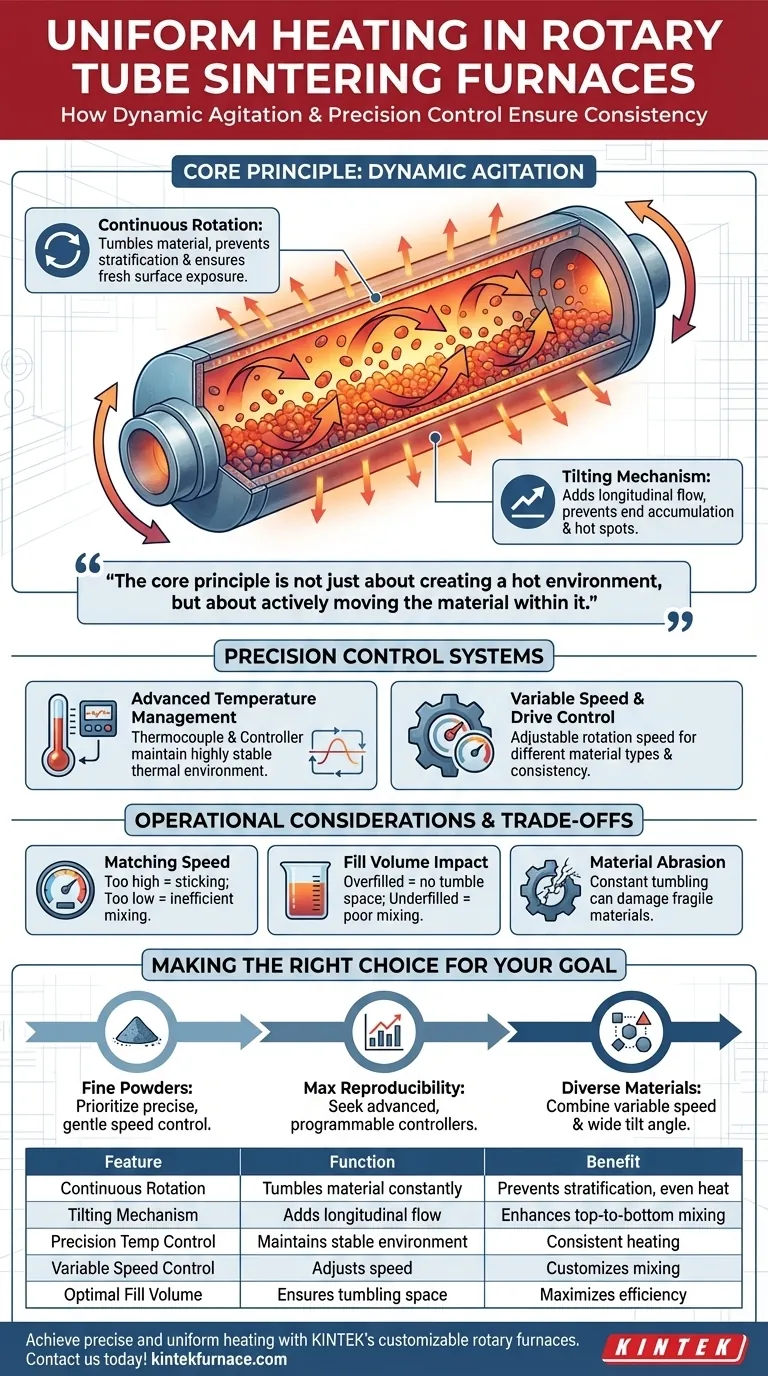
A rotary tube sintering furnace ensures uniform material heating primarily through the continuous rotation of its furnace tube. This mechanical action constantly tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is equally exposed to the heat source. Many furnaces enhance this effect with a tilting mechanism, which further promotes comprehensive mixing and prevents localized hot or cold spots.
The core principle is not just about creating a hot environment, but about actively moving the material within it. While precise temperature control establishes a stable thermal zone, it is the mechanical agitation from rotation and tilting that guarantees every part of the material experiences that temperature uniformly.
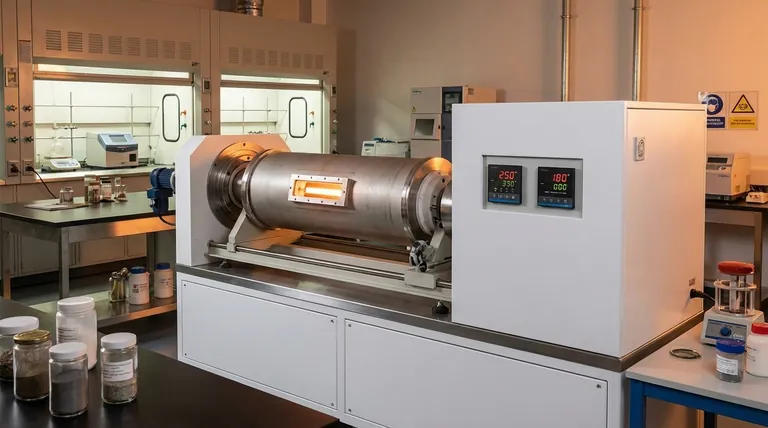

The Core Principle: Dynamic Agitation
Static heating in a traditional furnace often leads to stratification, where the material at the bottom and sides gets hotter than the material in the center. A rotary furnace is engineered specifically to solve this problem through constant motion.
Continuous Rotation for Constant Mixing
The central component is a cylindrical furnace tube that is driven by an independent motor. As the tube rotates, the material inside is lifted up the side and then tumbles back down.
This continuous flipping and mixing action is the primary mechanism for distributing heat. It directly prevents powders or pellets from settling and ensures fresh surfaces are constantly being exposed to the radiant heat from the furnace walls.
Tilting for Top-to-Bottom Uniformity
In addition to rotation, many rotary furnaces can be tilted. This tilting introduces a longitudinal (top-to-bottom) flow to the material.
This is especially critical for preventing material from accumulating at one end of the tube. The combination of rotation and tilt creates a gentle, three-dimensional stirring effect, maximizing thermal homogeneity throughout the entire material batch.
The Role of Precision Control Systems
Mechanical agitation works in concert with sophisticated thermal management to achieve a truly uniform process. The system must create a stable temperature environment for the agitation to be effective.
Advanced Temperature Management
Modern rotary furnaces use advanced temperature control systems. A thermocouple measures the temperature inside the furnace and converts it into an electrical signal.
This signal is sent to a temperature controller, which compares the actual temperature to the user's setpoint. The controller then precisely adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements to maintain a highly stable and uniform thermal environment.
Variable Speed and Drive Control
The rotation itself is a controlled variable. The motor driving the tube allows for adjustable rotation speeds.
This is critical because different materials behave differently. Fine powders may require a slower, gentler tumble to prevent dust-up, while larger pellets might need a faster speed for effective mixing. This control enhances process consistency and reproducibility for a wide range of materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly effective, achieving perfect uniformity requires an understanding of key operational parameters.
Matching Speed to Material Type
The optimal rotation speed is not universal. If the speed is too high, centrifugal force can cause material to stick to the furnace tube wall, defeating the purpose of tumbling. If the speed is too low, mixing will be inefficient.
The Impact of Fill Volume
The efficiency of the tumbling action is also dependent on how much material is in the tube. An overfilled tube will not have enough free space for the material to tumble properly. An underfilled tube may not mix effectively. Finding the optimal fill volume for your specific material is crucial.
Potential for Material Abrasion
The constant tumbling action, while excellent for heat transfer, can cause mechanical abrasion. This is a key consideration when processing fragile or brittle materials, as it may generate unwanted fine particles or damage the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right setup depends entirely on your material and processing objectives.
- If your primary focus is processing fine powders: Prioritize a furnace with highly precise and adjustable rotation speed control to achieve gentle mixing without creating excessive dust.
- If your primary focus is maximum process reproducibility: Seek out models with advanced, programmable PID temperature controllers to ensure every batch runs under identical thermal conditions.
- If your primary focus is handling diverse material types: A furnace that combines both variable speed control and a wide tilting angle provides the most flexibility for effective agitation.
By understanding how these mechanical and thermal systems work together, you can leverage a rotary furnace to achieve superior thermal uniformity and product quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Rotation | Tumbles material constantly | Prevents stratification and ensures even heat exposure |
| Tilting Mechanism | Adds longitudinal flow | Enhances top-to-bottom mixing and avoids hot spots |
| Precision Temperature Control | Maintains stable thermal environment | Works with agitation for consistent heating |
| Variable Speed Control | Adjusts rotation speed | Customizes mixing for different materials (e.g., powders or pellets) |
| Optimal Fill Volume | Ensures proper tumbling space | Maximizes mixing efficiency and heat distribution |
Ready to achieve precise and uniform heating for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, designed for diverse applications. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring optimal performance with features like dynamic agitation and precision controls. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your material processing and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control



















