Modern vacuum furnaces represent a fundamental shift in heat treatment, achieving significant energy and environmental gains through superior design principles and advanced materials. Their efficiency comes from advanced insulation and electrical heating within a sealed environment, while their primary environmental benefit stems from eliminating the need for combustible atmospheres, thereby preventing the creation of process emissions at the source.
The key advancement is not just better components, but a different philosophy. Instead of inefficiently burning fuel to create and maintain an atmosphere, vacuum furnaces use electricity with precision in a closed system, eliminating the largest source of energy waste and emissions found in traditional furnaces.
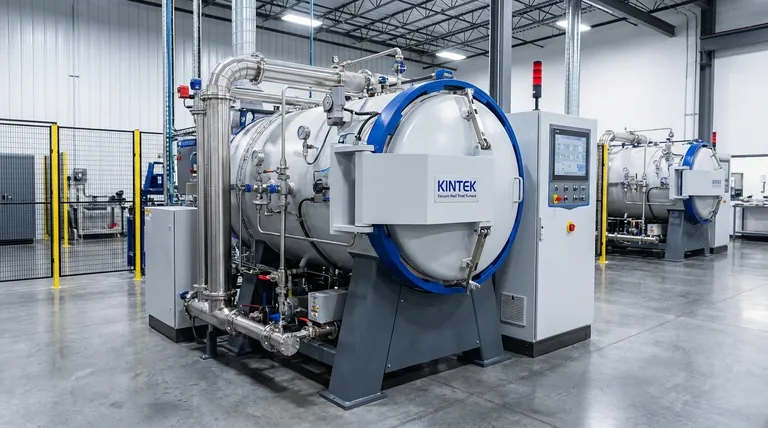

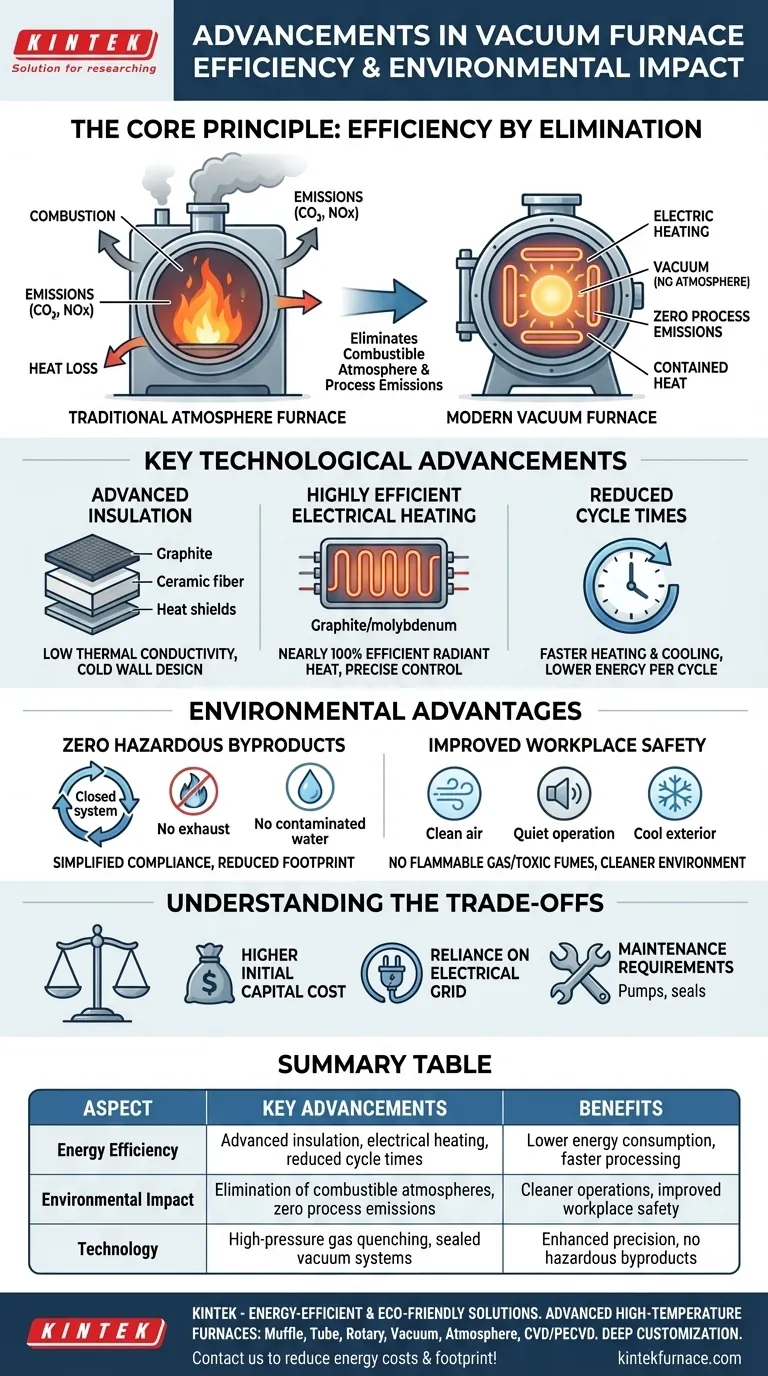
The Core Principle: Efficiency by Elimination
The most significant advancement in vacuum furnace technology is what it removes from the heat-treating equation: the combustible atmosphere. This single change has cascading benefits for both energy use and environmental impact.
No Atmosphere, No Combustion
In a traditional furnace, a specific atmosphere (e.g., endothermic gas) is generated by burning natural gas. This process is inherently inefficient.
A vacuum furnace requires no such process. The vacuum itself—the absence of an atmosphere—provides the perfect, inert environment for most heat-treatment applications, eliminating the fuel and energy needed to generate and maintain a gaseous atmosphere.
Eliminating Emissions at the Source
Because there is no ongoing combustion, a vacuum furnace produces zero process emissions.
This means no carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), or nitrogen oxides (NOx) are created as a byproduct of the heat-treating process itself, making it a fundamentally cleaner technology.
Preventing Convective Heat Loss
Atmosphere furnaces must be constantly vented to maintain pressure and gas purity, carrying huge amounts of heat out of the system. This represents a major and continuous energy loss.
A vacuum furnace is a sealed, closed system. All the energy put into the heating elements stays within the hot zone, directed only at the workload.
Key Technological Advancements
Beyond the core principle, specific hardware improvements have drastically reduced the energy required per cycle.
Advanced Hot Zone Insulation
Modern furnaces use multi-layered insulation packages made of high-purity graphite board, ceramic fiber, or reflective metallic heat shields.
These materials have extremely low thermal conductivity, preventing heat from escaping the hot zone. This is complemented by a water-cooled "cold wall" outer vessel, which contains all the thermal energy.
Highly Efficient Electrical Heating
Vacuum furnaces use electrical resistance heating elements, typically made of graphite or molybdenum. This method is nearly 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into radiant heat within the sealed chamber.
This direct, radiant heating is far more precise and less wasteful than heating a large volume of flowing gas, as is done in an atmosphere furnace.
Reduced Cycle Times
The combination of superior insulation and efficient heating allows the furnace to reach target temperatures faster.
Likewise, modern high-pressure gas quenching systems can cool the load rapidly and uniformly. Shorter heat-up and cool-down times directly translate to lower energy consumption per cycle.
Understanding the Environmental Advantages
The environmental benefits of vacuum technology extend beyond simply cutting emissions.
Zero Hazardous Byproducts
The closed-loop design means there is no release of exhaust gases or contaminated process water that would otherwise require expensive secondary treatment.
This simplifies environmental compliance and reduces the total environmental footprint of the manufacturing facility.
Improved Workplace Safety and Environment
Eliminating flammable natural gas and toxic carbon monoxide from the shop floor creates a significantly safer and cleaner working environment for operators.
Vacuum furnaces run quietly and do not radiate excessive heat into the surrounding workspace, further improving occupational conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, vacuum furnaces present their own set of considerations.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
Vacuum furnaces typically have a higher upfront purchase price compared to conventional atmosphere furnaces due to the complexity of the vacuum pumps, chamber, and control systems.
Reliance on Electrical Grid
The energy source is electricity. While the furnace itself is highly efficient, its overall carbon footprint is tied to the carbon intensity of the electrical grid providing the power.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining a high-vacuum system requires specialized knowledge. Pumps, seals, and instrumentation need regular, expert service to ensure optimal performance and prevent leaks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine if a vacuum furnace is the correct investment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing direct operational emissions: A vacuum furnace is the definitive choice, as it completely eliminates process gas emissions like CO2 and NOx.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operational costs: The superior energy efficiency and elimination of consumable atmospheres often result in a lower total cost of ownership, justifying the higher initial investment.
- If your primary focus is process control and part quality: The clean, inert vacuum environment prevents surface oxidation and decarburization, producing brighter, cleaner parts that often require no post-processing.
By fundamentally rethinking the heat treatment environment, modern vacuum furnaces offer a clear path toward more efficient, cleaner, and higher-quality manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Advancements | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Advanced insulation, electrical heating, reduced cycle times | Lower energy consumption, faster processing |
| Environmental Impact | Elimination of combustible atmospheres, zero process emissions | Cleaner operations, improved workplace safety |
| Technology | High-pressure gas quenching, sealed vacuum systems | Enhanced precision, no hazardous byproducts |
Ready to upgrade your lab with energy-efficient and eco-friendly heat treatment solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to learn how our vacuum furnaces can reduce your energy costs and environmental footprint!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















