Finalizing a rotary kiln's design is an iterative, data-driven process that moves from theoretical calculations to physical validation. It begins with a deep analysis of the material to be processed, which informs preliminary sizing. This initial design is then rigorously tested and refined using pilot-scale kilns and computer modeling until it meets all performance, efficiency, and safety criteria.
A rotary kiln is not an off-the-shelf product. Its final design is a unique blueprint dictated by the specific thermal and chemical transformation required for a particular material, validated through empirical testing and computational simulation.

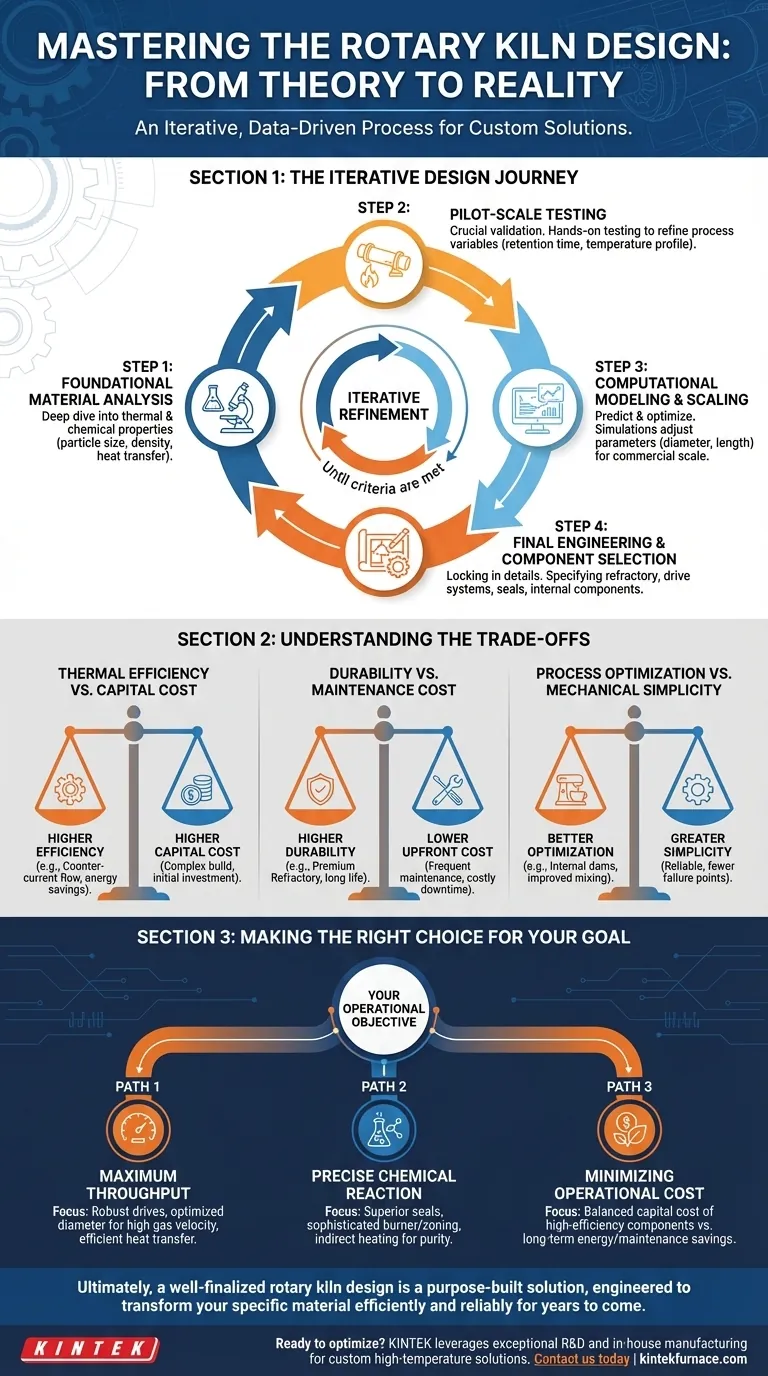
From Theory to Reality: The Iterative Design Journey
The final design is the result of a multi-stage refinement process where each step builds upon the last. The goal is to eliminate uncertainty and ensure the commercial-scale kiln will perform exactly as required.
Step 1: Foundational Material Analysis
Everything begins with the material. Designers conduct a thorough thermal and chemical analysis to understand its specific characteristics under heat.
Key properties like particle size distribution, bulk density, and heat transfer behavior are the primary inputs that dictate the entire design. For example, a high-density material requires a more robust drive system.
Step 2: Pilot-Scale Testing
Once the material's properties are understood, it is tested in batch or pilot-scale rotary kilns. This is the most critical validation stage.
This hands-on testing allows engineers to refine crucial process variables like retention time, required temperature profile, and the ideal internal atmosphere. The data gathered here is the empirical proof needed to design the full-scale unit.
Step 3: Computational Modeling and Scaling
Data from pilot testing is fed into sophisticated computer models. These simulations predict material behavior, heat transfer, and gas flow within the proposed commercial-scale kiln.
Designers use this modeling to iteratively adjust parameters—such as kiln diameter or length—to optimize performance. The design is tweaked and re-simulated until all process criteria are met on paper.
Step 4: Final Engineering and Component Selection
With a validated process and a scaled-up model, the final engineering details are locked in. This involves specifying every component of the kiln system.
This includes selecting the appropriate refractory lining to protect the steel shell from heat and abrasion, designing the drive assembly and support structures (riding rings, trunnion wheels), and engineering the kiln seals to ensure precise atmosphere control. Internal components like dams or lifters may also be added to optimize material mixing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Finalizing a kiln design involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for aligning the final product with your operational goals.
Thermal Efficiency vs. Capital Cost
A kiln with a counter-current heat flow (where gas flows opposite the material) is more thermally efficient but can be more complex and expensive to build. The final choice depends on the long-term value of energy savings versus the initial project budget.
Durability vs. Maintenance Cost
The choice of refractory lining is a primary example of this trade-off. Higher-grade, more expensive refractory materials offer longer service life and better insulation but increase the initial investment. A lower-grade refractory may save money upfront but lead to more frequent and costly downtime for replacement.
Process Optimization vs. Mechanical Simplicity
Adding internal structures like dams can improve mixing and heat transfer, but they also introduce mechanical complexity and potential failure points. The design must balance the need for process control against the goal of operational simplicity and reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The final design should be a direct reflection of your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: The design will emphasize robust drives, a diameter optimized for high gas velocity without material loss, and an efficient heat transfer system.
- If your primary focus is a precise chemical reaction: The design will prioritize superior kiln seals for atmosphere control, a sophisticated burner and zoning system for precise temperature gradients, and potentially indirect heating to prevent product contamination.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: The design will carefully balance the capital cost of high-efficiency components and durable refractories against their long-term impact on energy consumption and maintenance schedules.
Ultimately, a well-finalized rotary kiln design is a purpose-built solution, engineered to transform your specific material efficiently and reliably for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Assess thermal and chemical properties to inform initial sizing and design. |
| Pilot-Scale Testing | Validate process variables like retention time and temperature in small-scale kilns. |
| Computational Modeling | Use simulations to optimize kiln parameters and predict performance at scale. |
| Final Engineering | Select components like refractory lining, drive systems, and seals for reliability. |
Ready to optimize your material processing with a custom rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for industries like mining, cement, and chemicals. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















