaller footprint for a given processing capacity and should be your first consideration.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity: You should evaluate a vertical furnace, as its design can offer advantages in reducing particle contamination.
Ultimately, choosing a horizontal furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize batch efficiency and operational versatility.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Volume Batch Processing | Processes large batches simultaneously, increasing throughput and reducing costs. |
| Exceptional Temperature Uniformity | Provides stable, uniform heating for repeatable, high-quality results. |
| Versatility and Process Control | Supports controlled atmospheres and vacuum conditions for diverse applications. |
| Ease of Operation and Maintenance | Straightforward loading and durable design for minimal upkeep. |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique needs in industries like semiconductor manufacturing and materials science. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your batch processing and drive success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















