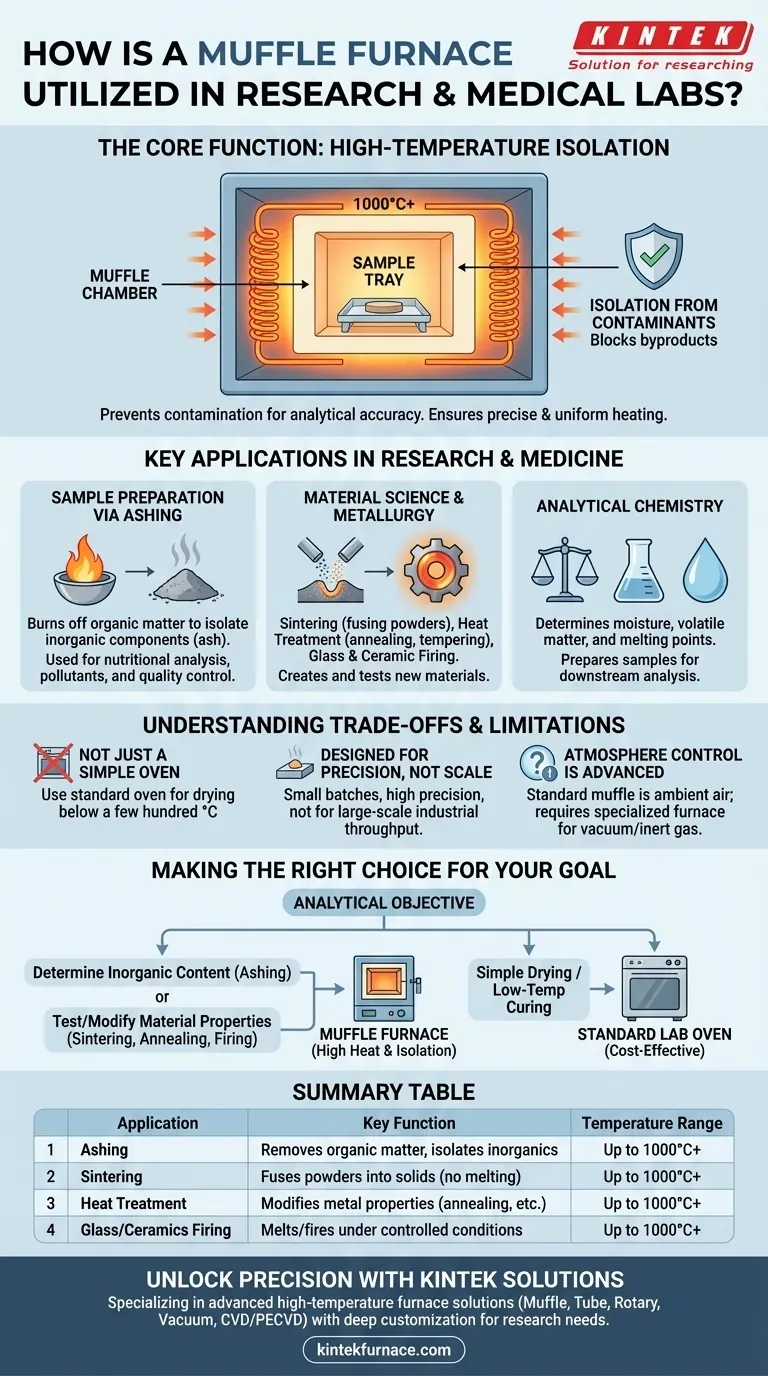
In research and medical laboratories, a muffle furnace is primarily utilized to heat samples to extremely high, precisely controlled temperatures in a contaminant-free environment. Its core function is to determine the inorganic, non-combustible portion of a sample—a process known as ashing—or to execute material science applications like sintering, annealing, and glass firing where sample purity is critical.
The essential value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to generate intense heat, but its design that isolates the sample from the heating elements. This "muffle" prevents contamination, ensuring that any changes to the sample are a direct result of heat alone, a non-negotiable requirement for analytical accuracy in research.
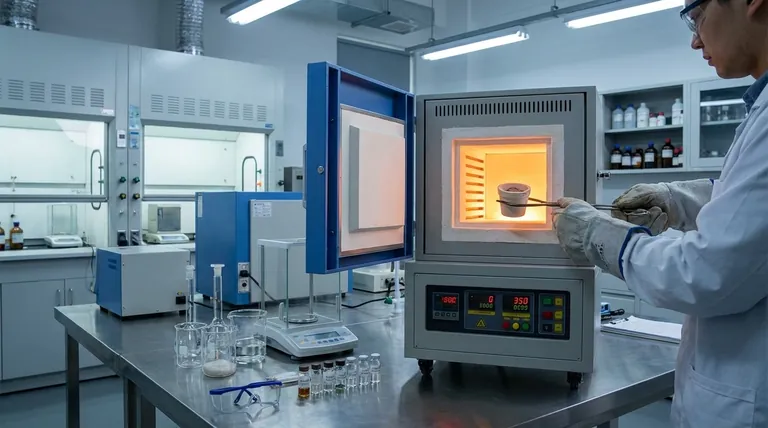

The Core Function: High-Temperature Isolation
A muffle furnace is more than just a powerful oven. Its unique design is central to its role in sensitive laboratory work.
What is a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is a laboratory device designed for high-temperature applications, often reaching 1000°C or higher.
The name comes from its key component: a "muffle," which is an insulating chamber, typically made of ceramic, that contains the sample. This chamber separates the material being heated from the furnace's electric heating elements.
Think of it like cooking food in a sealed ceramic pot placed inside a larger oven. The pot protects the food from direct contact with the heating source and any gases it might produce, ensuring it cooks only with radiant heat.
Why Isolation Matters in a Lab
In analytical settings, preventing contamination is paramount. The muffle ensures that byproducts from the heating elements do not interact with the sample.
This is crucial for applications like elemental analysis, where the goal is to measure the exact composition of the material after heating. Any added impurities would render the results invalid.
The Importance of Precision and Uniformity
Beyond isolation, muffle furnaces provide extremely precise temperature control and uniform heating throughout the chamber.
This consistency ensures that experiments are repeatable and that the entire sample is subjected to the exact same conditions, which is a foundational principle of sound scientific research.
Key Applications in Research and Medicine
The combination of high heat, isolation, and precision makes the muffle furnace indispensable for several key laboratory processes.
Sample Preparation via Ashing
Ashing is the process of burning off all organic and volatile substances from a sample to isolate the inorganic, non-combustible components (the "ash").
The furnace heats the sample in the presence of air, causing the organic matter to oxidize and turn into carbon dioxide and water, which vent away. What remains is the mineral content.
This technique is standard in food science to determine nutritional mineral content, in environmental science to analyze pollutants in soil, and in the pharmaceutical industry for quality control.
Material Science and Metallurgy
Muffle furnaces are central to creating and testing new materials.
Key uses include:
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials, like ceramics or metals, into a solid piece using high heat without melting them.
- Heat Treatment: Modifying the physical and chemical properties of metals through processes like annealing (softening), tempering (increasing toughness), or quenching (hardening).
- Glass and Ceramics: Firing technical ceramics, melting glass, or applying enamel coatings under controlled conditions.
Analytical Chemistry
The furnace serves as a critical tool for fundamental chemical analysis.
It is used to accurately determine a sample's moisture content, the quantity of volatile matter, and its melting point. It prepares samples for more sophisticated downstream analysis, ensuring the starting material is in a known, stable state.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool, and it's important to understand its boundaries.
Not Just a High-Temperature Oven
If your only goal is to dry a sample or cure it at temperatures below a few hundred degrees Celsius without concerns for minor contamination, a standard laboratory oven is a more practical and cost-effective choice. The muffle furnace is designed specifically for applications demanding both high heat and isolation.
Designed for Precision, Not Scale
Laboratory muffle furnaces are relatively small, benchtop devices. They are designed for processing individual samples or small batches with high precision, not for the large-scale throughput required in industrial manufacturing.
Atmosphere Control is an Advanced Feature
A standard muffle furnace heats a sample in ambient air. While it isolates the sample from the heating elements, it does not control the atmosphere within the chamber itself. For applications requiring a vacuum or an inert gas environment (like argon or nitrogen), a more specialized and expensive type of furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct heating instrument, you must first define your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample (ashing): A muffle furnace is the standard tool for completely removing organic material without contaminating the remaining ash.
- If your primary focus is testing or modifying material properties: A muffle furnace provides the precise, uniform high heat needed for processes like sintering ceramics, annealing metals, or firing glass.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or low-temperature curing: A standard laboratory oven is often more suitable and cost-effective than a muffle furnace.
By understanding its core principle of isolated heating, you can effectively leverage the muffle furnace for applications demanding high temperatures and analytical purity.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Removes organic matter to isolate inorganic components | Up to 1000°C+ |
| Sintering | Fuses powdered materials into solids without melting | Up to 1000°C+ |
| Heat Treatment | Modifies metal properties (e.g., annealing, tempering) | Up to 1000°C+ |
| Glass/Ceramics Firing | Melts or fires materials under controlled conditions | Up to 1000°C+ |
Unlock Precision in Your Laboratory with KINTEK Solutions
Are you striving for contaminant-free, high-temperature processing in your research or medical lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our furnaces precisely meet your experimental requirements, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and reliability.
Don't let equipment limitations hold back your discoveries—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can elevate your laboratory's performance and deliver the purity and control your work demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















