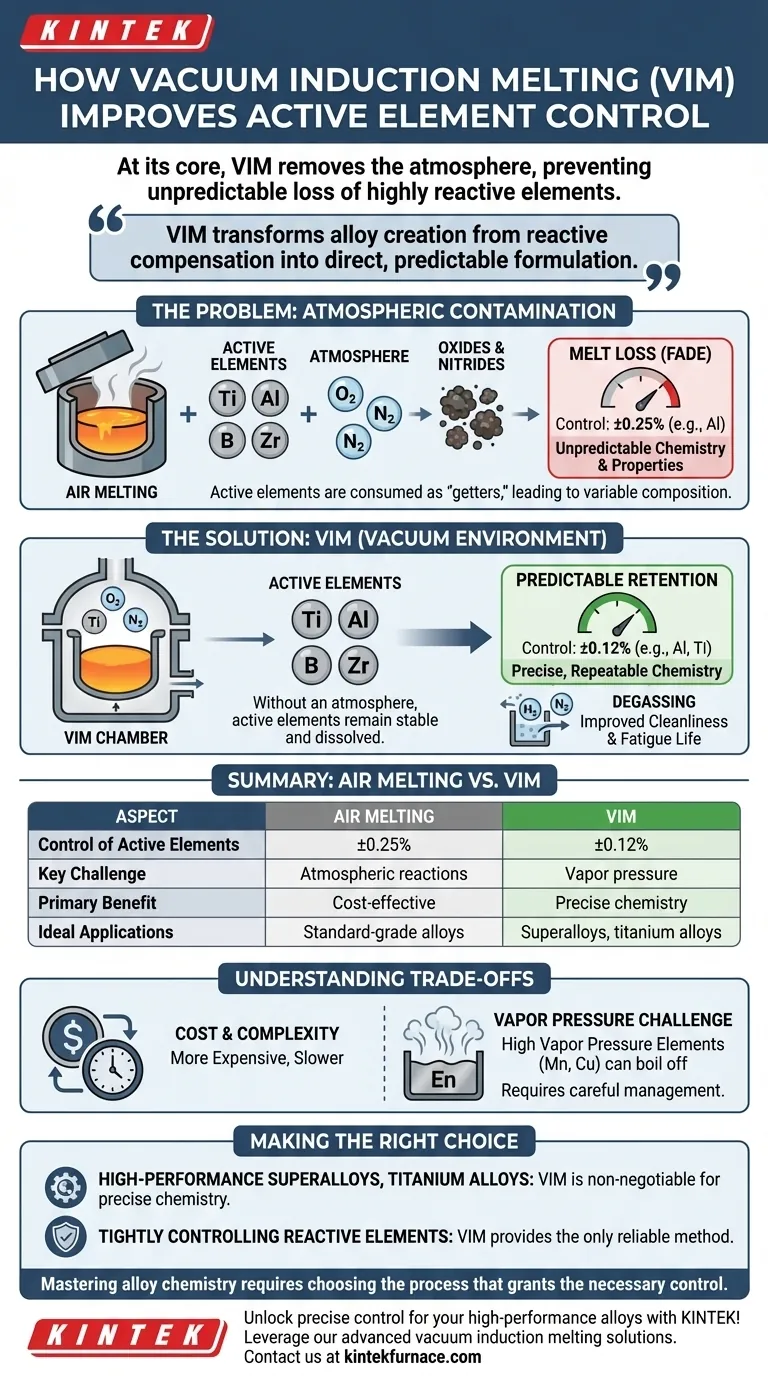
At its core, vacuum induction melting (VIM) improves the control of active elements by removing the primary cause of their unpredictable loss: the atmosphere. By melting material inside a vacuum, the process eliminates the oxygen and nitrogen that would otherwise react with and consume highly reactive elements like aluminum and titanium. This prevents the formation of oxides and nitrides, ensuring the elements you add to the melt are the elements that remain in the final product.
The central challenge in precision alloy manufacturing is not just adding the correct amount of an element, but ensuring it isn't lost during the melting process. VIM provides a protected environment, transforming alloy creation from a process of reactive compensation into one of direct, predictable formulation.
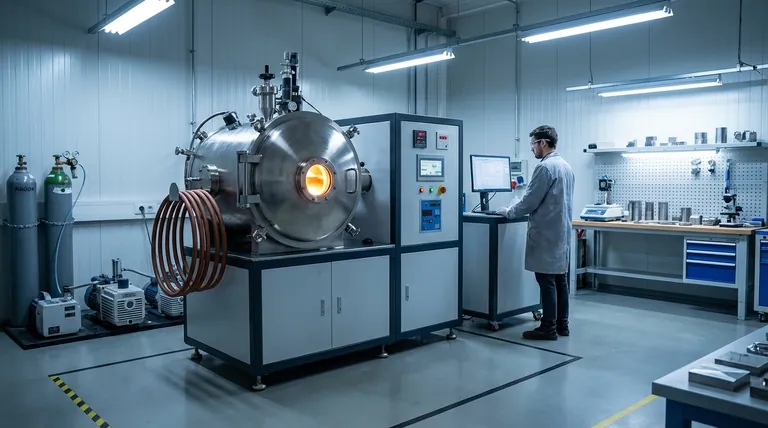

The Fundamental Problem: Atmospheric Contamination
To understand why vacuum is so effective, we must first understand the challenge of melting in air. The atmosphere is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen, both of which are highly reactive at the elevated temperatures required for melting metals.
What Makes an Element "Active"?
Active elements—such as titanium (Ti), aluminum (Al), boron (B), and zirconium (Zr)—have a very high affinity for oxygen and nitrogen. Chemically, this means they are more stable as an oxide or a nitride than as a pure element dissolved in the molten metal.
When exposed to the atmosphere, these elements act as "getters," effectively sacrificing themselves to react with any available oxygen or nitrogen.
The Inevitability of "Melt Loss" in Air
When melting is performed in air, these active elements are consumed in reactions that form unwanted inclusions (oxides and nitrides). This consumption is known as melt loss or fade.
Because the rate of this loss is difficult to predict and control, metallurgists must add an excess of the active element, essentially guessing how much will be lost to the atmosphere.
The Result: Unpredictable Chemistry and Properties
This guesswork leads to a wide variability in the final chemical composition. As the reference data indicates, an element like aluminum might be controlled to ±0.25% in an air-melt process.
This level of variance is unacceptable for high-performance materials, where a deviation of even a fraction of a percent can dramatically alter mechanical properties like strength, ductility, and creep resistance.
How Vacuum Induction Melting Provides a Solution
VIM directly confronts the problem of atmospheric reaction by removing the reactants. The entire process—melting, refining, and casting—takes place within a sealed, evacuated chamber.
Creating a Chemically Inert Environment
By pumping the air out of the chamber, the VIM process removes the vast majority of oxygen and nitrogen molecules. This starves the potential chemical reactions of their fuel.
Without an atmosphere to react with, the active elements remain stable and dissolved within the molten bath.
From Reactive Loss to Predictable Retention
In a vacuum, the amount of an active element added to the melt is almost exactly the amount retained in the final alloy. The "melt loss" variable is effectively eliminated.
This is why VIM can achieve compositional control within extremely narrow ranges, such as ±0.12% for aluminum and titanium. The process becomes repeatable and highly precise.
A Secondary Benefit: Degassing
The vacuum environment also helps to remove unwanted dissolved gases, particularly hydrogen and nitrogen, that were already present in the raw materials.
As these gases are pulled from the melt, the final alloy has lower porosity and improved cleanliness, which contributes to superior fatigue life and mechanical integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VIM offers superior control, it is not the solution for every application. Its benefits come with practical trade-offs that must be considered.
Cost and Complexity
VIM furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than air-melt furnaces. The process is also slower due to the time required to pump down the vacuum chamber for each batch.
The Challenge of Vapor Pressure
One critical limitation of operating under a hard vacuum is the vapor pressure of the elements themselves. Elements with a high vapor pressure, such as manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), and to some extent chromium (Cr), can boil off from the melt.
Controlling this requires careful management of temperature and the vacuum level, sometimes by backfilling the chamber with a slight positive pressure of an inert gas like argon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use VIM depends entirely on the chemical specifications and performance requirements of the final alloy.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance superalloys, specialty steels, or titanium alloys: VIM is often non-negotiable to guarantee the precise chemistry required for extreme temperature, high stress, and mission-critical applications.
- If your primary focus is tightly controlling highly reactive elements (Al, Ti, B, Zr): VIM provides the only reliable method to prevent their unpredictable loss and ensure the batch-to-batch consistency demanded by stringent specifications.
- If your primary focus is producing standard-grade alloys with wider tolerance bands: Simpler and less expensive methods like air melting or argon-oxygen decarburization (AOD) are often more cost-effective and perfectly suitable.
Ultimately, mastering alloy chemistry requires choosing the process that grants you the necessary control over the melting environment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Air Melting | Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) |
|---|---|---|
| Control of Active Elements | ±0.25% (e.g., Al) | ±0.12% (e.g., Al, Ti) |
| Key Challenge | Atmospheric reactions (O₂, N₂) | Vapor pressure of elements |
| Primary Benefit | Cost-effective for standard alloys | Precise, repeatable chemistry |
| Ideal Applications | Standard-grade alloys | Superalloys, specialty steels, titanium alloys |
Unlock precise control for your high-performance alloys with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced vacuum induction melting solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our expertise in high-temperature furnaces, including custom VIM systems, ensures superior element retention and consistent results for demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your alloy production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















