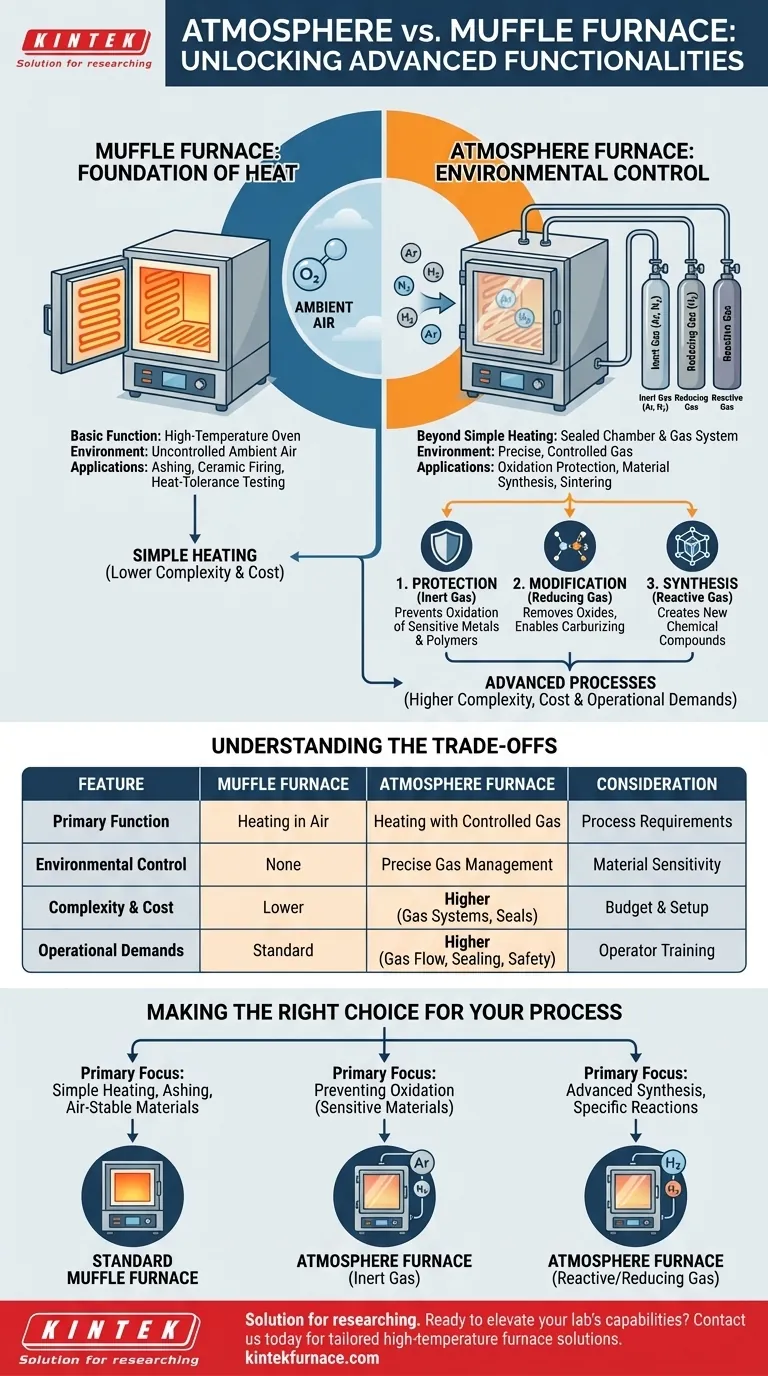
At its core, the primary difference is control. An atmosphere furnace adds the critical ability to precisely manage the gaseous environment around a sample, while a standard muffle furnace is fundamentally designed for heating in ambient air. This single capability moves beyond simple heating to enable advanced processes that protect, modify, and even synthesize materials.
Your choice is not about which furnace is "better," but which is necessary for your specific process. If your material is sensitive to oxygen or requires a specific gas to react, you need an atmosphere furnace. For simple high-temperature heating, a muffle furnace is the correct and more economical tool.

The Muffle Furnace: A Foundation of Heat
The Basic Function
A standard muffle furnace is, in essence, a high-temperature oven. Its sole purpose is to heat a sample to a precise temperature within an insulated chamber, which separates the heating elements from the processing area.
The Uncontrolled Environment
Crucially, the environment inside a basic muffle furnace is ambient air. This is perfectly suitable for processes where interaction with oxygen at high temperatures is acceptable or even desired, such as ashing, basic ceramic firing, or heat-tolerance testing.
Atmosphere Furnace: Adding Environmental Control
Beyond Simple Heating
An atmosphere furnace builds upon the muffle furnace design by incorporating a sealed chamber and a gas delivery system. This allows you to purge the ambient air and introduce a specific, controlled gas or a precise mixture of gases.
The Power to Protect
The most common additional function is protection. By filling the chamber with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, you can heat a sample without the risk of oxidation or other unwanted reactions with air. This is vital for processing sensitive metals, alloys, and certain polymers.
The Power to Modify and Synthesize
This control also allows you to actively change the material. Using a reducing atmosphere (e.g., with hydrogen) can remove oxides from a surface. Using other reactive gases can create new chemical compounds, enabling advanced processes like specific types of sintering, carburizing, and the synthesis of novel materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Requirements Define the Tool
The term "atmosphere muffle furnace" can be confusing, but it simply refers to a muffle-style furnace that includes atmosphere control. The key distinction is the presence or absence of a gas management system.
Your process dictates the need. If the chemical composition of the atmosphere does not impact your results, the added complexity of an atmosphere furnace is unnecessary.
Cost and Complexity
The gas delivery systems, vacuum pumps, and superior seals required for atmosphere control make these furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than their standard muffle furnace counterparts.
Operational Demands
Operating an atmosphere furnace requires more careful procedure. Managing gas flow rates, ensuring a proper seal, and handling potentially reactive or flammable gases demand greater operator training and attention to detail to achieve consistent and safe results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision depends entirely on the chemical requirements of your material at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is simple heating, ashing, or processing air-stable materials: A standard muffle furnace is the efficient and correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of sensitive metals or materials: You require an atmosphere furnace with an inert gas supply like argon or nitrogen.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis or heat treatments requiring a specific chemical reaction: You need an atmosphere furnace capable of handling reactive or reducing gas mixtures.
Understanding this fundamental difference in environmental control empowers you to select the precise tool needed to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | High-temperature heating in ambient air | Heating with controlled gaseous environment |
| Environmental Control | None (ambient air) | Precise gas management (inert, reducing, etc.) |
| Key Applications | Ashing, ceramic firing, heat testing | Oxidation protection, material synthesis, sintering |
| Complexity and Cost | Lower | Higher due to gas systems and seals |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with the right furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need reliable heating or sophisticated atmosphere control, we're here to help—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















