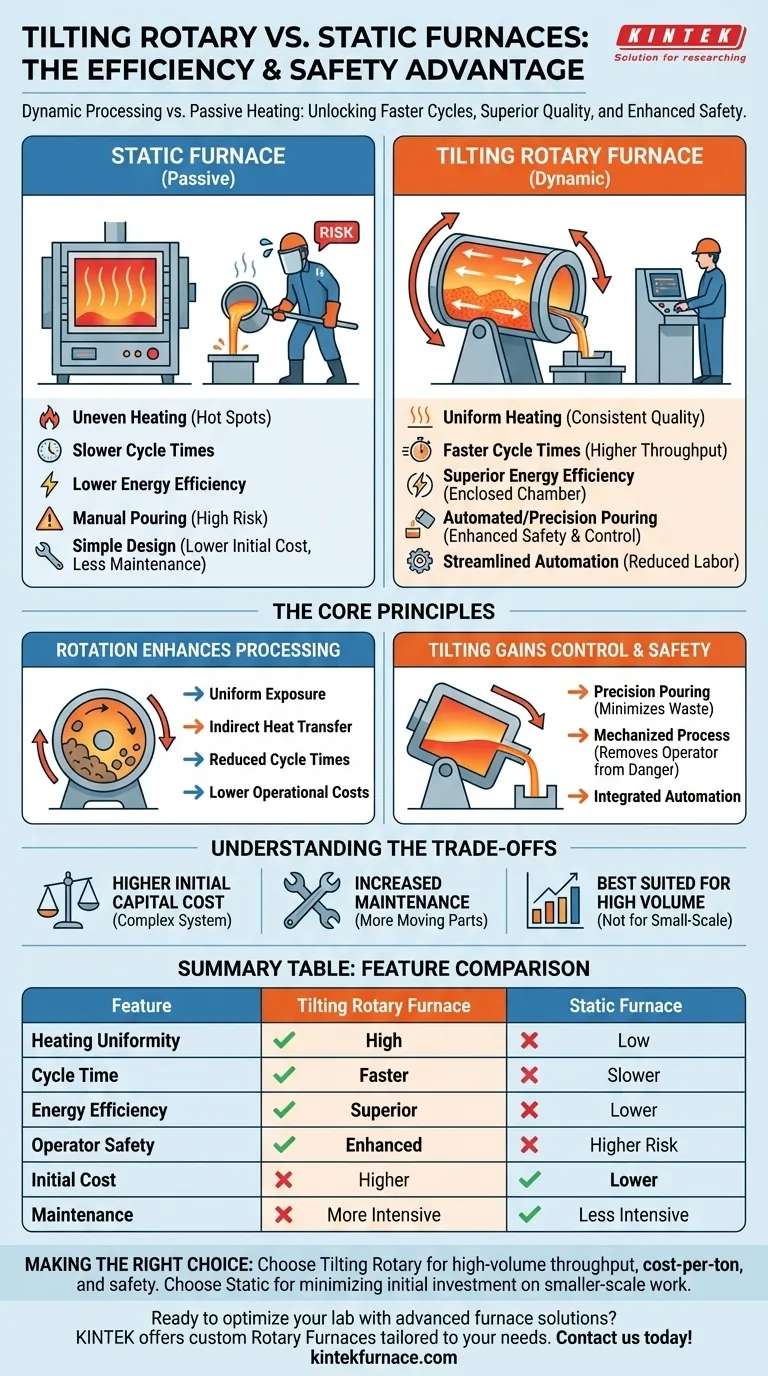
In short, a tilting rotary furnace offers significant advantages over a static model by combining two key actions: rotation for process efficiency and tilting for material handling control. This dual-motion capability leads to faster cycle times, higher energy efficiency, superior product quality, and a dramatically safer operating environment, particularly during the critical pouring stage.
The fundamental difference is a shift from a passive, static heating process to an active, dynamic one. While a static furnace simply contains the heat, a tilting rotary furnace actively mixes the charge for uniform heating and then provides mechanical assistance for a controlled, safe pour, optimizing the entire operational workflow.
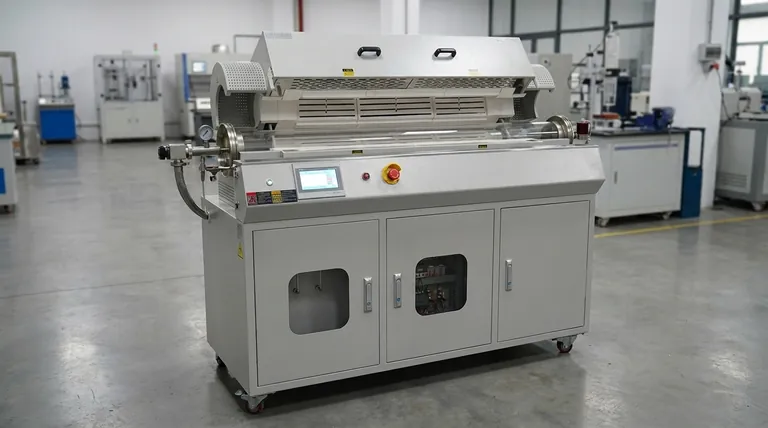

The Core Principle: How Rotation Enhances Processing
The primary advantage of any rotary furnace begins with its ability to rotate the main chamber. This simple action fundamentally improves the efficiency of the heating or melting process compared to a static design where the material remains stationary.
Uniform Heating and Heat Transfer
In a static furnace, heat is applied from the outside in, often creating hot spots and an unevenly processed batch. A rotary furnace solves this by constantly tumbling the material, ensuring all parts of the charge are uniformly exposed to the heat source. This indirect heat transfer is far more efficient and consistent.
Reduced Cycle Times and Increased Throughput
Because the material heats more evenly and quickly, the overall time required for each batch (the "cycle time") is significantly reduced. This directly translates to higher throughput, allowing you to process more material in the same amount of time.
Superior Energy Efficiency
The rotating, enclosed chamber design minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment. By efficiently transferring energy into the material load and preventing it from escaping, these furnaces consume less fuel or electricity per ton of processed material, lowering operational costs.
The Tilting Advantage: Gaining Control and Safety
While rotation boosts efficiency, the tilting mechanism adds a critical layer of control, automation, and safety that static furnaces cannot match. This is especially crucial in metal melting applications.
Precision Pouring and Control
A tilting furnace allows an operator to pour molten metal with a high degree of precision by controlling the angle and speed of the tilt. This minimizes spillage, reduces waste, and allows for flexible and accurate filling of molds or ladles.
Enhanced Operator Safety
Manually tapping or ladling molten material from a static furnace is one of the most hazardous jobs in a foundry. A tilting furnace mechanizes this process, moving the operator away from the immediate danger of splashes and intense heat, drastically improving workplace safety.
Streamlined Automation and Reduced Labor
The tilting action can be easily integrated into an automated production line. This reduces the need for manual labor during the pouring process, leading to lower labor costs, improved consistency, and further enhanced safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are substantial, tilting rotary furnaces are not the universal solution. Their advantages come with specific considerations that may not be suitable for every operation.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
The mechanical complexity of a rotating and tilting system—including the drive motors, bearings, seals, and hydraulic controls—results in a significantly higher upfront investment compared to a simple static furnace.
Increased Maintenance Requirements
More moving parts inherently require a more rigorous maintenance schedule. The rotating seals, drive mechanism, and tilting components must be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure reliable and safe operation, which can add to the long-term cost of ownership.
Best Suited for High Volume
The efficiency gains of a tilting rotary furnace are most apparent in high-volume, semi-continuous, or large-batch operations. For very small-scale, infrequent, or highly specialized tasks, the complexity and cost may not be justified.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision between a tilting rotary and a static furnace depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput and cost-per-ton: A tilting rotary furnace is the clear choice for its faster cycles and superior energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and process consistency: The automated, controlled pouring of a tilting furnace significantly reduces operational risk and improves repeatability.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment for smaller-scale work: A simpler static furnace remains a viable, cost-effective option, provided you can manage the trade-offs in efficiency and manual handling.
Ultimately, investing in a tilting rotary furnace is a strategic decision to optimize your process for efficiency, safety, and quality at scale.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tilting Rotary Furnace | Static Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Uniformity | High (due to rotation) | Low (risk of hot spots) |
| Cycle Time | Faster | Slower |
| Energy Efficiency | Superior | Lower |
| Operator Safety | Enhanced (automated pouring) | Higher risk (manual handling) |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | More intensive | Less intensive |
| Best For | High-volume operations | Small-scale tasks |
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency and safety with advanced furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary Furnaces, tailored to your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can enhance your experimental processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















