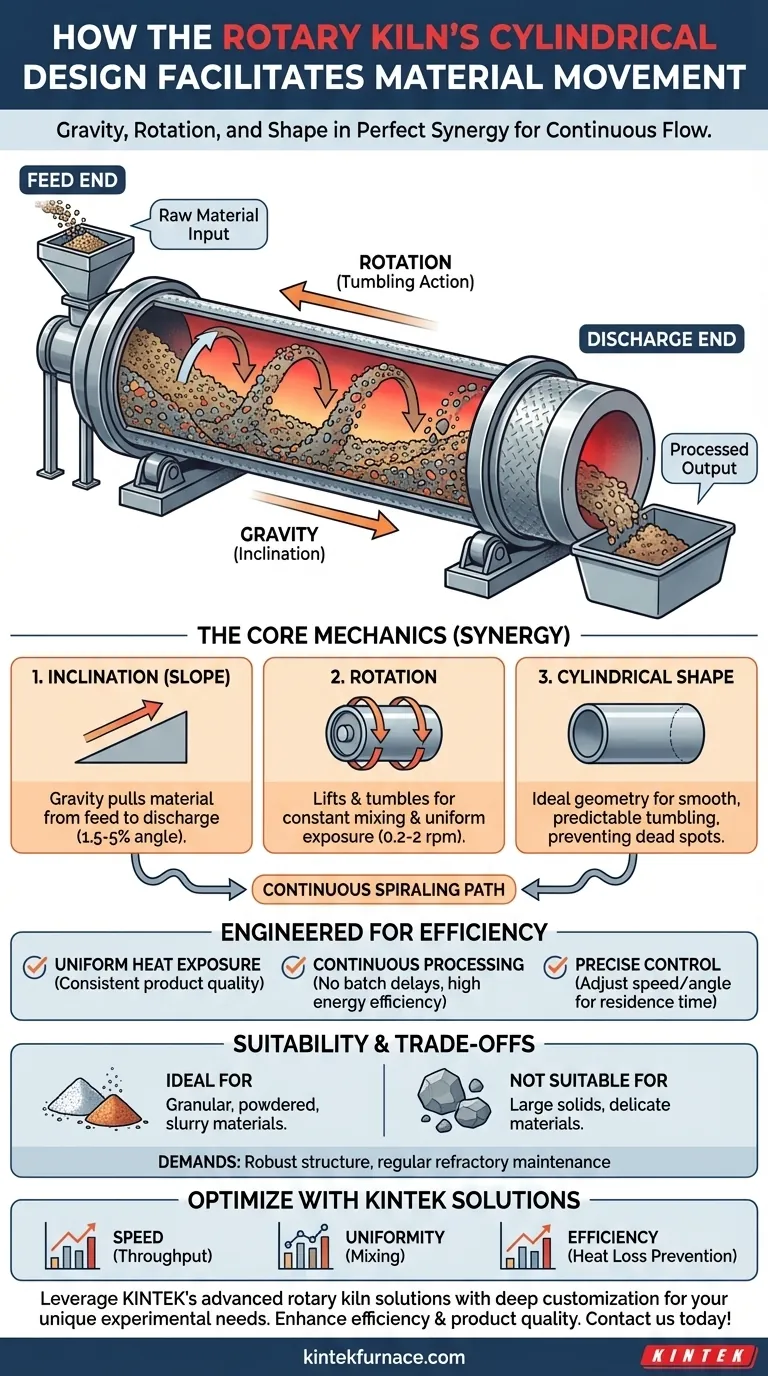
In essence, the cylindrical design of a rotary kiln facilitates material movement through a precise combination of three factors: the cylinder's shape, its slight downward inclination, and its slow, constant rotation. These elements work in concert to create a continuous, controlled flow, using gravity as the primary motivator while the rotation ensures the material is constantly mixed and tumbled as it travels from the feed end to the discharge end.
The genius of the rotary kiln is not just its ability to move material, but to do so in a way that guarantees continuous processing and uniform heat exposure. The cylindrical design is the lynchpin that makes this highly efficient, controlled tumbling motion possible.

The Core Mechanics of Material Transport
To understand the system, it's best to break down how each design element contributes to the overall function. These components are not independent; they are engineered to work in perfect synergy.
The Role of Inclination (Slope)
The entire kiln vessel is mounted at a slight downward angle, typically between 1.5% and 5%.
This inclination is the primary driver of material flow. Gravity naturally pulls the material from the higher feed end of the kiln toward the lower discharge end.
The Function of Rotation
The kiln rotates slowly on its axis, usually at speeds between 0.2 and 2 revolutions per minute (rpm).
This rotation continuously lifts material partway up the interior wall of the cylinder before it tumbles back down into the bed of material. This tumbling action is critical for mixing and preventing clumps.
The Synergy of Cylinder, Slope, and Rotation
The cylindrical shape is the ideal geometry for this process. It allows for a smooth, predictable tumbling motion without corners or dead spots where material could get stuck.
Combined, the slope and rotation create a slow, spiraling path for the material. This ensures every particle moves steadily through the kiln while being thoroughly mixed.
Why This Design is Engineered for Efficiency
The rotary kiln's design is a deliberate solution to the challenge of processing large volumes of material uniformly and continuously. Its effectiveness becomes clear when compared to alternative, batch-based systems.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Exposure
The constant tumbling action is the key to uniformity. As material moves through different heating zones, this mixing guarantees that all particles are exposed to the heat source evenly.
This prevents hot spots and ensures a consistent, high-quality final product, which is critical in processes like cement manufacturing or mineral calcination.
Enabling Continuous Processing
Unlike a shuttle kiln that processes materials in discrete batches on carts, a rotary kiln operates continuously. Material is constantly fed in one end and discharged from the other.
This design eliminates the need for carts and doors, which dramatically improves energy efficiency by preventing the heat loss associated with cycling a kiln chamber open and closed.
Providing Precise Control
Operators can fine-tune the kiln's performance by adjusting the inclination angle and rotation speed.
These adjustments allow for precise control over the material's residence time—the total duration it spends inside the kiln. This control is essential for adapting the process to different raw materials and desired outcomes.
Understanding the Design's Trade-offs
While highly effective, the rotary kiln design has inherent characteristics that make it suitable for some applications but not others. Understanding these limitations is key.
Material Suitability
The design is ideal for granular, powdered, or slurry-based materials that can flow and tumble freely.
It is generally not suitable for large, solid objects or delicate materials that would be damaged by the constant tumbling and abrasive action inside the kiln.
Structural and Maintenance Demands
Rotary kilns are massive, heavy structures. The welded steel shell must be incredibly robust to support its own weight and rotation.
Furthermore, the internal refractory lining, which protects the steel from extreme heat, is subject to intense thermal and mechanical stress. It requires regular inspection and maintenance to prevent catastrophic failure and energy loss.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The operational parameters of a rotary kiln are adjusted based on the specific processing goal. The interplay between speed, angle, and material properties dictates the final outcome.
- If your primary focus is process speed: Increasing the rotation speed and/or the inclination angle will increase material throughput, but this must be balanced to ensure the residence time is still sufficient for proper treatment.
- If your primary focus is product uniformity: A slower rotation speed and a shallower inclination angle will increase the residence time and the number of tumbles, promoting maximum mixing and heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: The continuous, doorless design is inherently efficient, but maintaining the integrity of the refractory lining is the single most important factor in preventing heat loss and maximizing performance.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's design elegantly transforms the simple forces of gravity and rotation into a powerful, controlled, and continuous industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Material Movement |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Shape | Enables smooth tumbling and prevents material stagnation |
| Inclination (Slope) | Uses gravity to drive material flow from feed to discharge end |
| Rotation | Lifts and tumbles material for mixing and uniform heat exposure |
| Synergy of Elements | Creates continuous, controlled spiraling path for efficient processing |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, designed for continuous operation and precise control. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















