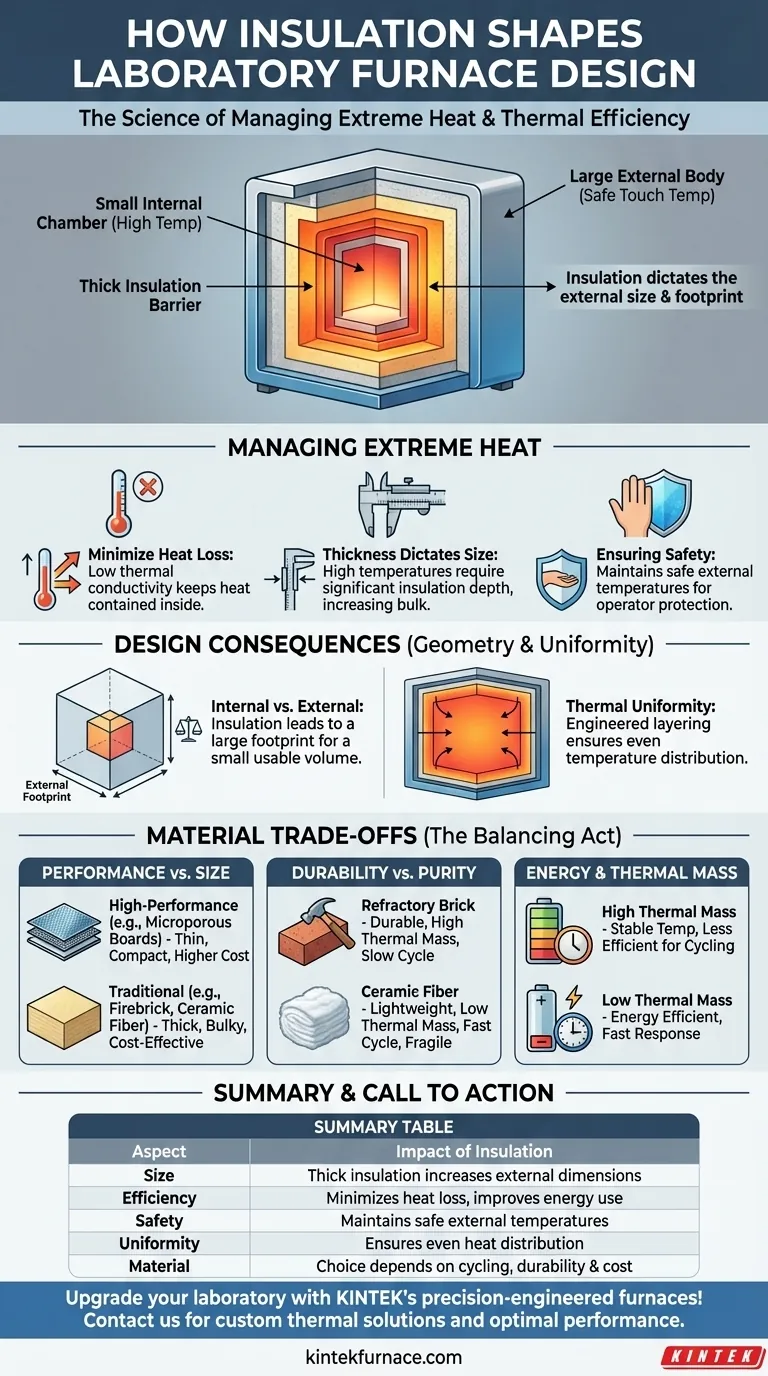
In short, insulation is the primary factor driving the significant size difference between a laboratory furnace's small internal chamber and its much larger external body. Because high temperatures require thick layers of insulating material to contain heat safely and efficiently, the external dimensions must expand to accommodate this protective barrier.
The design of a laboratory furnace is a direct expression of thermal management. The choice and thickness of insulation create a fundamental trade-off between the usable internal volume, the overall external footprint, and the furnace's energy efficiency.

The Core Principle: Managing Extreme Heat
The fundamental purpose of a laboratory furnace is to create and maintain a precise, high-temperature environment. The insulation's job is to keep that thermal energy contained within the chamber, which has several critical effects on the furnace's design and operation.
The Need to Minimize Heat Loss
A furnace without insulation would be incredibly inefficient and dangerous, radiating immense heat into the laboratory. Insulation materials are chosen for their low thermal conductivity, meaning they resist the transfer of heat.
This resistance is what keeps the heat inside the chamber where it's needed and prevents the external surfaces from reaching hazardous temperatures.
How Thickness Dictates External Size
To achieve the necessary level of heat containment, especially for temperatures exceeding 1000°C, a significant thickness of insulation is required.
This directly results in a bulky design. For a given internal chamber size, the need for thick walls of insulation dictates a much larger external casing to house both the chamber and the insulation itself.
Ensuring Operator Safety
Effective insulation is a critical safety feature. It ensures the furnace's outer shell, or "cold face," remains at a temperature safe enough for operators to work near the equipment without risk of severe burns.
Regulatory standards often mandate specific maximum external surface temperatures, which directly influences the minimum required insulation thickness.
How Insulation Shapes Furnace Geometry
The relationship between the internal chamber and the external body is the most visible design consequence of insulation. However, its influence goes deeper, affecting uniformity and practical use.
Internal Volume vs. External Footprint
Think of the furnace chamber as a small, hot core. The insulation is a thick, protective shell built around it. This is why a furnace with an internal capacity of just a few liters can easily occupy the space of a large filing cabinet.
This disparity is a crucial consideration for lab space planning. The "effective footprint" of the furnace is always dictated by its external dimensions, not its usable internal volume.
Designing for Thermal Uniformity
Insulation isn't just packed in randomly. Its placement and layering are engineered to ensure uniform temperature distribution inside the chamber.
Poorly designed insulation can create hot and cold spots within the chamber, compromising the integrity of experiments or material processing. The design must manage heat flow in three dimensions to deliver consistent performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The type of insulation used is a balancing act between thermal performance, durability, and cost. There is no single "best" material, only the best material for a specific application.
Performance vs. Physical Size
High-performance insulation, like advanced microporous boards, can provide excellent thermal resistance with less thickness. This allows for a more compact furnace design but often comes at a significantly higher cost.
Conversely, traditional materials like refractory firebrick or ceramic fiber blankets are more cost-effective but typically require greater thickness to achieve the same insulating value, leading to a larger and heavier furnace.
Material Durability and Process Purity
Refractory brick is extremely durable and resistant to physical wear, making it ideal for applications with heavy loads. However, it also has high thermal mass, meaning it heats and cools very slowly.
Ceramic fiber is lightweight and has low thermal mass, allowing for much faster heat-up and cool-down cycles. Its drawback is that it can be more fragile and may release particulates, making it unsuitable for ultra-clean applications without a protective inner lining.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Mass
Insulation with high thermal mass (like dense brick) absorbs a large amount of energy during heat-up. This makes it less efficient for processes requiring frequent thermal cycling but excellent for maintaining a stable temperature over long periods.
Low thermal mass insulation (like ceramic fiber) requires far less energy to reach the target temperature, making it the more energy-efficient choice for applications with short, repeated cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace requires looking beyond the maximum temperature and internal dimensions. Understanding the insulation design is key to matching the equipment to your work.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling: Prioritize a furnace with lightweight ceramic fiber insulation for its low thermal mass and fast response.
- If your primary focus is process durability and stability: A furnace built with dense refractory brick will provide superior longevity and thermal stability, despite its larger size and slower cycle times.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lab space: Seek out high-end models that use advanced, thin-profile insulation, but be prepared for the higher initial investment.
Ultimately, understanding the role of insulation changes your perspective from buying a simple heat source to investing in a precisely engineered thermal system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Insulation |
|---|---|
| Size | Thick insulation increases external dimensions, reducing internal-to-external volume ratio |
| Efficiency | Low thermal conductivity minimizes heat loss, improving energy use |
| Safety | Maintains safe external temperatures, preventing operator burns |
| Thermal Uniformity | Proper layering ensures even heat distribution in the chamber |
| Material Choice | Ceramic fiber for fast cycling; refractory brick for durability and stability |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's precision-engineered furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with advanced high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental needs are met with optimal insulation and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















