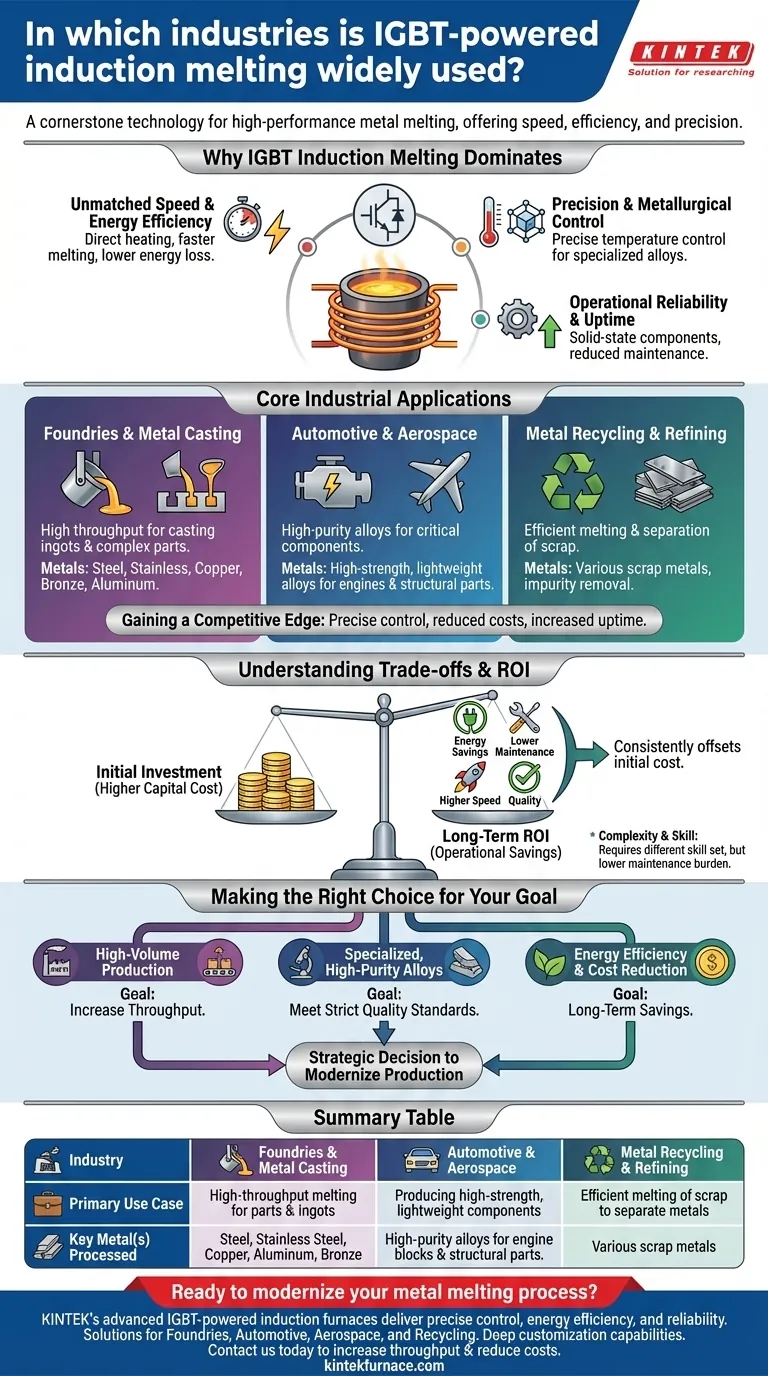
In short, IGBT-powered induction melting is a cornerstone technology in nearly every industry that requires the high-performance melting of metals. It is prominently used in foundries and casting, automotive and aerospace manufacturing, and large-scale metal recycling operations due to its superior efficiency, speed, and precision.
The widespread adoption of IGBT induction melting isn't just about melting metal; it's about gaining a competitive edge. Industries choose this technology because it provides precise control over metallurgical properties while simultaneously reducing operational costs and increasing production uptime.
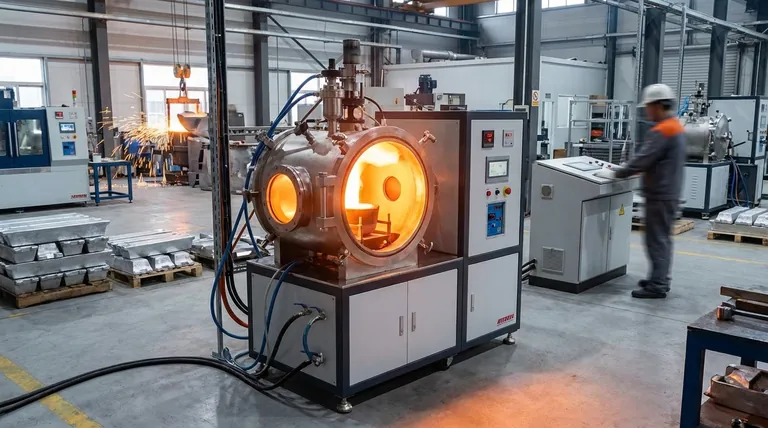

Why IGBT Induction Melting Dominates
The core of this technology is the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT), a high-power semiconductor that acts as an extremely fast and efficient switch. This allows for the precise control of high-frequency electrical currents needed for induction, delivering significant advantages over older heating methods.
Unmatched Speed and Energy Efficiency
IGBT-based systems use electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal itself, rather than relying on an external flame or heating element.
This direct heating method is incredibly fast and minimizes energy loss to the surrounding environment, making it far more energy-efficient than traditional resistance or gas-fired furnaces.
Precision and Metallurgical Control
The technology offers exceptionally precise temperature control. This is critical for producing specialized alloys with specific properties, as even minor temperature deviations can compromise the final product's quality.
This level of control is essential in high-stakes industries like aerospace, where material integrity is paramount.
Operational Reliability and Uptime
IGBT components are robust and solid-state, meaning they have fewer moving parts and are less prone to failure than older mechanical or gas-based systems.
This inherent reliability reduces maintenance requirements and minimizes costly production downtime, a crucial factor for any high-volume manufacturing or foundry operation.
Core Industrial Applications
While the technology is versatile, its impact is most profound in sectors where performance and consistency are non-negotiable.
Foundries and Metal Casting
This is the most common application. Furnaces powered by IGBTs are used to melt a wide range of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including steel, stainless steel, copper, bronze, and aluminum.
Their speed and efficiency allow foundries to achieve high throughput for casting everything from simple ingots to complex industrial parts.
Automotive and Aerospace
Both industries rely on high-strength, lightweight components. IGBT induction melting is used to produce the high-purity alloys required for engine blocks, transmission components, and structural aerospace parts.
The ability to consistently meet strict metallurgical specifications is the primary reason for its use here.
Metal Recycling and Refining
Efficiency is key in the recycling industry. Induction melting allows for the rapid and energy-efficient melting of scrap metal, which aids in separating different metals and removing impurities.
This makes the recycling process more economically viable and environmentally friendly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The primary decision is not whether induction heating is superior to flame—it is—but understanding the value of a modern IGBT system compared to older or alternative technologies.
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term ROI
IGBT induction furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to a simple gas-fired furnace. However, this initial cost is consistently offset by long-term operational savings.
The calculation must include reduced energy consumption, lower maintenance costs, higher production speed, and a dramatic reduction in rejected parts due to poor quality.
Complexity and Skill
While modern systems are designed for ease of operation, they are sophisticated pieces of electrical equipment. Proper operation and maintenance require a different skill set than managing a traditional furnace.
However, the diagnostic features and reliability of IGBT systems often result in a lower overall maintenance burden.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific goal will determine how you value the benefits of this technology.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and uptime: The speed and proven reliability of IGBT systems will directly increase your throughput and minimize costly disruptions.
- If your primary focus is producing specialized, high-purity alloys: The unparalleled temperature precision of IGBT technology is essential for meeting strict quality and performance standards.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and cost reduction: An IGBT furnace delivers significant and measurable long-term savings on energy bills compared to any traditional heating method.
Ultimately, adopting IGBT-powered induction melting is a strategic decision to modernize production for greater control, efficiency, and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use Case | Key Metal(s) Processed |
|---|---|---|
| Foundries & Metal Casting | High-throughput melting for casting parts and ingots | Steel, Stainless Steel, Copper, Aluminum, Bronze |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Producing high-strength, lightweight components | High-purity alloys for engine blocks and structural parts |
| Metal Recycling & Refining | Efficient melting of scrap to separate metals and remove impurities | Various scrap metals |
Ready to modernize your metal melting process?
KINTEK's advanced IGBT-powered induction furnaces deliver the precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and operational reliability your industry demands. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide solutions for foundries, automotive, aerospace, and recycling operations.
Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our high-performance melting solutions can increase your throughput and reduce operational costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















