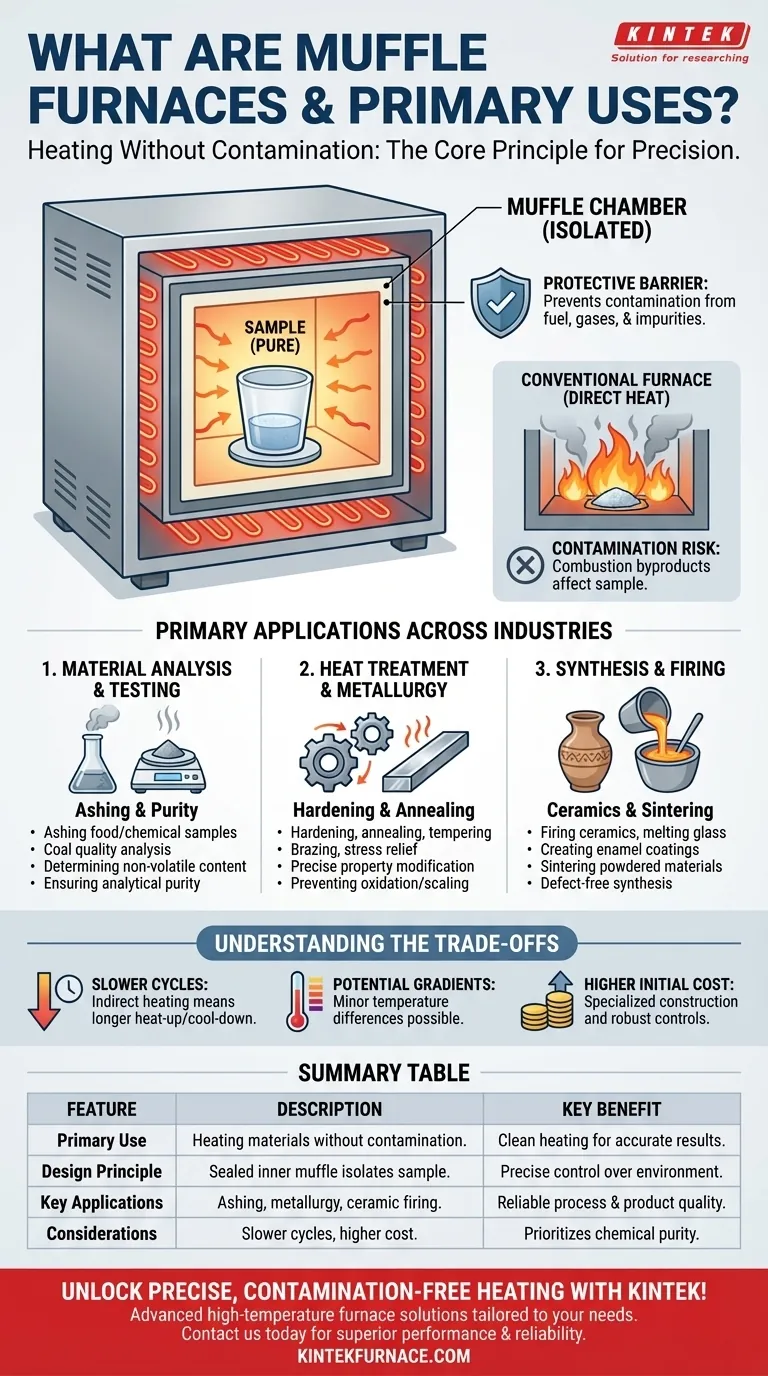
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven engineered for one critical purpose: to heat materials without contaminating them. Unlike a conventional furnace where the material may be exposed to flames or combustion byproducts, a muffle furnace uses a sealed inner chamber—the "muffle"—to isolate the sample. This ensures the heating process is exceptionally clean and controlled, making it indispensable for scientific analysis, material synthesis, and precise heat treatments.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace isn't just its high heat, but its ability to create a chemically isolated environment. This prevents combustion byproducts or atmospheric impurities from reacting with the sample, ensuring process purity and accurate analytical results.

The Core Principle: Heating Without Contamination
To understand the value of a muffle furnace, you must first understand the problem it solves. Many high-temperature processes are sensitive to their chemical environment.
What "Muffle" Means
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's core component: a separate, insulated chamber that houses the material being heated.
The heating elements are on the outside of this chamber. Heat radiates through the muffle's walls to the sample inside, without any direct contact between the sample and the heat source.
This design effectively creates a protective barrier, preventing contamination from fuel, gases, or other impurities present in the furnace.
Why Isolation is Critical
In many applications, even minor contamination can completely invalidate results or ruin a product.
For chemical analysis like ashing, the goal is to burn off all organic matter to weigh the remaining inorganic ash. If byproducts from combustion settle on the sample, the final weight will be inaccurate.
In metallurgy, exposing a hot metal alloy to reactive gases like oxygen can cause unwanted oxidation (scaling) or alter its fundamental properties, compromising the final component's strength and integrity.
Primary Applications Across Industries
A muffle furnace's unique capability makes it a fundamental tool in research, quality control, and production environments.
Material Analysis and Testing
The most common laboratory use is for preparing samples for analysis where purity is paramount.
Applications include ashing food or chemical samples, coal quality analysis, and determining the non-volatile content of materials. The controlled environment ensures that the only thing being measured is the material itself.
Heat Treatment and Metallurgy
The furnace provides the stable, non-reactive environment required for modifying the physical properties of metals and other materials.
This is essential for processes like hardening, annealing, tempering, brazing, and stress relief, where precise temperature control and a clean atmosphere are needed for predictable results.
Synthesis and Firing
Creating new materials often involves high-temperature chemical reactions that must be free from outside influence.
Muffle furnaces are used for firing ceramics, melting glass, creating enamel coatings, and sintering powdered materials into a solid mass. In each case, contamination could cause defects or alter the material's final characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, the design of a muffle furnace presents certain considerations that distinguish it from simpler, direct-heat ovens.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
Because heat must transfer indirectly through the walls of the muffle, these furnaces often have slower heat-up and cool-down times compared to direct-fired furnaces. This can impact throughput in high-volume production settings.
Potential for Temperature Gradients
While modern designs are highly optimized, the indirect heating method can sometimes lead to minor temperature differences within the chamber. For applications requiring extreme temperature uniformity, this is a factor to consider.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
The specialized construction, including the insulated muffle chamber and robust controls, typically makes these furnaces more complex and expensive than a standard high-temperature oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right heating equipment depends entirely on whether chemical isolation is a requirement for your process.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace is non-negotiable for applications like ashing, materials testing, or trace element analysis.
- If your primary focus is process control: The furnace provides the stable, non-reactive environment needed for predictable heat treatment, ceramic firing, or material synthesis.
- If your primary focus is simply bulk heating: If contamination is not a concern, a simpler and potentially more cost-effective direct-fired furnace might be a better solution.
Ultimately, selecting a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize chemical purity and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Heating materials without contamination for scientific analysis and synthesis. |
| Key Applications | Ashing, metallurgy (annealing, hardening), ceramic firing, and material testing. |
| Design Principle | Sealed inner chamber (muffle) isolates sample from heat source and impurities. |
| Benefits | Clean heating, precise temperature control, and accurate analytical results. |
| Considerations | Slower heating cycles, potential temperature gradients, higher initial cost. |
Unlock precise, contamination-free heating for your laboratory with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research, quality control, or production, KINTEK ensures superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your processes and deliver accurate results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















