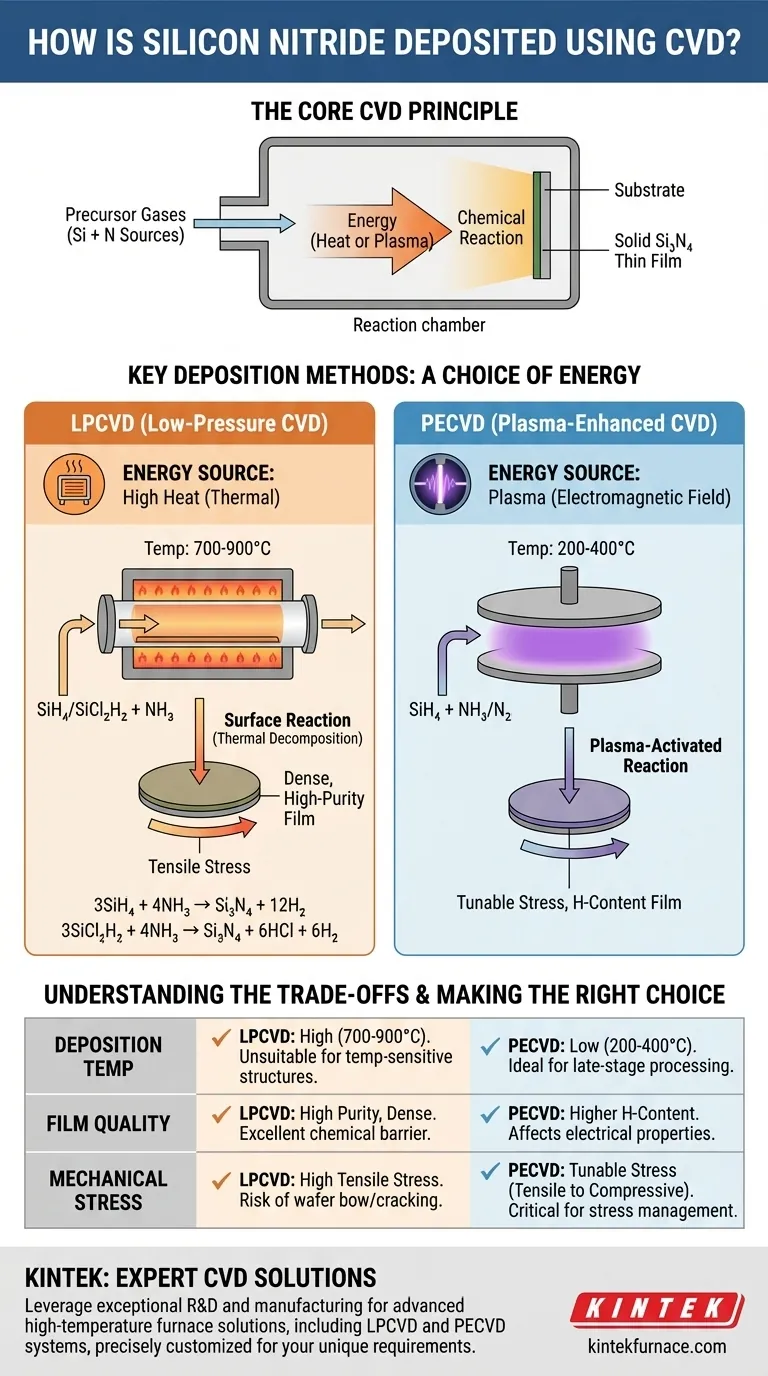
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) forms silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) by introducing silicon and nitrogen precursor gases into a reaction chamber where they react and deposit as a solid thin film onto a substrate. The most common reactions involve either silane (SiH₄) or dichlorosilane (SiCl₂H₂) as the silicon source, and ammonia (NH₃) as the nitrogen source, with energy supplied in the form of heat or plasma to drive the reaction.
The central challenge is not if you can deposit silicon nitride with CVD, but how to choose the right CVD method. The decision between high-temperature Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) and lower-temperature Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) dictates the film's properties and its suitability for a specific application.

The Fundamentals of Chemical Vapor Deposition
The Core Principle
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process where a substrate is exposed to one or more volatile precursor gases. These gases decompose or react on the substrate surface, leaving behind a solid deposit.
The entire process occurs within a controlled chamber, allowing for precise management of variables like temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates. This control is what enables the creation of high-purity, high-performance films.
Energy as the Catalyst
For the precursor gases to react and form a solid film, they need an input of energy. This energy breaks chemical bonds and initiates the deposition.
The two most common ways to supply this energy in silicon nitride deposition are through high heat (thermal energy) or an energized gas known as a plasma. The method chosen has profound effects on the final film.
Key Deposition Methods and Their Chemistry
The specific type of CVD process used is the single most important factor determining the final properties of the silicon nitride film.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD)
LPCVD is a high-temperature, thermal process. It operates at reduced pressure to improve film uniformity and reduce unwanted reactions in the gas phase, ensuring the reaction happens primarily on the substrate surface.
The typical reactions are:
- Silane + Ammonia:
3SiH₄ + 4NH₃ → Si₃N₄ + 12H₂ - Dichlorosilane + Ammonia:
3SiCl₂H₂ + 4NH₃ → Si₃N₄ + 6HCl + 6H₂
Films deposited via LPCVD are known for their high density, excellent chemical purity, and superior ability to evenly coat complex surface topography.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD uses an electromagnetic field (typically radio frequency) to excite the precursor gases into a plasma. This plasma provides the energy needed to drive the chemical reaction at much lower temperatures than LPCVD.
While the precursors are often the same (silane and ammonia), the plasma activation allows deposition to occur at temperatures as low as 200-400°C. This makes PECVD essential for applications where the substrate cannot tolerate high heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: LPCVD vs. PECVD
Choosing between LPCVD and PECVD involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs. There is no single "best" method; the choice depends entirely on the requirements of the final device.
Deposition Temperature
LPCVD operates at high temperatures (typically 700-900°C). This is unsuitable for substrates that already contain lower-melting-point materials, such as aluminum wiring in an integrated circuit.
PECVD operates at much lower temperatures (200-400°C). This makes it the default choice for deposition steps late in the manufacturing process, as it will not damage previously fabricated components.
Film Quality and Hydrogen Content
LPCVD produces films that are very close to pure, stoichiometric silicon nitride. They are dense and serve as excellent chemical barriers.
PECVD films inevitably incorporate a significant amount of hydrogen (often up to 8% or more) from the precursor gases. This hydrogen content affects the film's electrical properties, density, and chemical etch rates.
Mechanical Stress
LPCVD silicon nitride films characteristically have high tensile stress. This internal "pulling" can be a significant issue, potentially causing wafers to bow or films to crack if they are too thick.
PECVD offers a major advantage here: film stress can be controlled. By tuning process parameters, it's possible to create films with low tensile stress or even compressive stress, which is critical for many mechanical and optical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines your process. Selecting the correct CVD method requires you to prioritize the most critical film property for your device's success.
- If your primary focus is high purity and thermal stability: Choose LPCVD for its dense, stoichiometric films that are ideal for creating robust insulation or etch masks early in the fabrication process.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive structures: Choose PECVD to avoid damaging underlying layers like aluminum interconnects or other materials with low thermal budgets.
- If your primary focus is managing mechanical stress: Choose PECVD for its unique ability to tune the film's stress from tensile to compressive, preventing wafer bow and film cracking.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the precise CVD method that meets your specific material and device requirements.
Summary Table:
| Method | Temperature Range | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPCVD | 700-900°C | High purity, dense film, tensile stress | Early-stage fabrication, thermal stability |
| PECVD | 200-400°C | Lower temperature, tunable stress, higher hydrogen content | Temperature-sensitive substrates, stress management |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right CVD furnace for your silicon nitride deposition? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for applications in semiconductor, MEMS, and other high-tech industries. Contact us today to optimize your CVD process and achieve superior film quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth



















