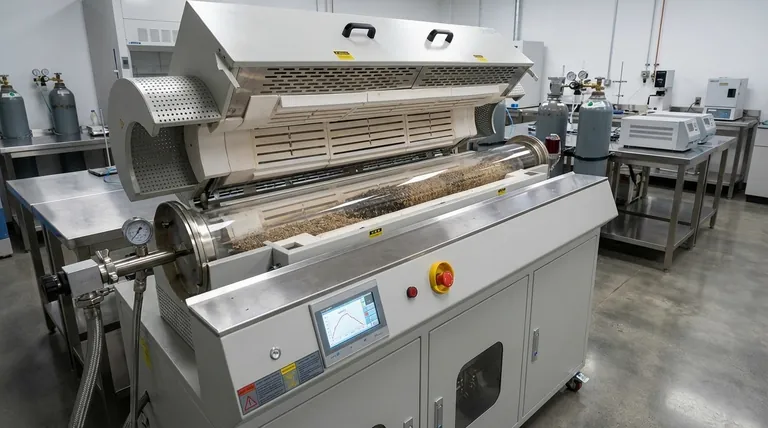
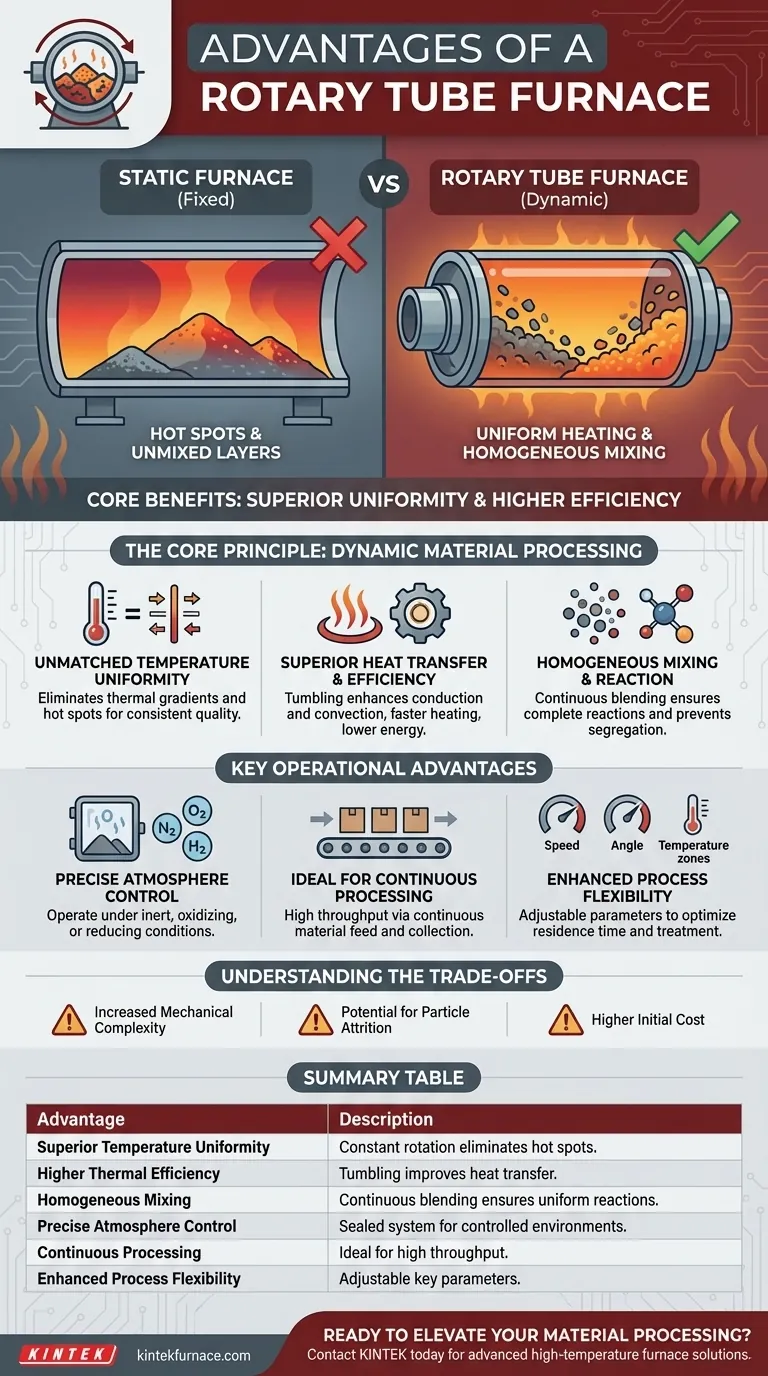
At their core, rotary tube furnaces offer two primary advantages over their static counterparts: superior processing uniformity and higher thermal efficiency. The continuous rotation of the process tube ensures that the material is constantly mixed, which guarantees every particle is exposed to the same temperature and atmospheric conditions, leading to a more consistent final product and faster processing times.
A static furnace heats material in a fixed position, inevitably creating hot spots and unmixed layers. A rotary tube furnace solves this fundamental problem by introducing dynamic motion, ensuring every part of the sample is treated identically for unparalleled process consistency.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Material Processing
The defining feature of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to rotate the tube containing the sample material. This simple mechanical action is the source of its most significant advantages over static designs.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
In a static furnace, material at the bottom and center of a pile heats more slowly than material at the surface and edges. The rotation in a rotary furnace constantly tumbles the material, eliminating these thermal gradients and hot spots.
This ensures that the entire batch reaches the target temperature uniformly, which is critical for processes like catalyst activation or sintering, where precise thermal history dictates product quality.
Superior Heat Transfer and Efficiency
The tumbling action dramatically enhances heat transfer. It brings cooler particles into direct contact with the hot furnace wall (conduction) and improves the mixing of the process gas around the particles (convection).
This increased efficiency means the material heats up faster and more thoroughly, reducing overall processing time and energy consumption compared to a static furnace of the same size.
Homogeneous Mixing and Reaction
For processes involving multiple components or chemical reactions, the continuous mixing is invaluable. It ensures reactants are well-integrated and prevents the segregation of materials with different densities or sizes.
This leads to more complete reactions and a more homogeneous final product, eliminating the need for separate mixing steps before or after heating.
Key Operational Advantages
Beyond the core principles of heat transfer and mixing, rotary tube furnaces provide distinct operational benefits that make them suitable for demanding research and production environments.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Like standard tube furnaces, rotary models are designed as sealed systems. This allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere.
You can run processes under inert (Nitrogen, Argon), oxidizing (Air), or reducing (Hydrogen mixtures) conditions, which is essential for preventing unwanted chemical reactions or promoting desired ones.
Ideal for Continuous Processing
The design of a rotary tube furnace is uniquely suited for continuous or semi-continuous operation. Material can be fed into one end of a tilted, rotating tube and collected as it exits the other.
This capability allows for much higher throughput than the batch-based nature of most static furnaces, making it a powerful choice for pilot-scale or full-scale production.
Enhanced Process Flexibility
Modern rotary furnaces offer a high degree of control. Key parameters like rotation speed, tube tilt angle, and temperature profiles across multiple heating zones can be precisely adjusted.
This flexibility allows you to optimize the residence time and thermal treatment for a wide variety of materials, from fine powders to larger granules.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is universally superior. While powerful, rotary tube furnaces have considerations that may make a static furnace a better choice in some situations.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor, drive system, and rotating seals, adds complexity compared to a simple static furnace. This introduces more potential points of failure and may require more maintenance over the long term.
Potential for Particle Attrition
The tumbling action that provides excellent mixing can also cause friable or delicate materials to break down. If preserving particle size and shape is absolutely critical, the gentle heating of a static furnace may be preferable.
Higher Initial Cost
Due to their added mechanical systems and more complex design, rotary tube furnaces typically represent a higher upfront investment than static tube furnaces of a comparable size and temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the specific goals of your material processing work.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and product quality: The unmatched heating uniformity of a rotary furnace is your single greatest advantage.
- If your primary focus is high throughput for production: The suitability for continuous processing makes a rotary furnace the clear choice over batch-based static systems.
- If your primary focus is research on diverse materials: The flexibility to control rotation speed, tilt, and temperature profiles gives you the control needed to optimize a wide range of processes.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and lowest initial cost for basic heating: A static tube furnace is a simpler and more economical option, provided you can tolerate potential non-uniformity in your results.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary tube furnace is an investment in process control and consistency.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Constant rotation eliminates hot spots and thermal gradients for consistent heating. |
| Higher Thermal Efficiency | Tumbling action improves heat transfer, reducing processing time and energy use. |
| Homogeneous Mixing | Continuous blending ensures uniform reactions and prevents material segregation. |
| Precise Atmosphere Control | Sealed system allows operation under inert, oxidizing, or reducing conditions. |
| Continuous Processing | Ideal for high-throughput applications with material feed and collection. |
| Enhanced Process Flexibility | Adjustable rotation speed, tilt angle, and multi-zone temperature control. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, designed to deliver unmatched uniformity and throughput for diverse laboratory needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















