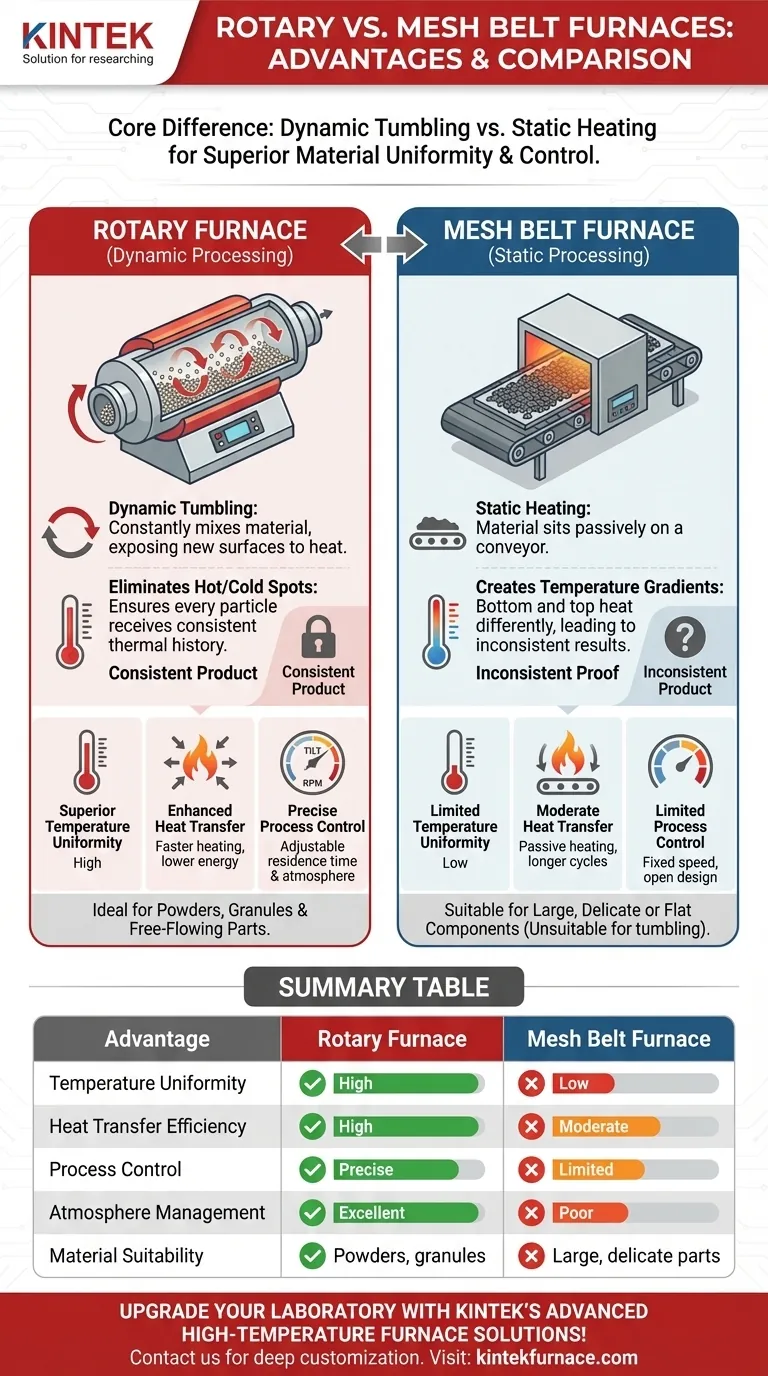
At its core, a rotary furnace provides superior material uniformity, thermal efficiency, and process control compared to traditional mesh belt furnaces. The fundamental advantage comes from its ability to continuously tumble the material, ensuring every particle receives consistent exposure to heat and the processing atmosphere. This dynamic treatment eliminates the hot spots and temperature gradients inherent in static-heating equipment.
The primary difference between a rotary and a mesh belt furnace isn't just hardware; it's a shift from static to dynamic processing. By actively moving the material, a rotary furnace solves the fundamental challenge of achieving uniform heat transfer, which directly translates to a higher quality and more consistent final product.
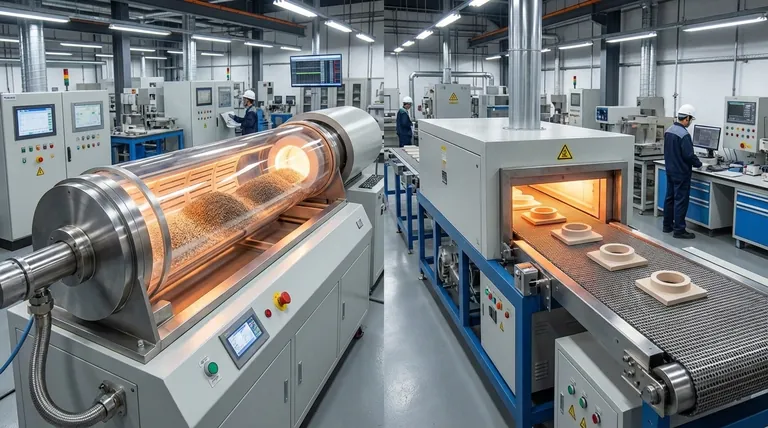

The Core Advantage: Dynamic vs. Static Heating
The most significant benefits of a rotary furnace stem from the simple but powerful act of rotation. This contrasts sharply with a mesh belt furnace, where material sits passively on a conveyor.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
In a mesh belt furnace, material rests on a flat surface. The bottom of the material bed is heated differently than the top, creating significant temperature gradients and inconsistent processing.
A rotary furnace solves this by gently tumbling the material. This action constantly exposes new surfaces to the heat source, breaks up agglomerations, and averages out the temperature across the entire batch, eliminating hot and cold spots.
Enhanced Heat Transfer
The tumbling motion dramatically increases the efficiency of heat transfer. By continuously mixing the material, every particle is more effectively exposed to the furnace's controlled atmosphere and radiant heat.
This leads to faster heating and cooling cycles compared to a static bed of material, which can improve throughput and reduce energy consumption per unit of product.
Consistent Material Properties
The direct result of uniform temperature and heat transfer is a highly consistent final product. Whether you are calcining powders, synthesizing materials, or performing thermal decomposition, every particle undergoes nearly the same thermal history.
This prevents issues common in mesh belt furnaces, such as having some material that is over-processed while other parts are under-processed, ensuring uniform chemical and physical properties.
Unlocking Greater Process Control and Efficiency
Beyond uniformity, the design of a rotary furnace offers operators a higher degree of control and operational efficiency.
Precise Control Over Residence Time
The time material spends in the hot zone is a critical process parameter. In a rotary furnace, residence time is precisely controlled by adjusting both the angle of tilt and the speed of rotation.
This provides a level of immediate and fine-tuned control that is difficult to achieve with a fixed-speed mesh belt system.
Improved Atmosphere Management
Rotary furnaces operate within a sealed tube. This enclosed design is inherently more effective at maintaining a pure, controlled atmosphere and preventing air leakage compared to the open entry and exit points of a typical mesh belt furnace.
This is critical for processes that are sensitive to oxygen or require a specific reactive gas, leading to reduced gas consumption and higher product purity.
Higher Thermal Efficiency
Modern rotary furnaces combine the benefits of rotation with high-quality ceramic fiber insulation and efficient heating element design.
Because the system is sealed and heat transfer to the material is so effective, less energy is wasted heating the furnace structure or lost to the surrounding environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is universally superior. A rotary furnace's advantages are specific to certain applications, and it's critical to understand its limitations.
Material Suitability
Rotary furnaces excel with powders, granules, and small, free-flowing parts that can be tumbled without damage.
They are unsuitable for large, flat, or delicate components that would be damaged by the tumbling action. For these applications, a mesh belt or batch oven is the appropriate choice.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating tube, drive system, and especially the high-temperature seals at the inlet and outlet introduce mechanical complexity not present in a simpler mesh belt design.
This can translate to a higher initial investment and specific maintenance requirements focused on the seals and drive components to ensure reliable, long-term operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology requires aligning its core strengths with your primary processing goals.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material uniformity and quality: The dynamic tumbling of a rotary furnace is unmatched for producing a homogenous product from powders or granules.
- If your primary focus is high throughput of large or delicate parts: A mesh belt furnace provides the gentle, continuous transport needed for components that cannot be tumbled.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and efficiency: A rotary furnace offers superior control over residence time and atmosphere, along with higher thermal efficiency.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace requires matching the technology's fundamental mechanism to your material's specific physical properties and processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Rotary Furnace | Mesh Belt Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | High (due to tumbling) | Low (static heating causes gradients) |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | High (continuous mixing) | Moderate (passive heating) |
| Process Control | Precise (adjustable tilt and rotation) | Limited (fixed speed) |
| Atmosphere Management | Excellent (sealed design) | Poor (open entry/exit points) |
| Material Suitability | Powders, granules | Large, delicate parts |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior uniformity, efficiency, and control. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















