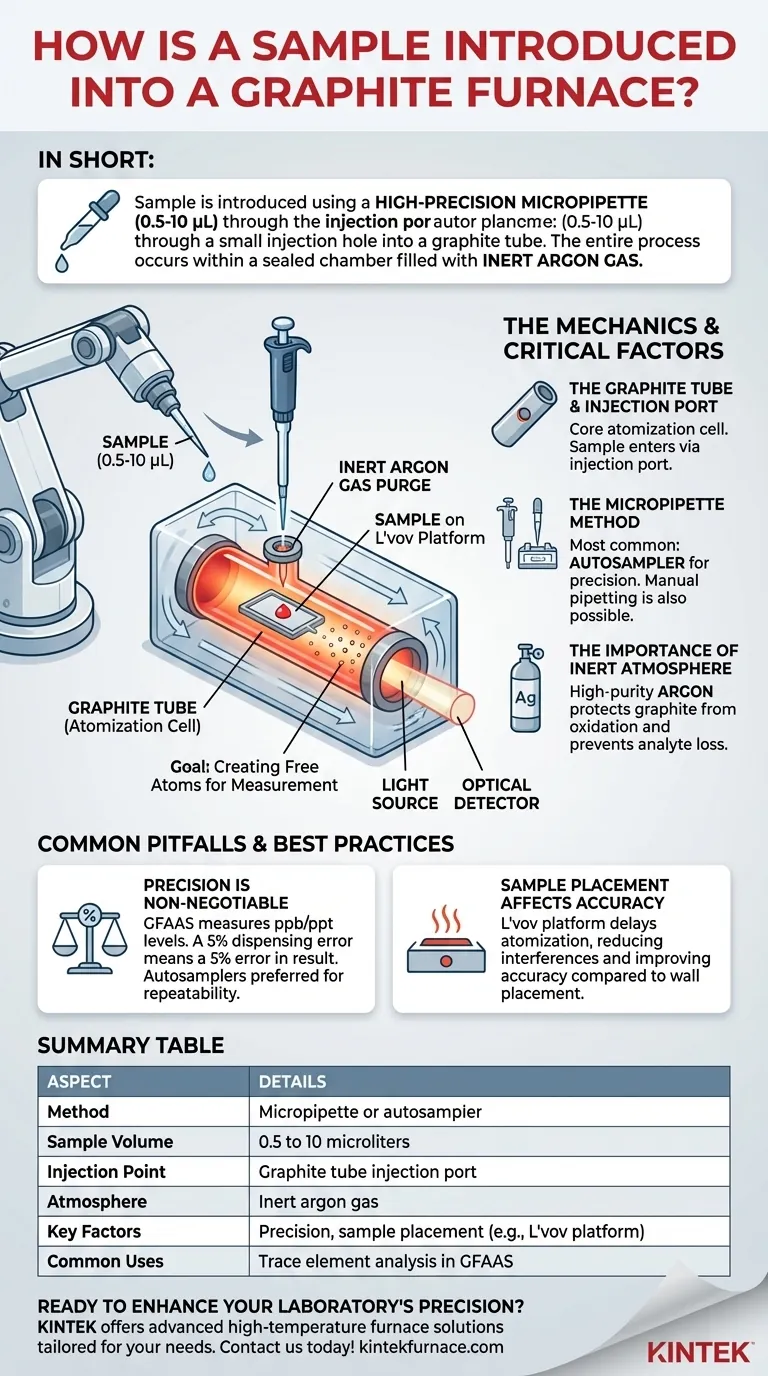
In short, a sample is introduced into a graphite furnace using a high-precision micropipette to dispense a very small volume, typically between 0.5 and 10 microliters. This liquid is carefully placed inside a graphite tube through a small injection hole. The entire process occurs within a sealed chamber filled with an inert argon gas to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
The method of sample introduction in Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS) is not merely about transfer; it is a critical step designed for absolute precision. The entire analysis hinges on accurately delivering a minute, known quantity of sample into a controlled environment for complete atomization.

The Role of the Graphite Furnace in Analysis
What is a Graphite Furnace?
A graphite furnace is a small, electrically heated graphite tube that serves as the atomization cell in GFAAS. This technique is designed for measuring trace and ultra-trace concentrations of specific elements in a sample.
The furnace's function is to execute a programmed temperature sequence. This sequence first dries the sample, then pyrolyzes (ashes) the matrix, and finally atomizes the element of interest, creating a cloud of free atoms that can be measured.
The Goal: Creating Free Atoms
The ultimate purpose of the furnace is atomization. Light from a specific lamp is passed through the graphite tube. For the analysis to work, the element being measured must be converted into a cloud of neutral, ground-state atoms. These free atoms will absorb the light, and the amount of absorption is directly proportional to their concentration.
The Mechanics of Sample Introduction
The Graphite Tube and Injection Port
The core of the furnace is a graphite tube, typically a few centimeters long. A small hole, the sample injection port, is drilled into the side of the tube. This port is the entry point for the liquid sample.
The Micropipette Method
The most common method for introducing a sample is with a micropipette. This can be done manually by a skilled analyst, but it is far more common to use an autosampler.
An autosampler uses a robotic arm with a pipette tip to aspirate a precise sample volume and dispense it through the injection port. The tip is carefully positioned to place the droplet onto the inner surface of the tube or onto a specialized insert called a L'vov platform.
The Importance of the Inert Atmosphere
The entire furnace is continuously purged with a flow of high-purity argon gas. This inert atmosphere is critical for two reasons:
- It protects the graphite tube. At the high temperatures required for atomization (often >2000°C), the graphite would instantly incinerate in the presence of oxygen.
- It prevents analyte loss. The argon purge prevents the formation of stable, refractory oxides from the sample elements, which would be difficult to atomize and would lead to inaccurate, low readings.
Common Pitfalls and Critical Factors
Precision is Non-Negotiable
GFAAS measures concentrations at parts-per-billion (ppb) or even parts-per-trillion (ppt) levels. The final calculated concentration is based on the tiny, initial volume. A 5% error in dispensing a 10-microliter sample means a 5% error in the final result. This is why autosamplers are overwhelmingly preferred for their superior repeatability.
Sample Placement Affects Accuracy
Where the sample is placed inside the tube matters. If dispensed directly onto the tube wall, the sample atomizes as the wall heats up. If placed on a L'vov platform (a small graphite plate sitting inside the tube), the platform heats primarily by radiation. This delays atomization until the surrounding gas inside the tube has reached a stable, high temperature, which helps reduce chemical and matrix interferences.
Spray Systems are an Alternative
While less common for GFAAS, a spray system or nebulizer can also be used. This device turns the liquid sample into a fine aerosol, a portion of which is then directed into the furnace. This method is more typical for other atomic spectroscopy techniques like ICP-OES or Flame AA.
How to Apply This to Your Analysis
- If your primary focus is routine, high-throughput analysis: An autosampler is the only acceptable choice. Its unmatched precision and repeatability are essential for generating reliable and defensible data.
- If your primary focus is method development or very low sample loads: Manual pipetting can be sufficient, but it demands exceptional operator skill and meticulous practice to minimize volume variations between injections.
- If your primary focus is analyzing challenging samples: Understanding sample placement is key. Using a L'vov platform and modifying the temperature program can significantly reduce interferences and improve accuracy.
Mastering the precise and clean introduction of your sample is the foundational step for achieving accurate and sensitive results in graphite furnace analysis.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Method | Micropipette or autosampler |
| Sample Volume | 0.5 to 10 microliters |
| Injection Point | Graphite tube injection port |
| Atmosphere | Inert argon gas |
| Key Factors | Precision, sample placement (e.g., L'vov platform) |
| Common Uses | Trace element analysis in GFAAS |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's precision in trace element analysis? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse labs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your graphite furnace processes and deliver reliable, accurate results for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















