In industrial settings, a cartridge heater is a powerful tool for delivering concentrated heat precisely where it is needed. It is a cylindrical, tube-shaped heating element designed to be inserted into a drilled hole in a metal object, transferring its energy primarily through direct conduction. This makes them ideal for applications like heating dies, molds, and platens in manufacturing processes.
The core principle to understand is that a cartridge heater's performance is intrinsically linked to its installation. Its greatest strength—intense, localized heating via conduction—becomes its biggest point of failure if the fit between the heater and the surrounding material is not precise.
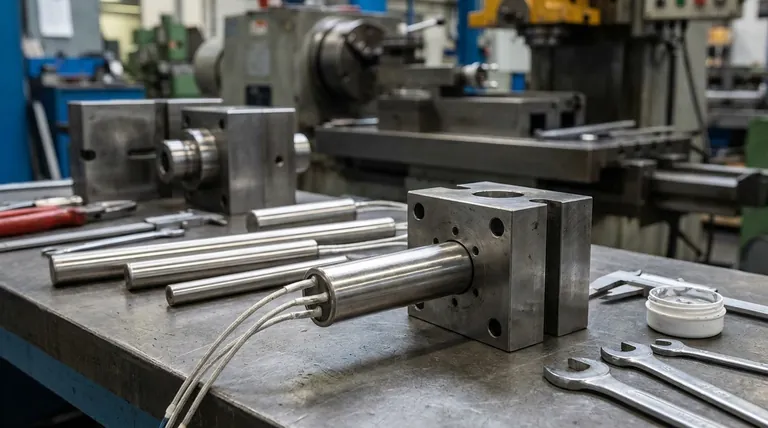

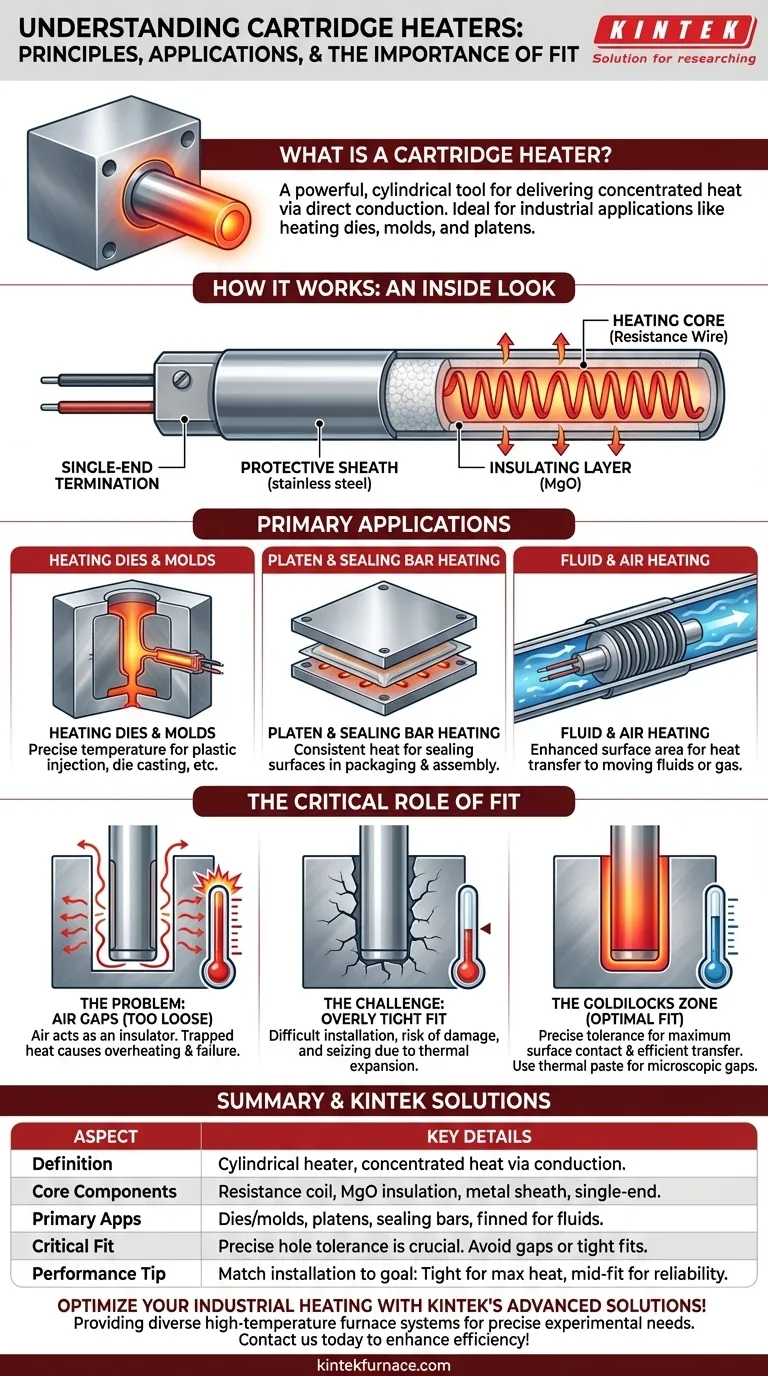
How a Cartridge Heater Works: An Inside Look
A cartridge heater's design is optimized for efficient heat transfer and durability in demanding industrial environments.
The Heating Core
At the center of the heater is a resistance wire coil, typically made of a nickel-chromium alloy. When electrical current passes through this coil, it generates heat due to its electrical resistance.
The Insulating Layer
The coil is surrounded by a highly compacted powder, most commonly Magnesium Oxide (MgO). This material is a superb thermal conductor but an excellent electrical insulator, allowing heat to flow outwards efficiently while preventing any electrical short circuits to the outer casing.
The Protective Sheath
An outer metal sheath, usually made of stainless steel, encases the internal components. This sheath protects the heater from the environment and provides the durable surface needed for direct contact and conductive heat transfer.
The Single-End Termination
A key design feature is that all electrical leads exit from one end of the heater. This configuration greatly simplifies wiring and installation, especially in confined spaces or complex machinery.
Primary Applications and Use Cases
Cartridge heaters are valued for their ability to deliver high watt densities (a large amount of heat from a small surface area) directly into a part.
Heating Dies and Molds
This is the most common application. In processes like plastic injection molding, die casting, and rubber molding, cartridge heaters are inserted directly into the steel mold or die to maintain a precise and uniform temperature.
Platen and Sealing Bar Heating
In packaging and assembly, flat plates (platens) or bars used for heat sealing are often heated by multiple cartridge heaters. This ensures the sealing surface remains at a consistent, effective temperature.
Fluid and Air Heating
While less common than dedicated immersion heaters, some cartridge heaters are fitted with fins along the sheath. These fins dramatically increase the surface area, allowing the heater to more effectively transfer heat to a moving fluid or gas stream via convection.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Role of Fit
The physics of heat transfer governs the success or failure of a cartridge heater installation. Because they rely on conduction, any barrier to that direct contact is a major problem.
The Problem with Air Gaps
Air is an extremely poor conductor of heat. If the hole drilled for the heater is too large, an air gap will exist between the heater's sheath and the surrounding metal.
This gap acts as an insulator, trapping heat within the cartridge heater. Unable to dissipate its energy effectively, the heater's internal temperature will rise dramatically, quickly leading to overheating and premature failure.
The Challenge of an Overly Tight Fit
Conversely, a hole that is too small or imperfectly drilled makes installation difficult. Forcing a heater into a tight hole can damage the sheath. More importantly, thermal expansion during operation can cause the heater to seize, making it nearly impossible to remove for maintenance or replacement without damaging the heater or the tool it's installed in.
The "Goldilocks" Zone
Success requires precision. The hole must be drilled and reamed to the exact diameter tolerance specified by the heater manufacturer. This ensures maximum surface contact for efficient heat transfer while still allowing for removal when necessary. Using a thermal transfer paste can help bridge microscopic air gaps in an optimal fit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To implement a cartridge heater successfully, you must align your installation strategy with your operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat transfer and performance: Prioritize precision machining of the receiving hole to the tightest end of the recommended tolerance for a near-perfect fit.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and ease of service: Aim for a fit in the middle of the tolerance range and use a thermally conductive paste to ensure good heat transfer while simplifying future removal.
- If your primary focus is heating a liquid or gas: Ensure you are using a specialized finned cartridge heater, but first verify that a purpose-built immersion or circulation heater would not be a more efficient solution for your system.
Ultimately, mastering the precise installation of a cartridge heater is the key to unlocking its powerful and efficient heating capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Cylindrical heating element for concentrated heat via conduction. |
| Core Components | Resistance wire coil, MgO insulation, metal sheath, single-end termination. |
| Primary Applications | Heating dies/molds, platens, sealing bars, and fluids/gas with fins. |
| Critical Fit Factors | Precise hole tolerance to avoid air gaps or tight fits; use thermal paste for gaps. |
| Performance Tips | Match installation to goals: tight fit for max heat, mid-fit for reliability, finned for fluids. |
Optimize your industrial heating with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and reliability in your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key differences between SiC and MoSi2 heating elements in sintering furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure



















