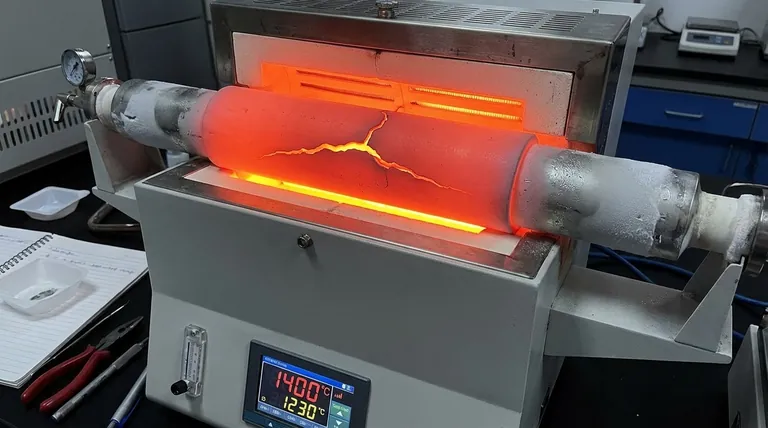
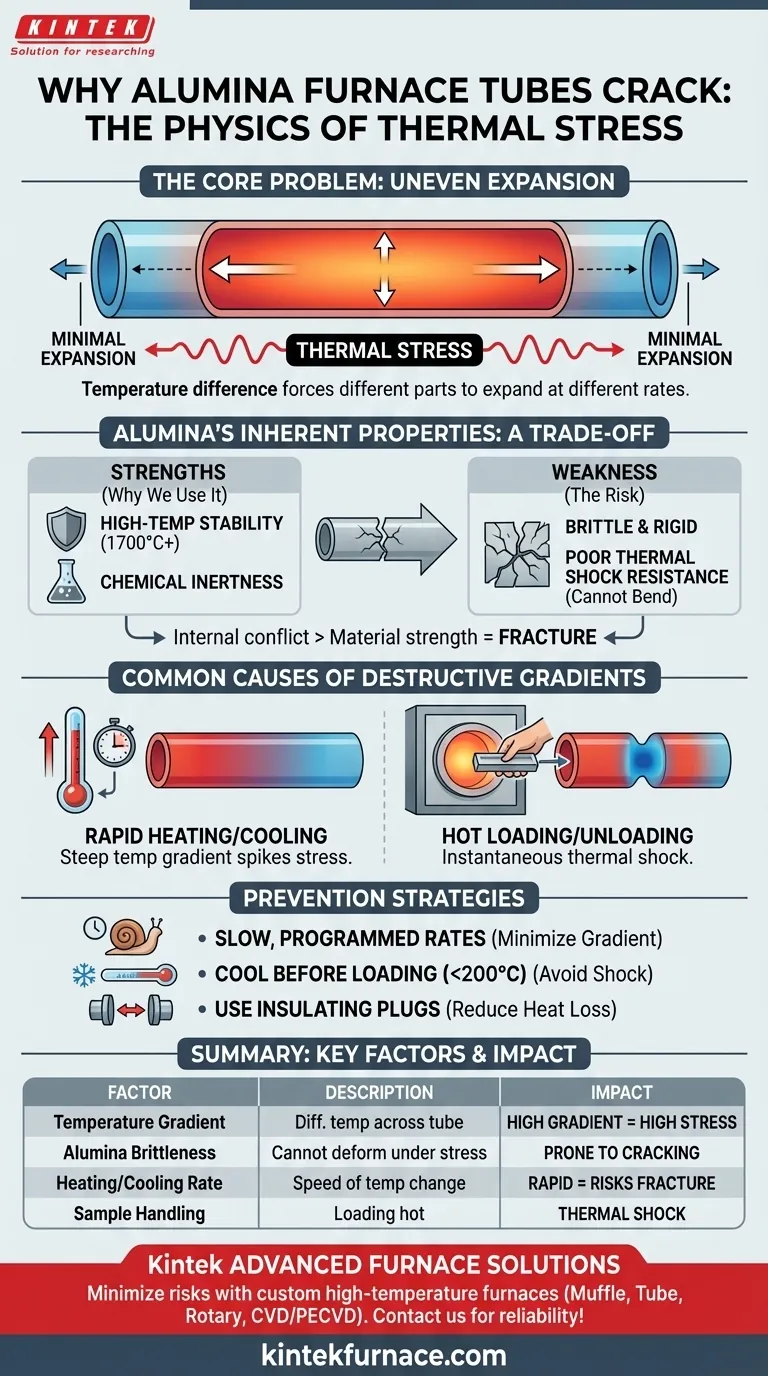
At its core, a significant temperature difference forces different parts of the alumina tube to expand or contract at different rates. Because alumina is a rigid, brittle ceramic, it cannot bend to accommodate this uneven movement. This internal conflict creates immense physical tension, known as thermal stress, which ultimately exceeds the material's strength and causes it to fracture.
The fundamental issue is a mismatch between alumina's properties and operational demands. While prized for its high-temperature stability, alumina's inherent brittleness makes it extremely vulnerable to the thermal stress generated by rapid or uneven temperature changes.

The Physics of Thermal Stress in Alumina
To prevent cracking, it is crucial to understand the mechanism of failure. The problem is not high temperature itself, but the difference in temperature across the tube's length.
Uneven Thermal Expansion
All materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. In a furnace tube, the central heating zone gets very hot and expands significantly.
The ends of the tube, which are outside the heating zone, remain much cooler and expand very little. This difference in expansion creates a powerful internal tug-of-war within the material.
The Critical Role of Temperature Gradients
A temperature gradient is the rate of temperature change over a distance. A steep gradient means a large temperature difference over a short area.
In many furnace setups, the difference between the hot center and the cool ends can be over 1000°C. This extreme gradient is the direct cause of high thermal stress.
Alumina's Inherent Brittleness
Metals often respond to stress by bending or deforming. Alumina, however, has poor thermal shock resistance.
This means it is a brittle material that cannot relieve stress by changing shape. When the internal thermal stress surpasses its structural limit, its only failure mode is to crack.
Common Scenarios Causing Destructive Gradients
These physical principles manifest during specific, often preventable, operational procedures.
During Normal Heating and Cooling
Even during a normal operational cycle, the ends of the tube will always be cooler than the center.
If you heat or cool the furnace too quickly, you don't give the heat enough time to distribute evenly. This steepens the temperature gradient temporarily, spiking the thermal stress and risking fracture.
During Sample Loading and Unloading
A catastrophic failure often occurs when operators introduce or remove samples at high temperatures.
Placing a room-temperature sample holder or boat into a 1000°C furnace creates a sudden, localized cold spot on the tube's inner wall. This instantaneous thermal shock is often enough to cause immediate cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Use Alumina?
Given its sensitivity to thermal shock, it's fair to ask why alumina is used at all. The answer lies in its other exceptional properties, which create a necessary engineering compromise.
Unmatched Temperature Stability
High-purity alumina can operate at extremely high temperatures (often above 1700°C) without melting, degrading, or deforming under its own weight.
Excellent Chemical Inertness
Alumina is highly resistant to chemical attack and does not readily react with most materials being processed. This ensures the purity of the sample.
The Inherent Compromise
Engineers choose alumina despite its poor thermal shock resistance because its high-temperature and chemical stability are non-negotiable for many applications. The responsibility then falls on the operator to respect the material's limitations through careful procedure.
How to Prevent Furnace Tube Cracking
You can dramatically extend the life of your furnace tubes by controlling the rate and distribution of temperature change.
- If your primary focus is operational longevity: Always use slow, programmed heating and cooling rates to minimize the temperature gradient between the hot zone and the ends.
- If your primary focus is safe sample handling: Never load or unload samples while the furnace is hot. Always wait for it to cool to a safe temperature (typically below 200°C).
- If your primary focus is mitigating design-inherent stress: Use ceramic fiber plugs at both ends of the tube to act as insulators, which helps reduce heat loss and soften the temperature gradient.
Ultimately, treating an alumina tube with an understanding of its brittle nature is the key to reliable and long-lasting performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Cracking |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Gradient | Difference in temperature across the tube | High gradient increases thermal stress |
| Alumina Brittleness | Material's inability to deform under stress | Makes it prone to cracking under stress |
| Heating/Cooling Rate | Speed of temperature change | Rapid changes steepen gradient and risk fracture |
| Sample Handling | Loading/unloading at high temperatures | Causes thermal shock and immediate cracking |
Protect your lab investments with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, minimizing risks like thermal stress and extending equipment life. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















