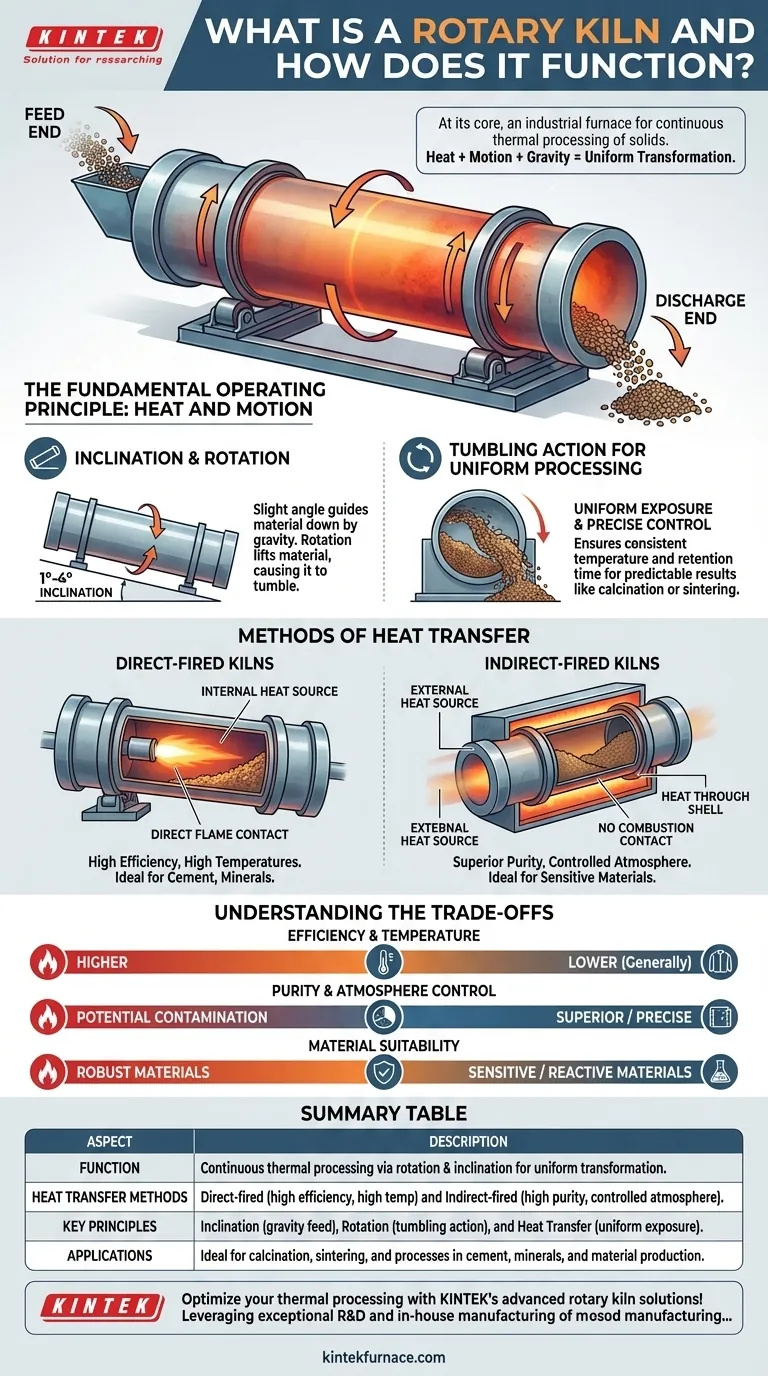
At its core, a rotary kiln is an industrial furnace designed for continuous thermal processing of solid materials. It consists of a large, rotating cylindrical drum that is slightly inclined from the horizontal, allowing materials to be heated to extremely high temperatures as they are tumbled and moved from one end to the other. This combination of heat, motion, and gravity induces specific chemical reactions or physical changes in the material.
The essential function of a rotary kiln is to use its unique design—a combination of slow rotation and a gentle incline—to ensure every particle of a material is uniformly exposed to a controlled, high-temperature environment. This guarantees a consistent and predictable transformation of the material being processed.
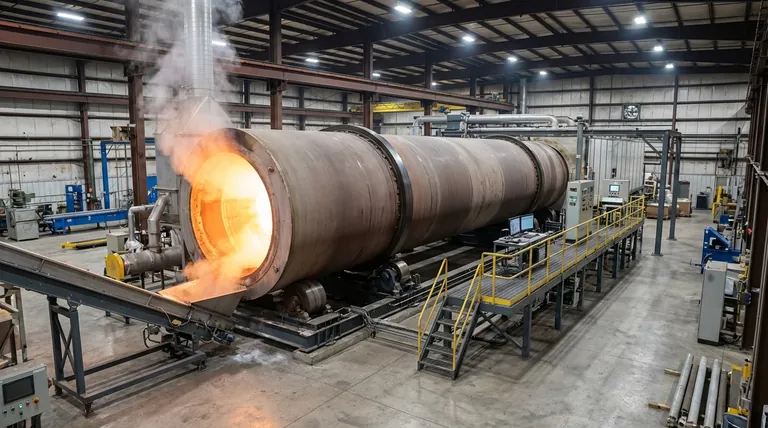

The Fundamental Operating Principle: Heat and Motion
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln is rooted in three simple yet powerful physical principles working in concert: inclination, rotation, and heat transfer.
The Role of Inclination and Rotation
A rotary kiln is mounted at a slight angle, typically between 1 and 4 degrees. This inclination uses gravity to guide material from the higher feed end down to the lower discharge end.
Simultaneously, the entire cylindrical drum rotates slowly on its longitudinal axis. This rotation lifts the material up the side of the drum until gravity causes it to cascade, or "tumble," back down.
The Tumbling Action for Uniform Processing
This continuous tumbling action is the most critical aspect of the kiln's function. It thoroughly mixes the material, ensuring that no single part of the batch is over- or under-exposed to the heat source.
This uniform exposure allows for precise control over the material's temperature and the duration it spends in the kiln, known as retention time. This predictability is essential for achieving desired outcomes like calcination or sintering.
Methods of Heat Transfer
Rotary kilns heat material using one of two primary methods, each suited for different process requirements. The choice between them depends on the material's sensitivity and the desired final product characteristics.
Direct-Fired Kilns
In a direct-fired system, the heat source—typically a powerful flame from a burner or hot process gas—is located inside the kiln drum.
The flame and hot combustion gases flow through the cylinder, coming into direct contact with the material. This method is highly efficient for achieving very high temperatures and is common in industries like cement and minerals processing.
Indirect-Fired Kilns
In an indirect-fired system, the drum is enclosed within an external furnace or fitted with an external heating jacket (often electric). The heat is transferred through the kiln's metal shell to the material inside.
This approach ensures the material never comes into contact with combustion byproducts, making it ideal for processes where purity is paramount or where a specific internal atmosphere (e.g., inert) must be maintained.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision between a direct and indirect kiln is a critical engineering choice based on a clear set of trade-offs between efficiency, purity, and cost.
Efficiency and Temperature
Direct-fired kilns are generally more thermally efficient and can reach higher process temperatures more economically because heat is transferred directly to the material.
Purity and Atmosphere Control
Indirect-fired kilns offer superior product purity and precise atmospheric control. By isolating the material from the heat source, any possibility of contamination from combustion is eliminated.
Material Suitability
Some materials are chemically sensitive to the gases produced by direct firing or may be physically damaged by direct flame impingement. For these applications, an indirect kiln is the only viable option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The selection of a rotary kiln configuration is dictated entirely by the end goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, high-temperature processing where contamination is not a concern: A direct-fired kiln offers the most cost-effective and thermally efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is product purity or requires a specific, controlled atmosphere: An indirect-fired kiln provides the necessary isolation and environmental control.
- If your primary focus is achieving perfectly uniform heat treatment across a batch of powder or granular material: The fundamental tumbling action of any rotary kiln is engineered to solve this exact problem.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln remains a cornerstone of modern industry by elegantly combining simple mechanical principles with powerful thermal energy to create essential materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Continuous thermal processing via rotation and inclination for uniform material transformation. |
| Heat Transfer Methods | Direct-fired (high efficiency, high temp) and Indirect-fired (high purity, controlled atmosphere). |
| Key Principles | Inclination (gravity feed), Rotation (tumbling action), and Heat Transfer (uniform exposure). |
| Applications | Ideal for calcination, sintering, and processes in cement, minerals, and material production. |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in industries such as cement, minerals, and materials science. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















