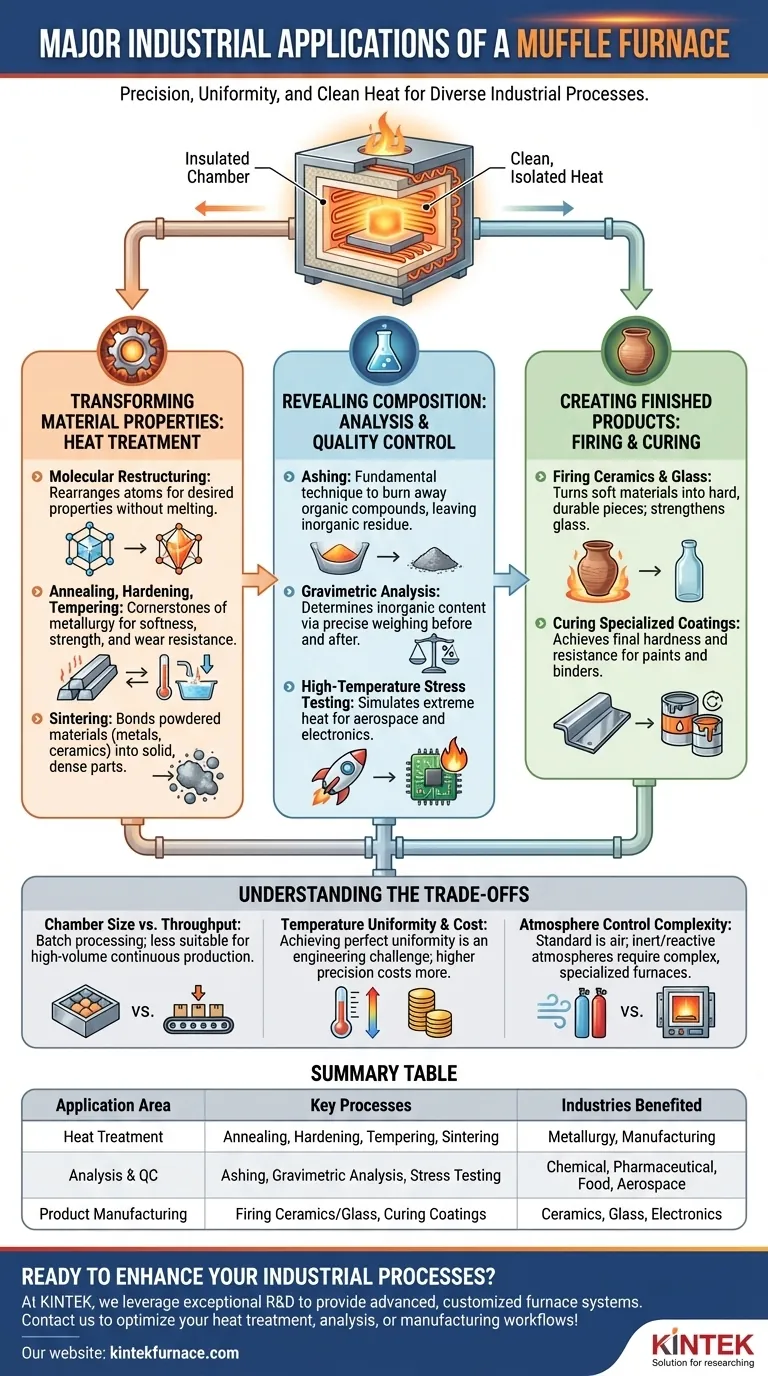
At its core, a muffle furnace is an industrial workhorse for providing a uniform, high-temperature environment that is isolated from the byproducts of fuel combustion. This precise and clean heating capability makes it indispensable across a vast range of industrial applications, primarily for heat-treating metals, conducting material analysis through ashing, and manufacturing specialized products like ceramics.
The true value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its "muffle"—an insulating chamber that isolates the sample from heating elements and contaminants. This ensures that the process is defined purely by temperature, not by a reactive chemical environment.
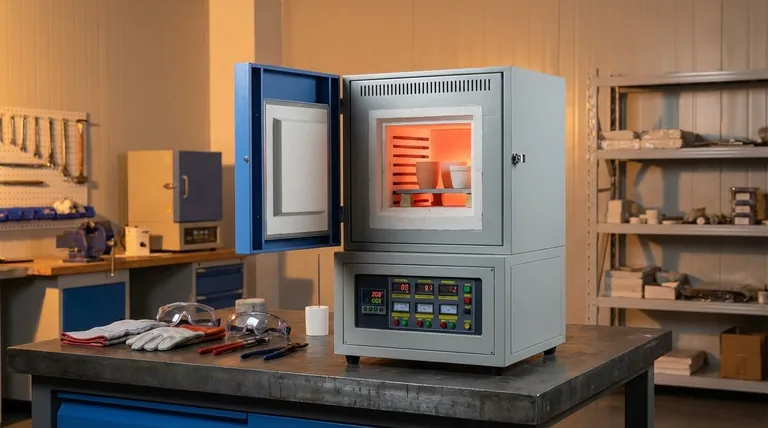

Transforming Material Properties: Heat Treatment
The most common industrial use for muffle furnaces is the heat treatment of materials, particularly metals. This involves heating and cooling a material under controlled conditions to alter its internal microstructure and, therefore, its physical and mechanical properties.
The Principle of Molecular Restructuring
Heat treatment does not melt the material. Instead, it gives the atoms within the material's crystal structure enough energy to rearrange themselves into a more desirable configuration, which becomes locked in upon cooling.
Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering
These are the cornerstones of metallurgy. A furnace is used to anneal metals, making them softer and more workable. Conversely, it can be used for hardening by heating and then rapidly cooling (quenching) a part to increase its strength and wear resistance, followed by tempering to reduce brittleness.
Sintering Powders into Solids
Muffle furnaces are critical for sintering, a process used for both metals and ceramics. Powdered materials are heated to a temperature below their melting point, causing the particles to bond and fuse into a solid, coherent mass with desired density and strength.
Revealing Composition: Analysis and Quality Control
When the goal is to understand what a material is made of, a muffle furnace is an essential analytical tool. It uses heat to break down samples for quantitative analysis.
The Critical Role of Ashing
In chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries, ashing is a fundamental technique. A sample is placed in the furnace and heated until all organic and volatile compounds burn away, leaving only the non-combustible inorganic residue (ash).
Gravimetric Analysis for Quality
By weighing the sample before and after ashing, analysts can precisely determine its inorganic content. This is crucial for quality control in food (mineral content), coal (ash content), and cement production.
High-Temperature Stress Testing
In industries like aerospace and electronics, components must withstand extreme conditions. Muffle furnaces are used to simulate intense heat, testing the flame retardancy of materials or the operational integrity of circuit boards to ensure they meet stringent safety and reliability standards.
Creating Finished Products: Firing and Curing
Beyond modification and analysis, muffle furnaces are directly involved in the manufacturing of certain goods. The controlled heat provides the necessary energy for chemical and physical transformations.
Firing Ceramics and Glass
The process of firing is what turns a soft clay object into a hard, durable ceramic piece. The furnace's uniform heat ensures the part is cured evenly, preventing cracks and weaknesses. Similar processes are used in glass manufacturing to strengthen or shape products.
Curing Specialized Coatings
Certain high-performance paints, coatings, and binders require a thermal curing process to achieve their final hardness and chemical resistance. A muffle furnace provides the consistent, clean environment needed for these reactions to occur properly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Chamber Size vs. Throughput
Muffle furnaces are fundamentally batch processors. Their chamber size limits the volume of material that can be processed at one time, making them less suitable for high-volume, continuous production lines compared to tunnel kilns.
Temperature Uniformity and Cost
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity throughout the chamber is an engineering challenge. Higher-specification furnaces with advanced controllers and multiple heating zones provide better uniformity but come at a significantly higher cost.
Atmosphere Control Complexity
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert (e.g., nitrogen, argon) or reactive atmosphere to prevent oxidation, a specialized and more complex furnace with gas-tight seals and input ports is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal application of a muffle furnace depends entirely on the industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical processing: You need precise temperature control, programmable heating/cooling ramps, and potentially an inert atmosphere for sensitive alloys.
- If your primary focus is analytical chemistry (ashing): Your priority is ensuring complete combustion of organic matter, temperature stability, and preventing cross-contamination between samples.
- If your primary focus is material testing or R&D: Versatility is key, so look for a furnace with a wide temperature range, programmable cycles, and robust construction to handle diverse materials.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a fundamental tool for manipulating and understanding materials where controlled, clean heat is the critical parameter.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Industries Benefited |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering, Sintering | Metallurgy, Manufacturing |
| Analysis & Quality Control | Ashing, Gravimetric Analysis, Stress Testing | Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Food, Aerospace |
| Product Manufacturing | Firing Ceramics/Glass, Curing Coatings | Ceramics, Glass, Electronics |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with tailored high-temperature solutions?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems for diverse laboratories and industries. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your heat treatment, analysis, or manufacturing workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















