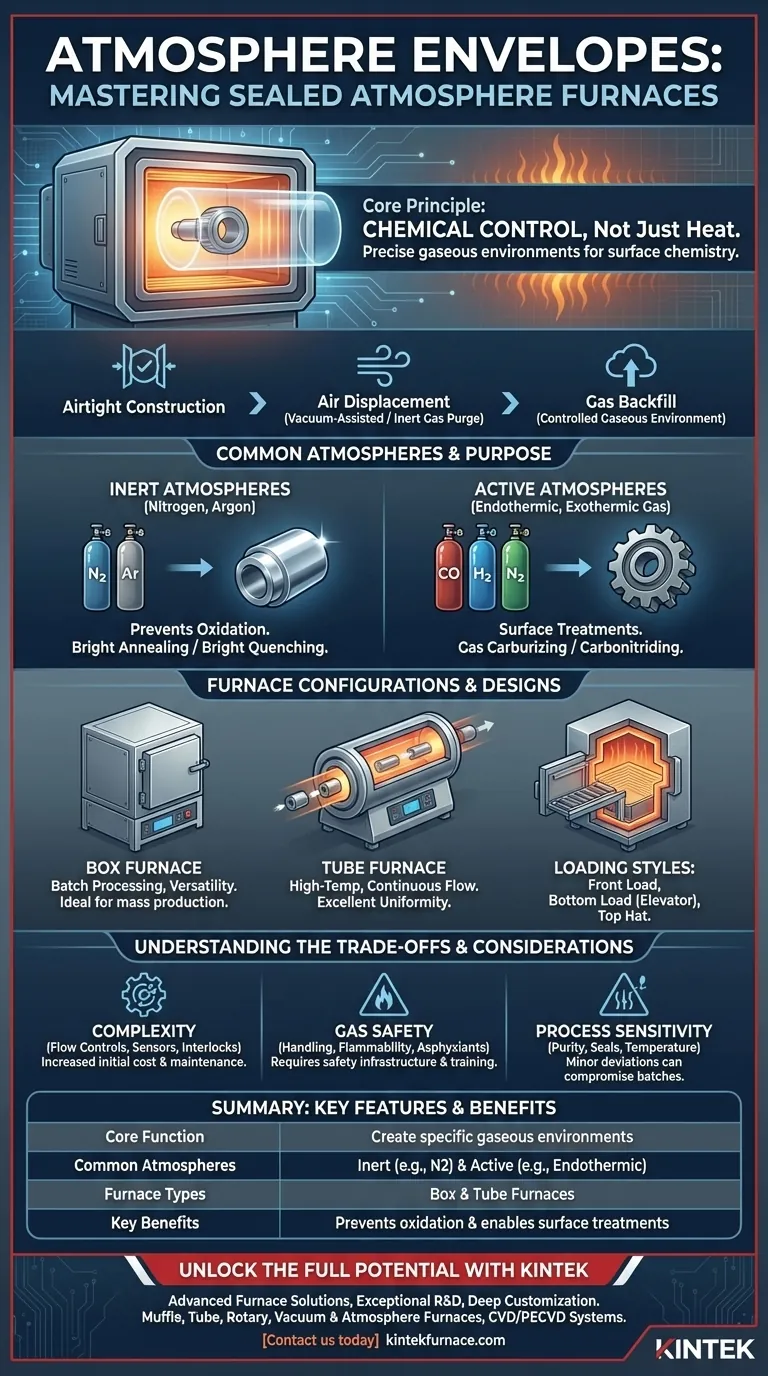
In the field of heat treatment, sealed atmosphere furnaces are most accurately referred to as atmosphere envelopes. Their defining feature is the ability to create and maintain a specific gaseous environment around a part during a thermal cycle, allowing for precise control over the material's surface chemistry. These furnaces are not just for heating; they are sophisticated tools for material transformation.
The core value of an atmosphere furnace is not just its ability to heat, but its power to control the chemical environment. This control prevents undesirable reactions like oxidation and enables specific surface treatments like hardening or case-hardening.

The Core Principle: Chemical Control, Not Just Heat
The fundamental purpose of a sealed atmosphere furnace is to displace the ambient air (roughly 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen) and replace it with a precisely managed gas or mixture of gases. This is critical for processes where interaction with oxygen would be detrimental.
How Atmosphere Control is Achieved
Airtight construction is the first requirement. To create the desired environment, the furnace chamber is first purged of ambient air.
This is often done using a vacuum-assisted evacuation, which removes the air before the chamber is backfilled with the chosen process gas. Alternatively, the chamber can be flooded with a high flow of inert gas to displace the oxygen.
Common Atmospheres and Their Purpose
The gas introduced determines the outcome of the heat treatment process.
- Inert Atmospheres (Nitrogen, Argon): Used for processes like bright annealing or bright quenching, where the primary goal is to heat and cool the metal without any surface oxidation, preserving its shiny finish.
- Active Atmospheres (Endothermic, Exothermic gas): These are complex gas mixtures used for case-hardening processes. Gas carburizing introduces carbon into the surface of steel to increase hardness, while carbonitriding introduces both carbon and nitrogen for similar purposes.
Common Furnace Configurations and Designs
Atmosphere furnaces are not one-size-fits-all. Their design is dictated by the production volume, part size, and specific process requirements.
Box Furnaces
These are rectangular or cube-shaped chambers with a single front-loading door. They are ideal for processing parts in batches and are a mainstay in commercial heat-treating shops for their versatility and suitability for mass production.
Tube Furnaces
Featuring a cylindrical chamber, these furnaces are well-suited for high-temperature applications, scientific research, and continuous-flow processes where parts can be pushed or pulled through the heated tube. Their geometry often provides excellent temperature uniformity.
Loading and Access Styles
Beyond the chamber shape, the method of loading parts varies.
- Front Load: The most common style, similar to a conventional oven.
- Bottom Load (Elevator): The furnace is elevated, and the hearth is raised into the chamber from below. This is excellent for heavy loads and minimizing heat loss.
- Top Hat: The furnace body (the "hat") is lifted off the hearth, allowing for easy access and loading with an overhead crane.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, atmosphere furnaces introduce complexities not found in simpler air-circulating ovens.
Increased System Complexity
Managing gas flow, ensuring a positive pressure to prevent air ingress, and monitoring atmospheric composition require additional controls, sensors, and safety interlocks. This adds to the initial cost and maintenance requirements.
Gas Handling and Safety
Storing and handling process gases, some of which may be flammable (like hydrogen) or asphyxiants (like nitrogen), requires significant safety infrastructure and operator training.
Process Sensitivity
The success of an atmospheric process is highly sensitive to the purity of the gas, the integrity of the furnace seals, and the precise temperature. Minor leaks or deviations can compromise an entire batch, making process control paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace configuration depends entirely on the material transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is high-volume case hardening: A batch-style box furnace with integrated controls for an active atmosphere is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on sensitive parts: A well-sealed furnace with a reliable inert gas backfill system is your critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is research or continuous processing: A tube furnace offers superior uniformity and is easily adapted for controlled, continuous material flow.
By understanding that these furnaces are precise tools for chemical control, you can select the exact configuration needed to achieve your desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Atmosphere Envelopes |
| Core Function | Create and maintain specific gaseous environments for precise surface chemistry control |
| Common Atmospheres | Inert (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) for bright annealing; Active (e.g., Endothermic gas) for case-hardening |
| Furnace Types | Box Furnaces (batch processing), Tube Furnaces (high-temperature, continuous flow) |
| Loading Styles | Front Load, Bottom Load (Elevator), Top Hat |
| Key Benefits | Prevents oxidation, enables surface treatments like carburizing, offers high temperature uniformity |
| Considerations | Increased complexity, gas handling safety, sensitivity to leaks and temperature control |
Unlock the full potential of your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can transform your material processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















