At its core, the primary benefit of an indirect-fired rotary kiln in the cement industry is superior process control. This method separates the combustion process from the material being heated, allowing for precise management of the kiln's internal atmosphere. This isolation prevents contamination from fuel byproducts, ensures exceptionally uniform heating, and produces a higher quality, more consistent cement clinker.
The decision to use an indirect-fired kiln is driven by a need for product purity and process precision. By heating the kiln externally, you separate the chemical reaction of calcination from the unpredictable variables of fuel combustion, gaining unparalleled control over the final product.
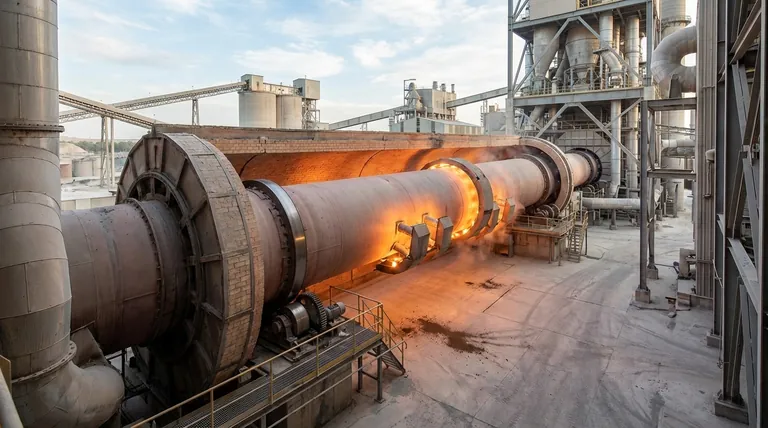

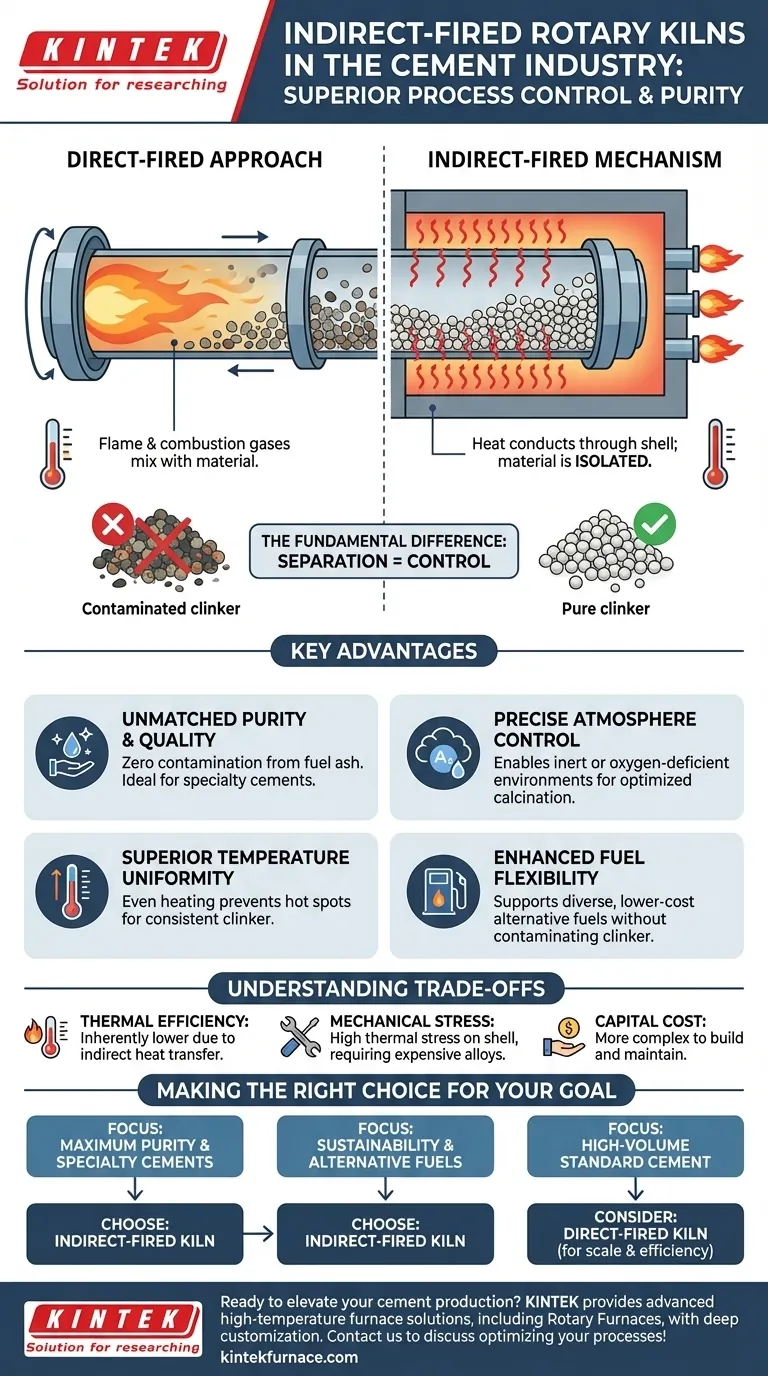
The Fundamental Difference: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
A rotary kiln is the heart of a cement plant, functioning as a chemical reactor that transforms raw materials into clinker through a process called calcination. The method of heating is what defines its primary characteristics.
The Direct-Fired Approach
In a conventional direct-fired kiln, a large flame is projected directly into the kiln cylinder. The raw material tumbles through the hot combustion gases, heating it via direct contact.
The Indirect-Fired Mechanism
An indirect-fired rotary kiln works differently. The entire rotating kiln cylinder is enclosed within a stationary furnace or heating chamber. Burners heat the outside of the kiln shell, and that heat is transferred by conduction through the shell wall to the material inside.
Why This Separation Matters
This design intentionally isolates the process material from the flame and its exhaust gases. This fundamental separation is the source of all the major advantages of the indirect-fired method.
Key Advantages in Clinker Production
By preventing direct contact between the fuel source and the raw materials, indirect kilns offer distinct benefits for creating high-quality cement clinker.
Unmatched Purity and Quality
Since the material never mixes with combustion gases, there is zero contamination from fuel ash or other chemical byproducts. This is critical for producing specialty cements or when the raw material feed is sensitive to impurities, resulting in a more predictable and higher-purity clinker.
Precise Atmosphere Control
The internal environment of the kiln can be tightly controlled. This allows calcination to occur in an inert or oxygen-deficient atmosphere, which can be crucial for specific chemical reactions and preventing unwanted oxidation. This level of control is impossible in a direct-fired system flooded with combustion gases.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
Heating the entire circumference of the rotating shell provides a more even and gentle heat distribution to the material bed inside. This uniform heating prevents hot spots and ensures that all the material is processed under the same temperature conditions, leading to a more consistent final product.
Enhanced Fuel Flexibility
Because the fuel combustion is external to the process, a wider variety of alternative fuels can be used without the risk of contaminating the clinker. This supports sustainability initiatives and can reduce operational costs by allowing the use of lower-grade or biomass fuels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. The design of an indirect-fired kiln introduces specific engineering and economic challenges that must be considered.
Thermal Efficiency
Transferring heat through the thick steel shell of the kiln is inherently less efficient than applying a flame directly to the material. This indirect heat transfer path can lead to higher energy consumption compared to a direct-fired kiln of similar size.
Mechanical and Material Stress
The kiln shell is subjected to extreme temperatures from the external furnace, creating significant thermal stress. This requires the use of high-performance, expensive alloys capable of maintaining structural integrity at high temperatures over long periods.
Scale and Capital Cost
Indirect-fired kilns are often more complex and expensive to build and maintain than their direct-fired counterparts. The external furnace and specialized materials add to the initial capital investment, and there can be practical limits to their maximum diameter and throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right kiln technology depends entirely on your specific production priorities and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum clinker purity and specialty cements: The process isolation and atmosphere control of an indirect-fired kiln are essential to meet stringent quality specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard cement: The scale, lower capital cost, and thermal efficiency of a large, direct-fired kiln often make it the more economical choice.
- If your primary focus is sustainability through alternative fuels: An indirect-fired kiln provides the flexibility to use diverse, lower-cost fuels without compromising the purity of the final product.
Ultimately, choosing an indirect-fired kiln is a strategic decision to prioritize product quality and process control over raw throughput and thermal efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Impact on Cement Industry |
|---|---|
| Superior Process Control | Enables precise management of kiln atmosphere for consistent clinker quality. |
| Unmatched Purity | Prevents contamination from fuel byproducts, ideal for specialty cements. |
| Precise Atmosphere Control | Allows inert or oxygen-deficient environments to optimize calcination. |
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Ensures even heating, reducing hot spots and improving product consistency. |
| Enhanced Fuel Flexibility | Supports use of alternative fuels without clinker contamination, aiding sustainability. |
Ready to elevate your cement production with advanced kiln solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need enhanced purity, precise control, or fuel flexibility, we can tailor our solutions to your goals. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















