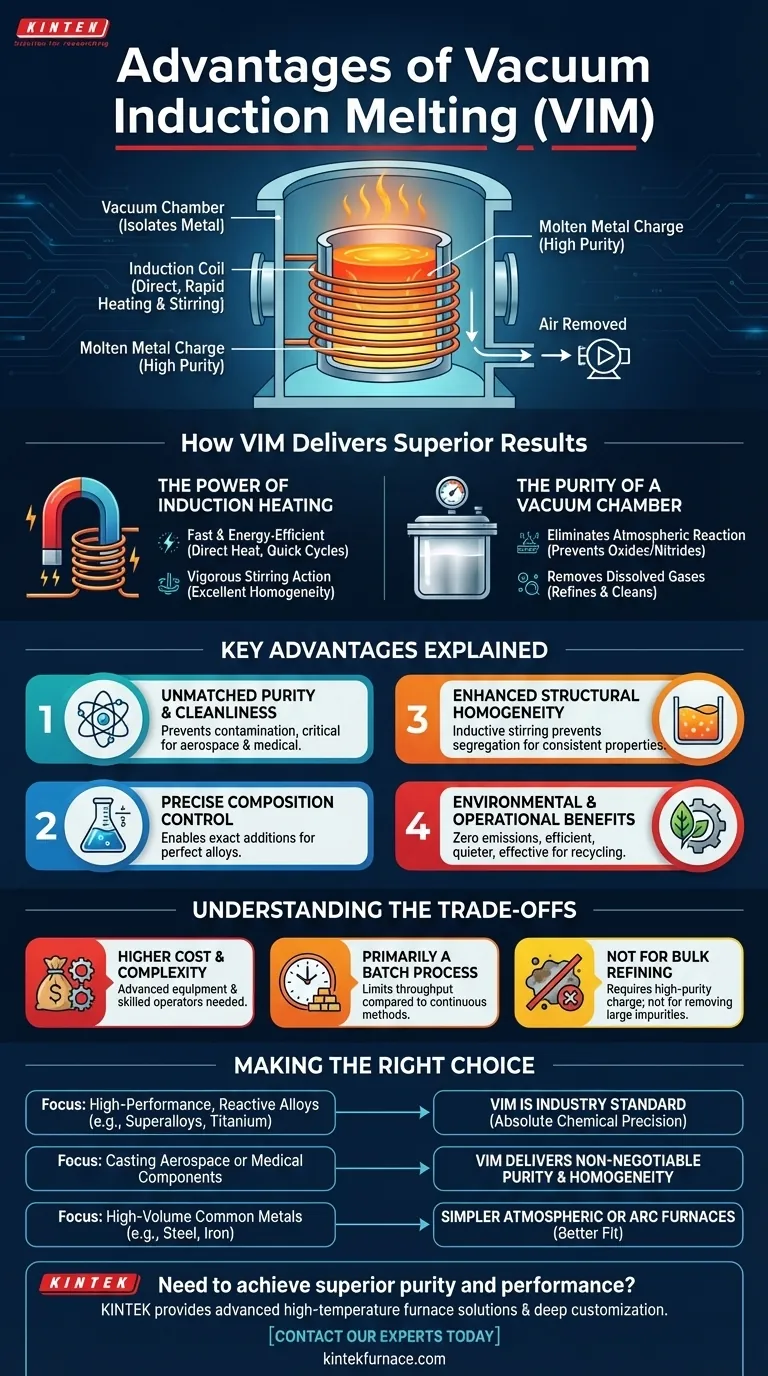
At its core, vacuum induction melting (VIM) offers unparalleled control over the purity and composition of metals and alloys. It achieves this by combining the clean, efficient, and rapid heating of electromagnetic induction with a vacuum environment that isolates the molten metal from atmospheric contamination.
The fundamental problem with melting reactive or high-performance metals is their tendency to react with the air, introducing impurities that degrade their properties. Vacuum induction melting solves this by creating a sterile environment, ensuring the final product is as pure and compositionally precise as possible.
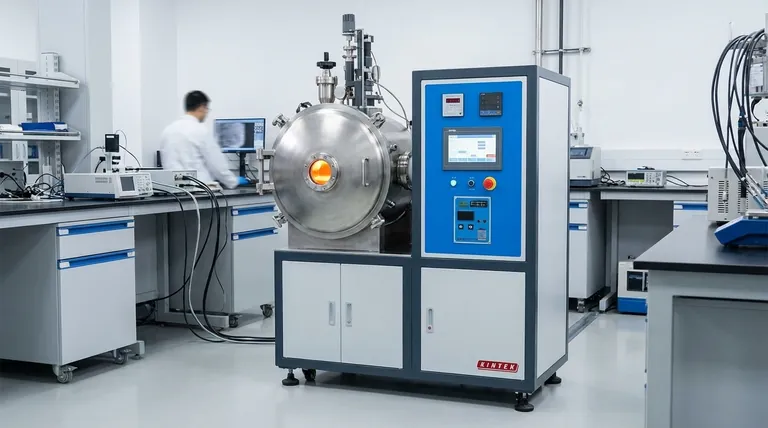

How VIM Delivers Superior Results
Vacuum induction melting is not just a single technology but the fusion of two powerful principles: induction heating and a vacuum atmosphere. Understanding how they work together reveals why this process is critical for advanced materials.
The Power of Induction Heating
Induction heating uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal charge. This is fundamentally different from external heating methods like flame or resistance furnaces.
This direct heating method is exceptionally fast and energy-efficient. Because the heat is generated inside the metal, there is very little wasted energy, leading to quicker melt cycles.
Furthermore, the magnetic field creates a natural, vigorous stirring action within the molten bath. This inherent stirring ensures the alloy mixes completely, resulting in excellent chemical and thermal homogeneity throughout the batch.
The Purity of a Vacuum Chamber
The "vacuum" part of VIM is what enables the production of the highest-quality materials. By removing the air from the melting chamber, the process eliminates the risk of reactions with oxygen and nitrogen.
This is non-negotiable for reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, and the elements used in superalloys. Exposed to air at high temperatures, these metals would form oxides and nitrides, creating inclusions that compromise strength and performance.
The vacuum also helps to remove dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen from the melt, further refining and cleaning the metal to achieve superior material properties.
Key Advantages Explained
The combination of these principles results in several distinct advantages that make VIM the preferred method for demanding applications.
Unmatched Purity and Cleanliness
By preventing reactions with air and helping to remove dissolved gases, VIM produces exceptionally clean metals. This is critical for applications where microscopic impurities can lead to catastrophic failure, such as in aerospace turbine blades or medical implants.
Precise Control Over Alloy Composition
The controlled, sterile environment of the VIM furnace allows for precise, minute additions of alloying elements to be made to the molten bath. This ensures the final product meets exact chemical specifications without loss or contamination.
Enhanced Structural Homogeneity
The inductive stirring effect is a significant advantage over other static melting processes. This continuous mixing prevents segregation of alloying elements and ensures the final cast ingot has consistent properties from top to bottom.
Environmental and Operational Benefits
Modern induction furnaces produce no combustion by-products, meaning zero emissions of dust, fumes, or pollutants. They are also significantly quieter than arc or cupola furnaces, creating a safer and cleaner working environment. They are also highly effective at melting recycled scrap with minimal material loss to oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, VIM is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not a universal solution for all melting needs.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
A vacuum induction furnace is a sophisticated piece of equipment. The vacuum chamber, pumps, and advanced control systems result in a higher capital investment and require more skilled operators compared to simpler atmospheric furnaces.
Primarily a Batch Process
The nature of loading a chamber, pumping it down to a vacuum, melting, and casting means VIM is inherently a batch process. This can limit total throughput compared to some continuous melting methods used for high-volume commodity metals.
Not Designed for Bulk Refining
VIM is best understood as a process for maintaining and improving purity, not for refining low-grade, dirty scrap metal. While it removes dissolved gases, it is not designed to remove the large quantities of slag and impurities that a primary steelmaking furnace would handle. It requires a high-purity starting charge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting process depends entirely on the material you are working with and the required properties of the end product.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance, reactive alloys (like superalloys or titanium): VIM is the industry standard because it is the only way to prevent contamination and ensure absolute chemical precision.
- If your primary focus is casting aerospace or medical-grade components: The cleanliness, purity, and homogeneity delivered by VIM are non-negotiable for meeting stringent safety and performance standards.
- If your primary focus is high-volume melting of common metals (like standard steel or iron): Simpler, more cost-effective atmospheric induction or arc furnaces are a better fit for the application.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum induction melting is a decision to prioritize material purity and performance above all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Purity | Prevents atmospheric contamination, removes dissolved gases for clean metals. |
| Precise Composition Control | Enables exact chemical specifications in a sterile environment. |
| Enhanced Homogeneity | Inductive stirring ensures consistent properties throughout the melt. |
| Operational & Environmental | Zero emissions, efficient melting, and effective for recycling scrap. |
Need to achieve superior purity and performance for your reactive alloys or high-performance components?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Let us help you select or customize the perfect vacuum induction melting system for your specific goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















