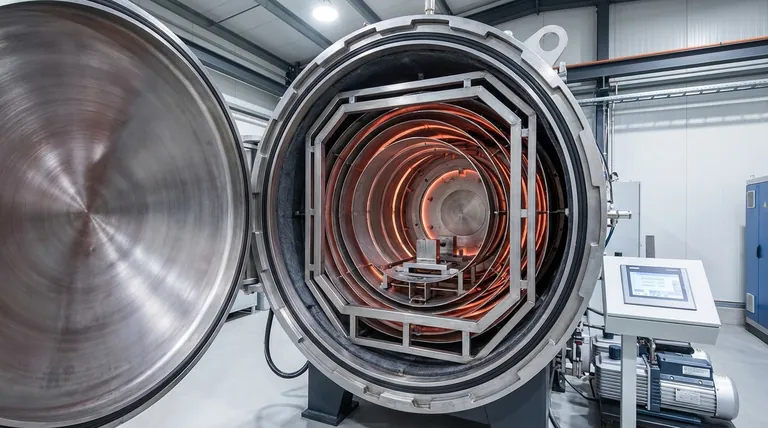
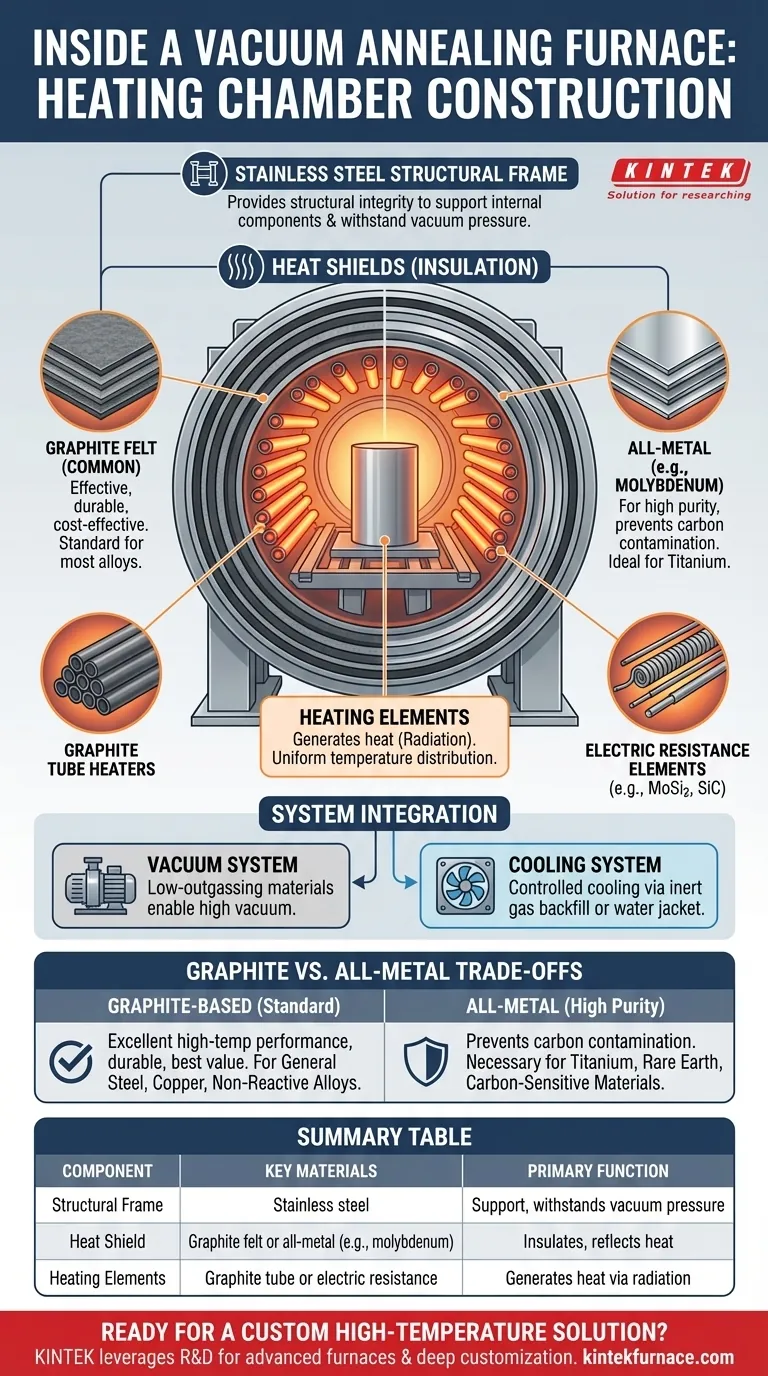
In short, a vacuum annealing furnace's heating chamber is typically constructed with a stainless steel structural frame. Internally, it is equipped with heating elements and surrounded by multiple layers of heat shields, which serve as insulation. The most common configuration uses graphite tube heaters and graphite felt heat shields, though an all-metal alternative is also widely available for specific applications.
The design of a heating chamber is a deliberate balance between thermal efficiency, cost, and material compatibility. The critical choice is not just what materials are used, but why they are chosen—primarily the decision between a standard graphite construction and a specialized all-metal one to prevent material contamination.

Deconstructing the Heating Chamber
To understand the furnace, we must first break down the heating chamber into its core functional components. Each part serves a distinct and vital purpose in creating a controlled, high-temperature vacuum environment.
The Structural Frame
The chamber's backbone is almost always a stainless steel frame. This provides the necessary structural integrity to support the internal components and withstand the pressure differential when under vacuum. Its primary role is support and containment.
The Heat Shield (Insulation)
Unlike conventional furnaces that use fiber or brick, a vacuum furnace requires insulation that performs in a vacuum. This is accomplished with multi-layer heat shields that reflect thermal energy back into the hot zone.
There are two primary types:
- Graphite Felt: This is the most common choice. Layers of graphite felt are extremely effective at high temperatures, durable, and relatively cost-effective.
- All-Metal Shields: For applications demanding high purity, shields are made from reflective metals like molybdenum or stainless steel. This design avoids the microscopic carbon particles that graphite can shed.
The Heating Elements
The elements are responsible for generating the heat, which is transferred to the workpiece primarily through radiation in the vacuum environment.
They are strategically arranged around the workpiece to ensure uniform temperature distribution. Common types include:
- Graphite Tube Heaters: These are efficient, robust, and relatively simple to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for general-purpose furnaces.
- Electric Resistance Elements: Other designs may use heating wires or specialized elements made from materials like Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC).
The Chamber's Role in the Overall System
The heating chamber does not operate in isolation. It is the heart of a larger system, and its design is deeply integrated with the furnace's other critical functions.
Interaction with the Vacuum System
The chamber is the vessel that holds the vacuum. All internal components—the frame, shields, and heaters—must be made of materials with low outgassing properties to allow the vacuum pumps (mechanical, diffusion, etc.) to achieve and hold the required low pressure.
Interaction with the Cooling System
After the heating cycle, the workpiece must be cooled in a controlled manner. The chamber is designed to work with the cooling system, which may involve backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) or circulating coolant through a water-cooling jacket built around the furnace body.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. All-Metal
The most significant design choice for a heating chamber is the selection between graphite and all-metal internals. This decision is driven entirely by the materials being processed and the required level of purity.
Why Choose Graphite?
A graphite-based heating chamber is the industry standard for a reason. It offers excellent high-temperature performance, is highly durable, and provides the best value for a wide range of applications, including the annealing of most steel alloys, stainless steels, and copper alloys.
The Case for an All-Metal Chamber
An all-metal chamber is specified when carbon contamination is a critical concern. Certain materials, like titanium alloys and other reactive or refractory metals, can be compromised by the trace amounts of carbon present in a graphite chamber. In these cases, a molybdenum-based "hot zone" is necessary to maintain material purity.
Material Compatibility is Key
The choice is not about which is "better" but which is appropriate for the material. Processing titanium in a graphite furnace can lead to surface contamination, while processing general steel in an expensive all-metal furnace provides no tangible benefit.
Choosing the Right Construction for Your Application
Your final decision must be aligned with the specific materials you intend to process and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose annealing of steels, copper, or non-reactive alloys: A graphite-based heating chamber is the standard, most cost-effective, and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing of titanium, rare earth metals, or other carbon-sensitive materials: An all-metal (e.g., molybdenum) chamber is a necessary investment to prevent product contamination and ensure metallurgical integrity.
- If your primary focus is ease of maintenance and high uptime: Both modern designs are robust, but graphite heating elements are often considered simpler and less costly to replace.
Ultimately, the construction of the heating chamber directly enables the unique benefits of vacuum annealing, protecting materials from oxidation and ensuring a clean, controlled thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Frame | Stainless steel | Provides support and withstands vacuum pressure |
| Heat Shield | Graphite felt or all-metal (e.g., molybdenum) | Insulates and reflects heat in vacuum environment |
| Heating Elements | Graphite tube or electric resistance (e.g., MoSi2, SiC) | Generates heat via radiation for uniform temperature |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for general-purpose annealing or high-purity processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your material processing and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















