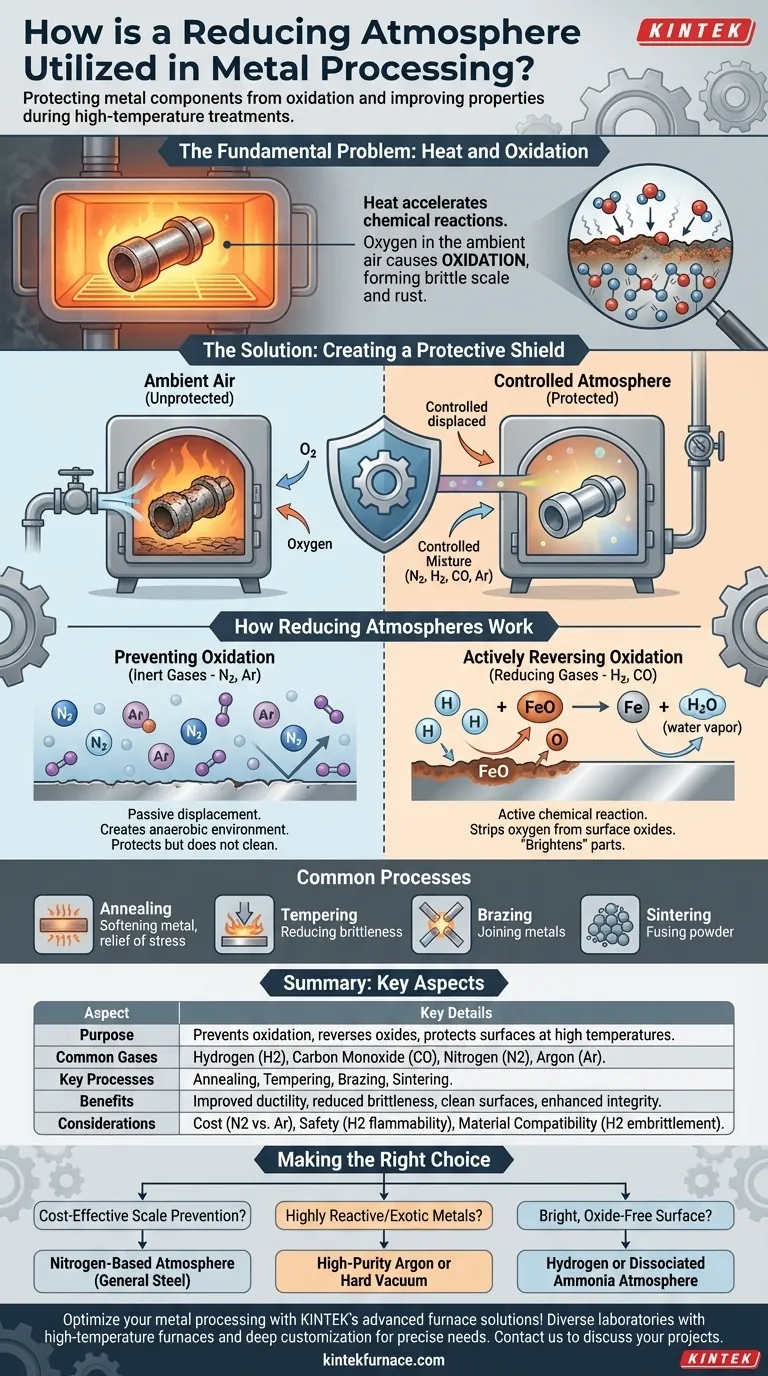
In metal processing, a reducing atmosphere is primarily used to protect metal components from oxidation and other harmful surface reactions during high-temperature treatments. By replacing oxygen with a controlled mixture of gases, processes like annealing can be performed to improve a metal's properties without causing discoloration, scaling, or corrosion.
At high temperatures, metals become highly reactive and vulnerable to oxygen in the air. A reducing atmosphere functions as a chemical shield, not only preventing damaging oxidation but often actively reversing it, ensuring the final product maintains its intended surface quality and structural integrity.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Oxidation
High-temperature metal processing is a balancing act. Heat is necessary to alter a metal's physical properties, but it also dramatically accelerates unwanted chemical reactions.
Why Heat Creates a Challenge
When metal is heated, its atoms vibrate more energetically, making it far more susceptible to reacting with oxygen in the ambient air. This reaction, known as oxidation, forms a brittle layer of scale or rust on the metal's surface.
This oxide layer is almost always undesirable. It compromises the metal's dimensions, degrades its surface finish, and can negatively impact its mechanical properties, such as fatigue resistance.
The Goal: Creating a Protective Shield
To solve this, critical heat-treating processes are performed inside sealed furnaces filled with a carefully controlled atmosphere.
This atmosphere displaces the ambient air, removing the oxygen and replacing it with gases that are either inert or actively hostile to the formation of oxides. This ensures the heat treatment achieves its goal without causing collateral damage to the material.
How Reducing Atmospheres Work
Controlled atmospheres operate on a spectrum, from simply preventing oxidation to actively reversing it.
Preventing Oxidation with Inert Gases
The simplest approach is to use an inert gas, most commonly nitrogen (N2) or argon (Ar). These gases do not react with the metal, even at high temperatures.
Their function is purely displacement. By flooding the furnace, they push out the oxygen, creating an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment where oxidation cannot occur. They protect the metal but do not clean or change its existing surface.
Actively Reversing Oxidation with Reducing Gases
A true reducing atmosphere goes a step further. It contains gases like hydrogen (H2) or carbon monoxide (CO) that actively seek out and react with any metal oxides present on the surface.
For example, hydrogen will strip oxygen atoms from iron oxide, reducing it back to pure iron and forming water vapor (H2O) as a byproduct. This process can "brighten" a part by removing existing light scale, resulting in a clean, pristine surface post-treatment.
Common Processes Requiring Controlled Atmospheres
- Annealing: Softening metal and relieving internal stresses to improve ductility.
- Tempering: Reducing the brittleness of hardened steel.
- Brazing: Joining metals using a filler material.
- Sintering: Fusing metal powders together to form a solid part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of atmosphere is a critical decision based on the material being treated, the desired outcome, and operational constraints like cost and safety.
Cost vs. Purity
Nitrogen is the workhorse of inert atmospheres because it is relatively inexpensive. However, for extremely sensitive or reactive metals like titanium, the higher purity and complete inertness of argon are required, despite its significantly higher cost.
Safety and Material Compatibility
Hydrogen is the most powerful and effective common reducing agent. However, it is highly flammable and presents an explosion risk if not handled with extreme care.
Furthermore, hydrogen can be absorbed by certain metals, particularly some steels, causing a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement, which makes the material brittle and prone to failure.
Simplicity vs. Control
Using a pure inert gas like nitrogen is simple, but its effect is purely passive. Creating a reducing atmosphere from exothermic or endothermic gas generators produces a complex mixture of CO, CO2, H2, and N2.
While more effective for active reduction, these systems require precise control over gas ratios (e.g., the CO:CO2 ratio) to maintain the desired chemical potential and prevent unwanted side effects like carburization (adding carbon to the metal surface).
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct atmosphere is essential for achieving the desired material properties while managing cost and risk.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective scale prevention: A nitrogen-based atmosphere is typically the most economical and effective choice for general-purpose heat treating of common steels.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive or exotic metals: A high-purity argon atmosphere or a hard vacuum furnace is necessary to provide the cleanest possible processing environment.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, oxide-free surface: An atmosphere containing a significant percentage of hydrogen or dissociated ammonia is required to actively reduce surface oxides.
Ultimately, mastering the atmosphere inside the furnace is fundamental to mastering the properties of the final metal component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents oxidation, reverses existing oxides, protects metal surfaces during high-temperature processes |
| Common Gases | Hydrogen (H2), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Nitrogen (N2), Argon (Ar) |
| Key Processes | Annealing, Tempering, Brazing, Sintering |
| Benefits | Improved ductility, reduced brittleness, clean surfaces, enhanced structural integrity |
| Considerations | Cost, safety (e.g., hydrogen flammability), material compatibility (e.g., hydrogen embrittlement) |
Optimize your metal processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects and deliver reliable, tailored equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















