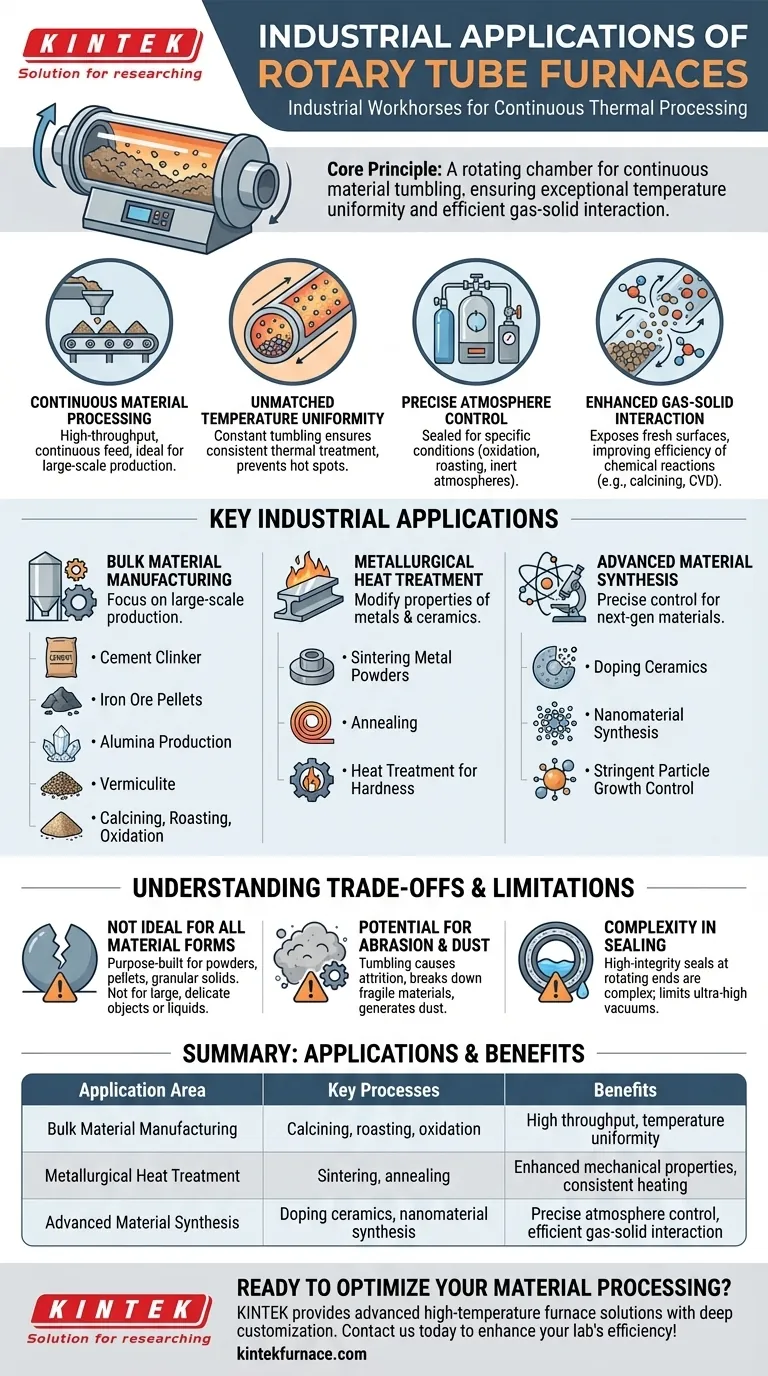
At their core, rotary tube furnaces are industrial workhorses designed for the continuous thermal processing of powders, granules, and other bulk solids. They are widely used for manufacturing essential materials like cement clinker, alumina, and iron ore pellets. These furnaces excel at processes requiring high temperatures and specific atmospheric conditions, such as calcining, roasting, and oxidation, making them vital in metallurgy, chemical production, and advanced materials science.
The key to understanding the value of a rotary tube furnace lies in its unique design: a rotating chamber that continuously tumbles material. This simple mechanical action provides exceptional temperature uniformity and efficient gas-solid interaction, which is why it has become indispensable for high-volume, high-quality material production.

The Core Principle: Why Rotary Furnaces Excel
To understand the applications, you must first understand the fundamental advantages of the design. A rotary furnace's value comes from a few key operational principles that static batch furnaces cannot easily replicate.
Continuous Material Processing
Unlike a batch furnace where material is loaded and unloaded in discrete cycles, a rotary furnace allows for a continuous feed. This makes it ideal for high-throughput industrial environments where constant production is a primary economic driver.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The constant rotation and tumbling of the material ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source evenly. This prevents hot spots and guarantees a highly consistent thermal treatment, which is critical for achieving specific material properties and ensuring product quality.
Precise Atmosphere Control
These furnaces can be sealed to maintain a specific atmosphere within the tube. This allows for processes like oxidation (introducing oxygen), roasting in a controlled gas, or running reactions in an inert atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical changes.
Enhanced Gas-Solid Interaction
The tumbling action constantly exposes fresh surfaces of the material to the internal atmosphere. This dramatically improves the efficiency of chemical reactions, such as in calcining, where volatile compounds are driven off, or when applying a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) coating.
Key Industrial Applications in Practice
The unique capabilities of rotary tube furnaces lead to their adoption across a wide range of industries, from producing bulk commodities to synthesizing highly specialized materials.
Bulk Material Manufacturing
This is the most common application, focused on large-scale production. The furnace's efficiency and continuous throughput are perfect for processes like producing cement clinker, drying and pelletizing iron ore, and manufacturing alumina and vermiculite.
Metallurgical Heat Treatment
In metallurgy, rotary furnaces are used to modify the properties of metals and ceramics. This includes sintering metal powders to form dense components, annealing to enhance mechanical properties, and heat-treating parts to achieve a desired hardness or crystalline structure.
Advanced Material Synthesis
The precise control offered by these furnaces is crucial for creating next-generation materials. Applications include doping ceramics with rare-earth metals to alter their optical or electrical properties and synthesizing nanomaterials that require stringent control over particle growth and structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, rotary tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Their design brings inherent trade-offs that make them unsuitable for certain tasks.
Not Ideal for All Material Forms
These furnaces are purpose-built for powders, pellets, and granular solids. They are not practical for processing large, single objects, delicate structures that could be damaged by tumbling, or liquid materials.
Potential for Abrasion and Dust
The constant tumbling motion can cause attrition, where particles grind against each other and the furnace wall. This can break down fragile materials and generate significant dust, which may require a robust collection system and can be problematic for processes requiring high purity.
Complexity in Sealing
While they offer good atmospheric control, achieving a perfect, high-integrity seal at the rotating ends of the tube can be more mechanically complex and expensive than in a static furnace. This can be a limiting factor for applications requiring ultra-high vacuums or extremely pure inert atmospheres.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material, desired throughput, and final product goals.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous production of bulk solids: A rotary tube furnace is likely the most energy-efficient and cost-effective solution due to its high throughput.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum uniformity in heat-treating powders: The tumbling action of a rotary furnace provides superior thermal consistency compared to most static batch furnaces.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing advanced or reactive materials: The precise temperature and atmospheric control make a rotary furnace a powerful tool for developing materials with specific chemical and physical properties.
Ultimately, understanding the core principles of how a rotary furnace operates is the key to leveraging its power for industrial success.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Material Manufacturing | Calcining, roasting, oxidation | High throughput, temperature uniformity |
| Metallurgical Heat Treatment | Sintering, annealing | Enhanced mechanical properties, consistent heating |
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Doping ceramics, nanomaterial synthesis | Precise atmosphere control, efficient gas-solid interaction |
Ready to optimize your material processing with a custom rotary tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















