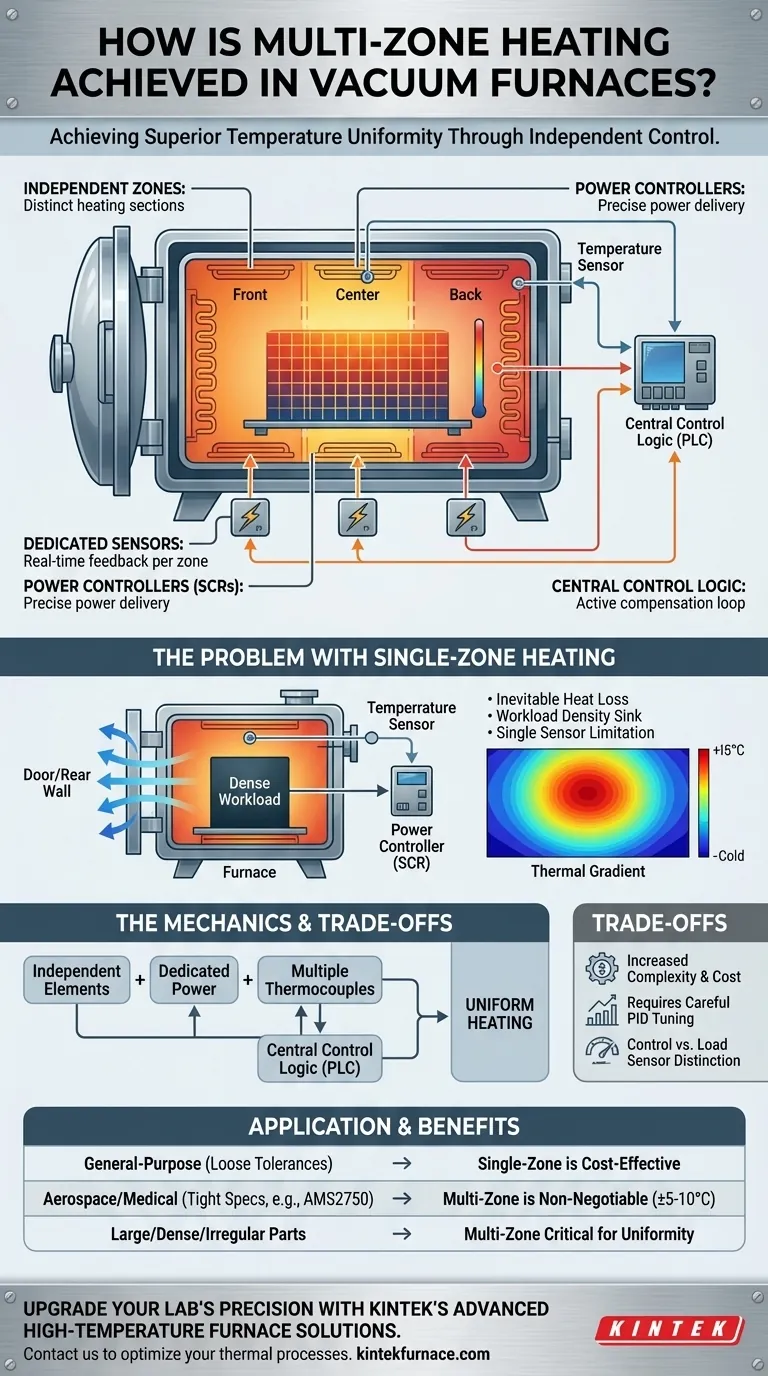
In essence, multi-zone heating in a vacuum furnace is achieved by dividing the furnace’s heating elements into distinct, independently controlled sections, or "zones." Each zone is equipped with its own power supply and dedicated temperature sensor (thermocouple). A sophisticated control system then delivers different amounts of power to each zone, actively compensating for temperature variations and ensuring the entire workload heats uniformly.
Multi-zone heating is not just about adding more heaters; it is a control strategy. By independently managing power to different furnace sections, it actively corrects for inevitable heat loss and variations in workload, achieving a level of temperature uniformity that a single-zone system cannot match.

The Core Problem: Why Single-Zone Heating Falls Short
To understand the value of a multi-zone system, we must first recognize the inherent limitations of a single-zone furnace, where one controller and one thermocouple attempt to manage the entire chamber.
The Inevitability of Heat Loss
A furnace chamber is never perfectly sealed thermally. Heat naturally escapes at a higher rate near doors, observation ports, gas quench nozzles, and thermocouple entries. A single control system cannot compensate for these localized cold spots.
The Challenge of Workload Density
A dense, heavy workload acts as a significant heat sink, absorbing far more energy than empty space or lighter sections of the load. In a single-zone system, areas near the dense mass will lag in temperature, while less dense areas may overshoot the target.
The Limitation of a Single Thermocouple
A single control thermocouple only measures the temperature at one specific point. The controller operates on the flawed assumption that the entire furnace volume is at that exact temperature, leading to significant thermal gradients across the actual parts.
The Mechanics of a Multi-Zone System
A multi-zone system overcomes these challenges by treating the furnace not as one large box, but as several smaller, interconnected chambers that can be managed individually.
Independent Heating Element Sections
The furnace's heating elements, typically made of graphite or high-nickel alloys, are physically and electrically divided. A common configuration is three zones: front, center, and back. This allows the system to direct more power to the front and back zones to compensate for heat loss at the door and rear wall.
Dedicated Power Controllers (SCRs)
Each zone is wired to its own power controller, most often a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR). The main furnace controller sends a separate, independent power request to each zone's SCR, allowing for precise and variable power delivery across the furnace.
Multiple Control Thermocouples
This is the critical feedback mechanism. Each zone has its own dedicated control thermocouple placed in that area. This gives the controller real-time temperature data from multiple points within the furnace, providing a far more accurate picture of the thermal environment.
The Central Control Logic
The furnace's central controller (a PLC or industrial computer) runs a continuous loop. It compares the desired setpoint temperature to the actual temperature reported by each zone's thermocouple. If a zone is too cool, it commands its SCR to deliver more power; if it's too hot, it reduces power, all while managing the other zones independently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, multi-zone control introduces factors that must be managed for it to be effective.
Increased Complexity and Cost
More zones mean more hardware: more thermocouples, more power wiring, and more SCRs. This not only increases the initial capital cost of the furnace but also adds to the number of components that may require maintenance or calibration over time.
The Importance of Proper Tuning
A multi-zone system requires careful PID loop tuning. If not tuned correctly, the zones can "fight" each other—one zone may overshoot the setpoint while trying to help a lagging neighbor, creating temperature oscillations that can be worse than in a single-zone system.
Control vs. Load Thermocouples
It is crucial to distinguish between the furnace's control thermocouples and the load thermocouples placed on the parts. The multi-zone system uses control thermocouples to manage the furnace environment, which in turn heats the part. Verifying that the part itself is at the correct temperature still requires separate load thermocouples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a multi-zone furnace should be driven by the specific requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating with loose tolerances: A well-designed single-zone furnace may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is meeting aerospace or medical specifications (like AMS2750): Multi-zone heating is non-negotiable for achieving the tight temperature uniformity (e.g., ±5-10°C) required by these standards.
- If your primary focus is processing large, dense, or irregularly shaped parts: A multi-zone system is critical for compensating for thermal variations and ensuring the entire part heats evenly and predictably.
Ultimately, implementing multi-zone heating is an investment in control, giving you the precision needed to guarantee uniform and repeatable results in demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Independent Zones | Heating elements divided into sections with separate controls for targeted power delivery. |
| Dedicated Sensors | Each zone has its own thermocouple for real-time temperature monitoring. |
| Power Controllers | Uses SCRs to manage power independently per zone, compensating for heat loss and workload variations. |
| Applications | Essential for tight tolerances in aerospace, medical specs, and large, dense parts. |
Upgrade your lab's precision with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide multi-zone vacuum furnaces that ensure superior temperature uniformity for demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and research fields. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all customizable to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can optimize your thermal processes and deliver reliable, repeatable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















