In essence, a vacuum condition transforms melting from a simple phase change into a high-purity refining process. By removing the atmosphere, a vacuum prevents destructive chemical reactions like oxidation, eliminates dissolved gas impurities, and provides precise control over the final alloy composition, resulting in cleaner, stronger, and more consistent materials.
The fundamental advantage of vacuum melting is not merely the absence of air, but the creation of a controlled environment where the molten metal is protected from contamination, allowing for the production of high-purity and high-performance alloys that are impossible to achieve in open-air conditions.

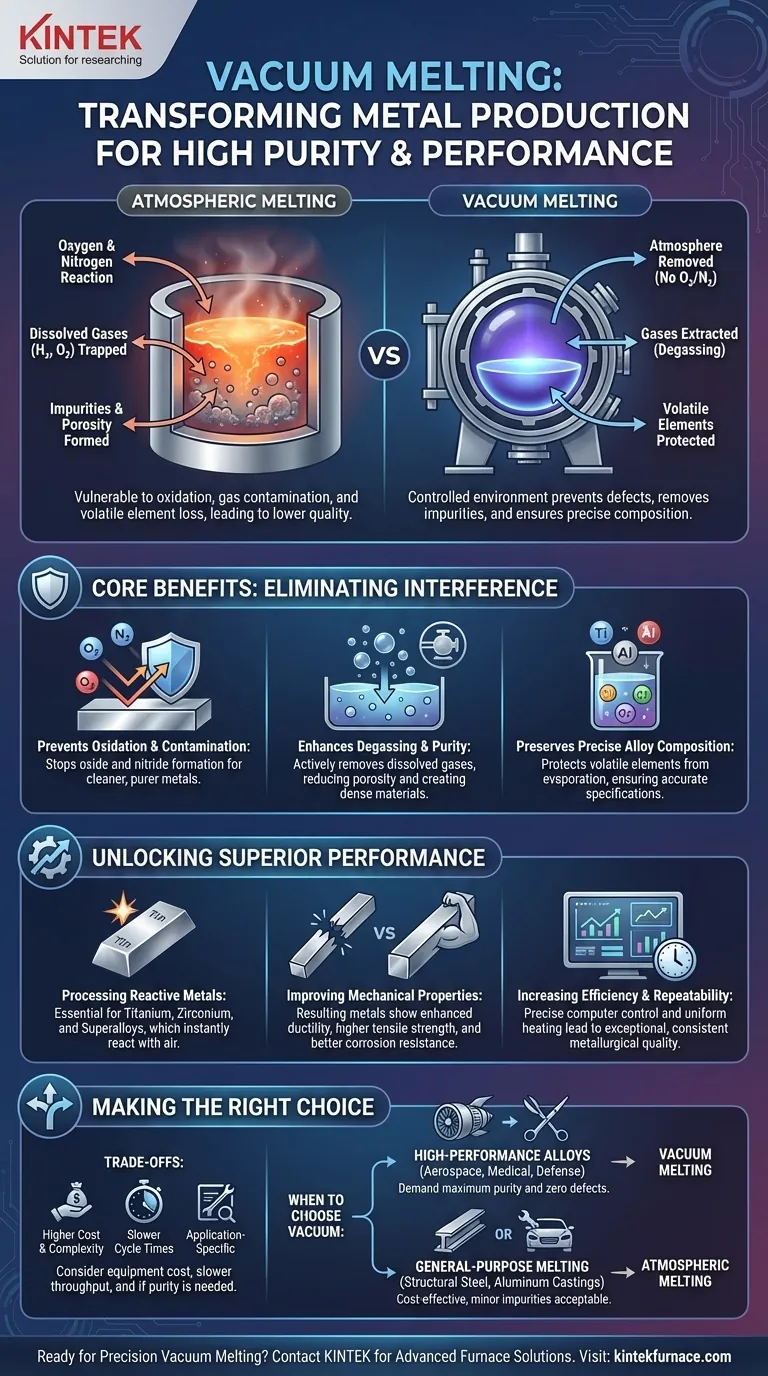
The Core Principle: Eliminating Atmospheric Interference
The air around us is not empty; it is a reactive mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen and oxygen. When metals are heated to their melting point, their reactivity skyrockets, making them vulnerable to contamination from these atmospheric gases. A vacuum directly addresses this core problem.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, molten metal readily reacts with oxygen to form oxides and with nitrogen to form nitrides. These compounds are impurities that get trapped in the metal as it solidifies.
This contamination creates internal defects, compromises the metal's structure, and degrades its performance. By removing the air, a vacuum furnace creates a "clean" environment that prevents these undesirable reactions from ever occurring.
Enhancing Degassing and Purity
Molten metals can hold a significant amount of dissolved gases, such as hydrogen and oxygen. These trapped gases can lead to porosity (tiny bubbles) in the final cast product, creating weak points that can lead to material failure.
The low-pressure environment of a vacuum actively pulls these dissolved gases out of the molten bath. This degassing effect is a critical refining step that significantly increases the purity and density of the final material.
Preserving Precise Alloy Composition
Many advanced alloys rely on a precise recipe of elements, some of which are highly reactive or have high vapor pressure (meaning they evaporate easily at high temperatures).
In a vacuum, these volatile and reactive alloying elements are protected. They are not lost to oxidation or excessive evaporation, ensuring the final chemical composition of the alloy matches the design specifications with extreme accuracy.
Unlocking Superior Performance and Process Control
By creating this ideal melting environment, vacuum technology unlocks a higher level of material quality and process repeatability that is essential for demanding industries.
Processing Highly Reactive Metals
Metals like titanium, zirconium, and other superalloys are so reactive that they will instantly and aggressively react with air when molten. For these materials, vacuum melting is not just an advantage; it is a necessity.
Processes like vacuum induction melting (VIM) and vacuum arc remelting (VAR) are specifically designed to handle these sensitive materials safely and effectively.
Improving Mechanical Properties
The direct result of higher purity and lower porosity is a significant improvement in the metal's mechanical characteristics.
Metals produced in a vacuum consistently exhibit enhanced ductility, greater tensile strength, and improved corrosion resistance. This is because the material has a more uniform and defect-free internal structure.
Increasing Efficiency and Repeatability
In a vacuum, there is no air to transfer heat away from the melt via convection. This makes the heating process more energy-efficient and allows for faster, more uniform temperature distribution throughout the molten metal.
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled, allowing for precise management of temperature, pressure, and process timing. This automation leads to exceptional metallurgical repeatability, ensuring every batch meets the exact same high standards required for critical applications in aerospace, defense, and medicine.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, vacuum melting is a specialized process with important considerations. It is not the default choice for every application.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated machines. The need for a robust, airtight chamber, powerful vacuum pumps, and high-temperature-resistant internal components makes the initial investment and ongoing maintenance significantly higher than for standard atmospheric furnaces.
Slower Overall Cycle Times
While heating can be efficient, the process of pumping down the chamber to achieve the required vacuum level adds considerable time to each melting cycle. This can impact overall production throughput compared to faster, open-air methods.
Application-Specific Need
For many common metals and alloys, the level of purity and performance achieved through atmospheric melting is perfectly adequate. For applications like structural steel or common aluminum castings, the added expense and complexity of vacuum processing are not justified.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting process depends entirely on the required quality and performance of the end product.
- If your primary focus is high-performance alloys: Vacuum melting is essential for aerospace, medical, or defense applications that demand maximum purity, specific mechanical properties, and zero tolerance for defects.
- If your primary focus is reactive metals: Vacuum processing is non-negotiable for materials like titanium or superalloys that cannot be exposed to air when molten.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose melting: Standard atmospheric melting is the more economical and practical choice for applications where minor impurities do not compromise the material's function.
Ultimately, choosing to melt in a vacuum is a deliberate decision to engineer a material's properties at the most fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Eliminates oxide and nitride formation for cleaner metals |
| Enhances Degassing | Removes dissolved gases like hydrogen to reduce porosity |
| Preserves Alloy Composition | Protects volatile elements for accurate chemical specs |
| Improves Mechanical Properties | Boosts strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance |
| Increases Process Control | Enables precise temperature and pressure management |
Ready to elevate your material quality with precision vacuum melting? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and defense. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve cleaner, stronger, and more consistent alloys!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















