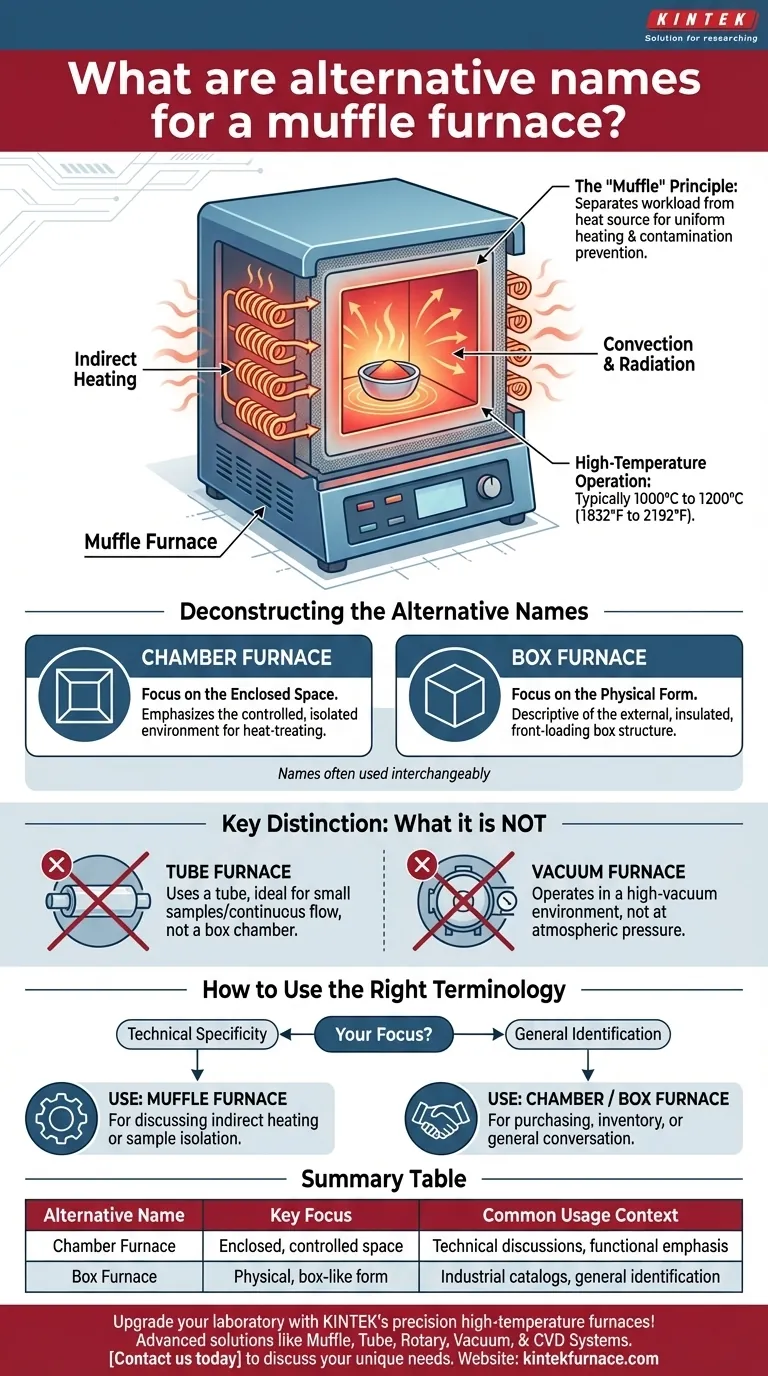
From a technical standpoint, a muffle furnace is also commonly known as a chamber furnace or a box furnace. These names are often used interchangeably and refer to the same fundamental piece of high-temperature heating equipment defined by its enclosed, box-like chamber.
The various names for a muffle furnace all describe its core design: an insulated, enclosed chamber ("muffle" or "box") that heats a sample indirectly, protecting it from direct contact with the heating elements. Understanding this principle is key to knowing which term to use.
What Defines a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is not just a hot box; its defining characteristic is the method of heating. It is designed for processes requiring high temperatures in a controlled atmosphere, free from the byproducts of combustion or direct radiation from the heating elements.
The "Muffle" Principle: Indirect Heating
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber that contains the sample. This chamber is heated from the outside by heating elements.
This design separates the workload from the heat source. It ensures that the sample is heated uniformly via convection and radiation within the chamber, rather than by direct exposure to the glowing-hot elements. This is critical for processes like ashing, where contamination must be avoided.
High-Temperature Operation
These furnaces are built to operate at very high temperatures, typically ranging from 1000°C to 1200°C (1832°F to 2192°F), with some specialized models reaching even higher. The heavy insulation is what allows them to safely contain this extreme heat.
Deconstructing the Alternative Names
The alternative names simply describe the furnace from different perspectives—one focusing on its function, the other on its form.
"Chamber Furnace": A Focus on the Enclosed Space
This name emphasizes the furnace's primary feature: a controlled, enclosed chamber. It highlights the functional aspect of having an isolated environment for heat-treating materials.
When you see the term "chamber furnace," the focus is on the quality and nature of the internal workspace where the process occurs.
"Box Furnace": A Focus on the Physical Form
This is the most descriptive name for the equipment's external appearance. Most of these furnaces are constructed as insulated, front-loading boxes.
This term is very common in industrial catalogs and general laboratory settings because it accurately describes what the equipment looks like.
Understanding the Key Distinction
While the names are often interchangeable, it's important not to confuse a muffle furnace with other high-temperature equipment. Its defining feature is always the indirect heating within an atmospheric chamber.
It Is Not a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical tube (often ceramic or quartz) as its chamber, which is ideal for processing small samples or for creating a continuous flow of gasses over a sample. A muffle furnace uses a larger, box-shaped chamber.
It Is Not a Vacuum Furnace
A standard muffle furnace operates at atmospheric pressure. A vacuum furnace is a specialized and far more complex system designed to heat materials in a high-vacuum environment to prevent oxidation or other atmospheric reactions.
How to Use the Right Terminology
Your choice of term depends on the context and what you need to emphasize.
- If your primary focus is technical specificity: Use muffle furnace when discussing the indirect heating method or processes where sample isolation from the heating elements is critical.
- If your primary focus is general identification: Use chamber furnace or box furnace in purchasing requests, inventory lists, or general conversation where the physical shape and enclosed nature are the most relevant details.
Understanding these terms ensures you are speaking the same language as engineers, suppliers, and lab technicians, clarifying both the function and form of the equipment you need.

Summary Table:
| Alternative Name | Key Focus | Common Usage Context |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Furnace | Enclosed, controlled space | Technical discussions, functional emphasis |
| Box Furnace | Physical, box-like form | Industrial catalogs, general identification |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's precision high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with reliable, tailored furnace technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of the thermal environment in calcination? Achieve Pure Ceramic Phases with KINTEK
- What is the significance of temperature control precision in high-temperature furnaces for carbon-doped titanium dioxide?
- What is the function of laboratory high-temperature box furnaces in T6 aluminum treatment? Key to Material Strength
- Why is calcination essential for NaFePO4 phase formation? Engineering High-Performance Sodium Iron Phosphate
- What role does a high-temperature box resistance furnace play in sintering? Mastering Electrolyte Tube Densification



















