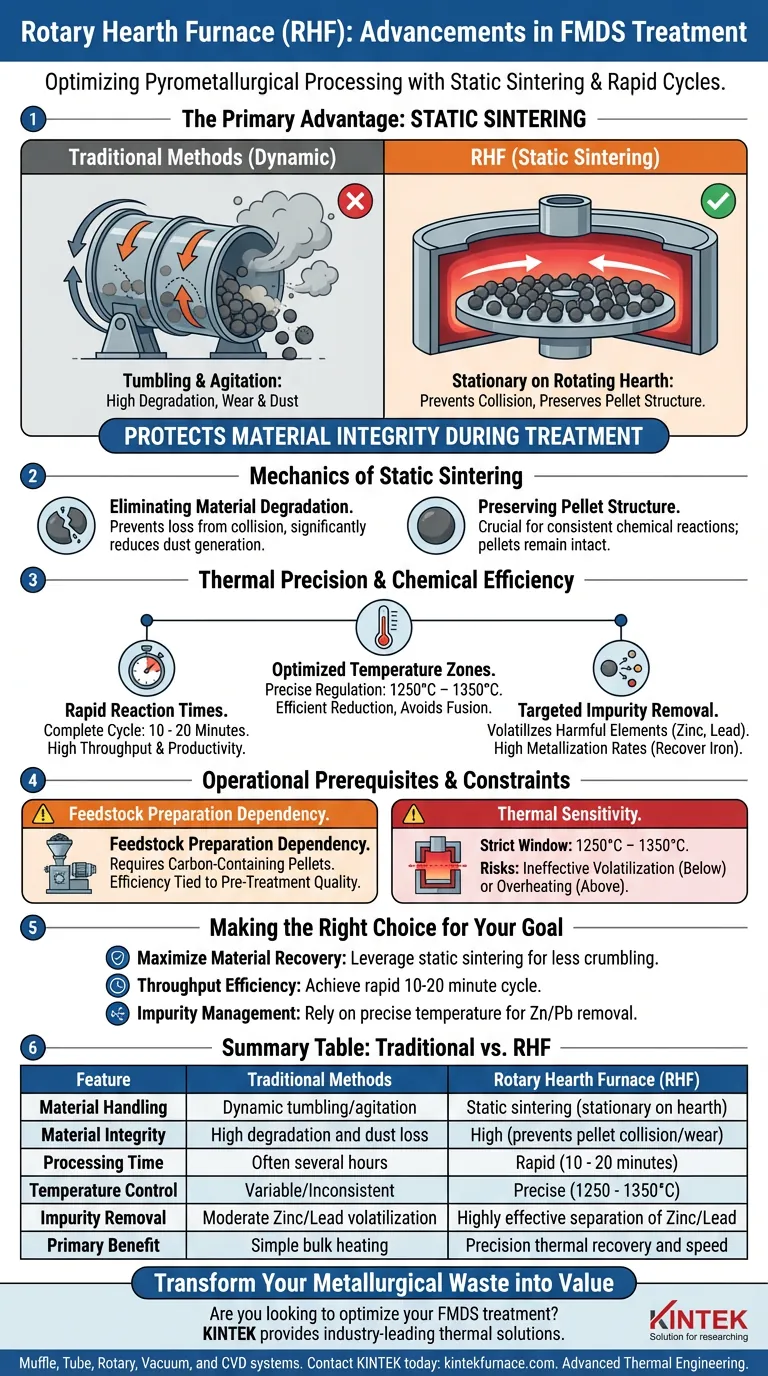
The primary advantage of the Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF) lies in its ability to facilitate "static sintering," which fundamentally protects the physical integrity of the material during treatment. Unlike traditional methods that may tumble or agitate the feedstock, the RHF uses a rotating hearth to transport carbon-containing pellets through a high-temperature zone without collision or wear.
The RHF solves the dual challenge of material degradation and processing speed by maintaining a static environment for pellets while executing rapid, high-temperature reduction. This ensures high metallization rates and efficient impurity removal in a fraction of the time required by conventional processes.
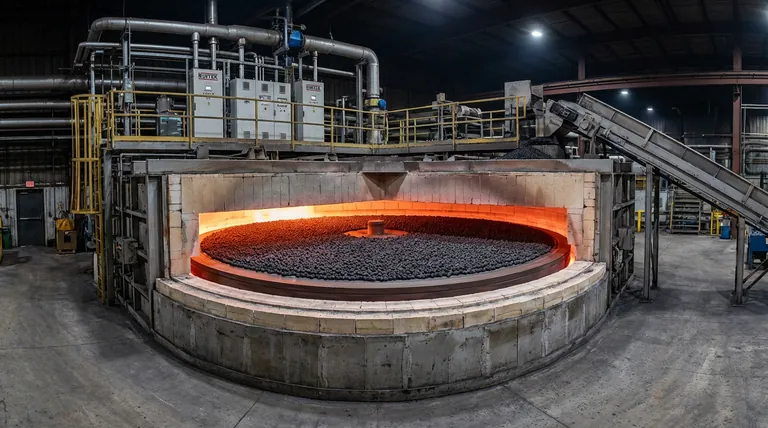

The Mechanics of Static Sintering
Eliminating Material Degradation
Traditional dynamic heating methods often result in material loss through tumbling and agitation.
The RHF design keeps the carbon-containing pellets stationary relative to the hearth as they rotate through the furnace.
This "static sintering" approach prevents pellet collision, significantly reducing wear and dust generation inside the furnace.
Preserving Pellet Structure
Maintaining the physical shape of the pellet is crucial for consistent chemical reactions.
By avoiding mechanical stress during transport, the RHF ensures that the pellets remain intact throughout the reduction process.
Thermal Precision and Chemical Efficiency
Optimized Temperature Zones
The RHF allows for precise temperature regulation, specifically maintaining a range between 1250 and 1350 degrees Celsius.
This temperature window is critical for efficiently reducing metal oxides without causing unwanted fusion or equipment damage.
Rapid Reaction Times
One of the most significant advantages of the RHF is its throughput speed.
The design facilitates a complete reaction cycle in a remarkably short duration of just 10 to 20 minutes.
This efficiency allows for higher productivity compared to slower, traditional thermal treatment methods.
Targeted Impurity Removal
The high-temperature environment is specifically tuned to manage the complex composition of iron and steel metallurgical dust (FMDS).
The process effectively volatilizes harmful elements like zinc and lead, separating them from the valuable metals.
Simultaneously, it achieves high metallization rates, recovering valuable iron units for reuse.
Operational Prerequisites and Constraints
Feedstock Preparation Dependency
The RHF process described specifically relies on carbon-containing pellets.
This implies that loose dust or sludge must undergo a rigorous pelletization process with a carbon reductant before it can be treated.
The efficiency of the furnace is therefore directly tied to the quality and consistency of this pre-treatment preparation.
Thermal Sensitivity
While the 1250–1350°C range is effective, it represents a strict operating window.
Falling below this range may fail to volatilize zinc and lead effectively, compromising the purity of the product.
Exceeding this range risks overheating the hearth or fusing materials, highlighting the need for sophisticated thermal monitoring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if an RHF is the correct solution for your FMDS treatment, evaluate your specific processing priorities:
- If your primary focus is maximizing material recovery: Leverage the static sintering process to prevent pellet crumbling and loss due to collision.
- If your primary focus is throughput efficiency: Utilize the RHF to achieve full reduction and volatilization in a rapid 10 to 20-minute cycle.
- If your primary focus is impurity management: Rely on the precise 1250–1350°C control to volatilize zinc and lead while maintaining high iron metallization.
The RHF represents a shift from simple heating to precision thermal processing, turning hazardous metallurgical waste into valuable resources through mechanical stability and speed.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Methods | Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Handling | Dynamic tumbling/agitation | Static sintering (stationary on hearth) |
| Material Integrity | High degradation and dust loss | High (prevents pellet collision/wear) |
| Processing Time | Often several hours | Rapid (10 - 20 minutes) |
| Temperature Control | Variable/Inconsistent | Precise (1250 - 1350°C) |
| Impurity Removal | Moderate Zinc/Lead volatilization | Highly effective separation of Zinc/Lead |
| Primary Benefit | Simple bulk heating | Precision thermal recovery and speed |
Transform Your Metallurgical Waste into Value
Are you looking to optimize your FMDS treatment with higher recovery rates and faster throughput? KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions designed for precision and durability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical and lab requirements.
Don't let valuable materials go to waste through inefficient processing. Let our experts help you design the perfect furnace configuration for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom project and experience the power of advanced thermal engineering!
Visual Guide
References
- Jiansong Zhang, Qianqian Ren. Multi-Source Ferrous Metallurgical Dust and Sludge Recycling: Present Situation and Future Prospects. DOI: 10.3390/cryst14030273
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials and processes can a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace accommodate? Versatile Thermal Processing for Powders and More
- How does material move through a rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Uniform Processing
- What customization options are available for rotary tube furnaces? Tailor Your Furnace for Precise Thermal Processing
- What role does the rotary kiln serve in coal-based DRI production? Unlock Cost-Effective Ironmaking Efficiency
- Which industries use rotary kilns and for what processes? Essential Guide to High-Temperature Industrial Applications
- What is a rotary kiln and how does it function? Unlock Efficient Thermal Processing for Your Materials
- How do indirect-fired rotary kilns benefit the cement industry? Achieve Superior Clinker Purity and Control
- How does the cylindrical design of a rotary kiln facilitate material movement? Uncover Efficient Processing Secrets



















