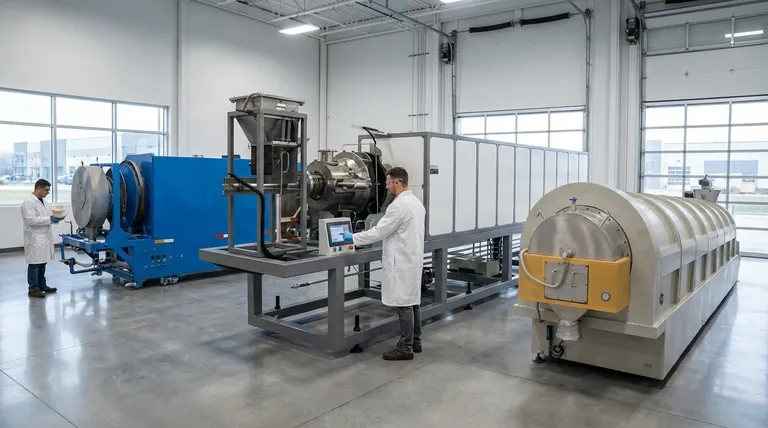
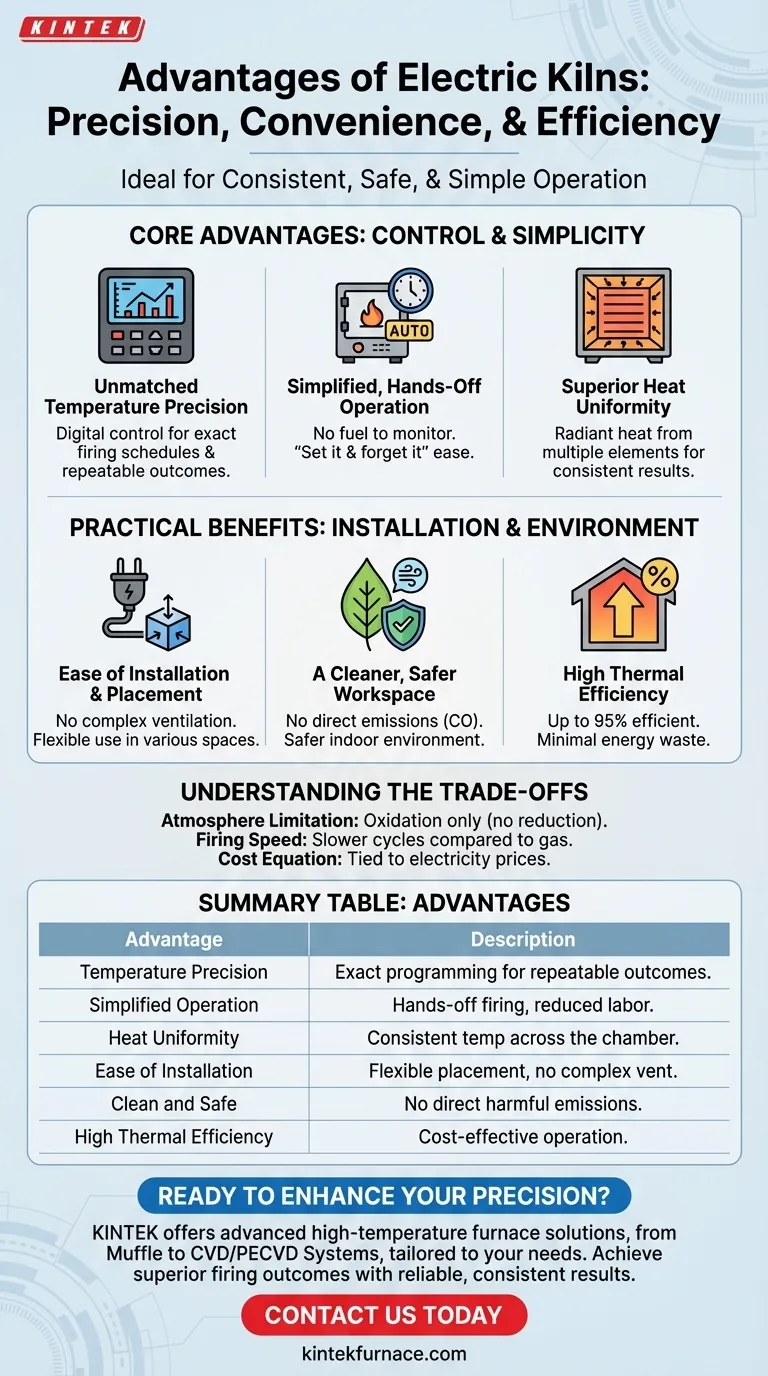
In short, the primary advantages of an electric kiln are its exceptional ease of use, precise digital control, and cleaner, safer operation. Because they don't burn fuel, they produce no direct emissions, are simpler to install in a wider variety of spaces, and provide highly repeatable, uniform heating for consistent results.
The decision to use an electric kiln is fundamentally a choice for predictability and convenience. While other kiln types offer unique atmospheric effects, the electric kiln excels at delivering precise, repeatable outcomes with minimal operational complexity, making it the dominant choice for many modern studios and workshops.

The Core Advantages: Control and Simplicity
The most significant benefits of an electric kiln revolve around its automated and highly controllable nature. This translates directly to more consistent results and a simpler workflow.
Unmatched Temperature Precision
Modern electric kilns are operated by digital controllers. This allows you to program exact firing schedules—controlling the rate of temperature increase, holding times (soaks), and cooling.
This level of precision is critical for achieving specific glaze results and minimizing defects. It makes the firing process a repeatable, scientific variable rather than an unpredictable art.
Simplified, Hands-Off Operation
Unlike fuel-fired kilns, electric models require no active management during firing. There is no fuel to monitor, no flame to adjust, and no flue to damper.
This "set it and forget it" operation frees the user to focus on other tasks and dramatically lowers the barrier to entry for achieving professional-quality firings.
Superior Heat Uniformity
Electric kilns use heating elements positioned around the interior chamber. This design provides radiant heat from multiple directions, resulting in highly uniform temperature distribution.
This uniformity reduces the risk of hot or cold spots within the kiln, ensuring that pieces in different locations receive a consistent heat treatment.
The Practical Benefits: Installation and Environment
Beyond firing quality, electric kilns offer significant practical advantages for the studio environment itself, related to safety, installation, and energy use.
Ease of Installation and Placement
Because they don't require complex ventilation for combustion byproducts, electric kilns are significantly easier and cheaper to install. Many smaller models simply plug into a standard high-voltage outlet.
Their smaller footprint and lack of fuel lines also make them more portable and suitable for home studios, classrooms, or spaces where a gas kiln would be impractical or prohibited.
A Cleaner, Safer Workspace
The defining feature of an electric kiln is the absence of combustion. This means it produces no direct emissions like carbon monoxide or other harmful fumes during operation.
This creates a much cleaner and safer indoor environment. While kilns still require ventilation for fumes released from clays and glazes, the requirements are far less stringent than for a gas kiln.
High Thermal Efficiency
Electric kilns are exceptionally well-insulated and transfer energy directly into the chamber via heating elements. This results in extremely high thermal efficiency, often up to 95%.
Less energy is wasted as exhaust heat compared to fuel-fired kilns, which can lead to more economical operation depending on local electricity versus gas prices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an informed decision, it is critical to understand that the advantages of an electric kiln come with inherent limitations.
The Atmosphere Limitation
Electric kilns fire in what is known as an oxidation atmosphere—a clean, oxygen-rich environment. This is perfect for producing bright, consistent colors.
However, they cannot natively create a reduction atmosphere (oxygen-starved), which is achieved in gas kilns by controlling the fuel-to-air ratio. Many classic and earthy glaze effects, like copper reds or celadons, depend on a reduction environment.
Firing Speed and Temperature Ceilings
While highly controlled, electric kilns often have slower firing cycles compared to the potential speed of a gas kiln. Furthermore, most standard electric kilns have a lower maximum temperature than their high-fire gas counterparts.
The Cost Equation: Upfront vs. Operating
While often easier to install, the long-term operating cost of an electric kiln is tied directly to the price of electricity, which can be high in some regions. Gas may be a cheaper fuel source, but gas kilns typically have higher upfront costs for the kiln, installation, and necessary safety infrastructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" kiln is the one that aligns with your artistic or production objectives.
- If your primary focus is consistent, repeatable results: An electric kiln is the definitive choice for its precise digital control and uniform heat.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific atmospheric glaze effects: A gas kiln is necessary for creating a reduction atmosphere required for certain classic glazes.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and safety: An electric kiln is unparalleled for its ease of use, making it ideal for schools, home studios, or high-turnover production environments.
Ultimately, choosing an electric kiln is a commitment to precision and convenience over the atmospheric possibilities of fuel-burning alternatives.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Precision | Digital controllers allow exact programming of firing schedules for repeatable outcomes. |
| Simplified Operation | Hands-off firing with no fuel monitoring, ideal for easy use and reduced labor. |
| Heat Uniformity | Radiant heat from multiple elements ensures consistent temperature across the chamber. |
| Ease of Installation | No complex ventilation needed; often plugs into standard outlets for flexible placement. |
| Clean and Safe | No direct emissions like carbon monoxide, creating a safer indoor environment. |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Up to 95% efficiency with minimal energy waste, leading to cost-effective operation. |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in a studio, workshop, or research lab, our electric kilns and other solutions deliver reliable, consistent results with minimal operational complexity. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior firing outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















