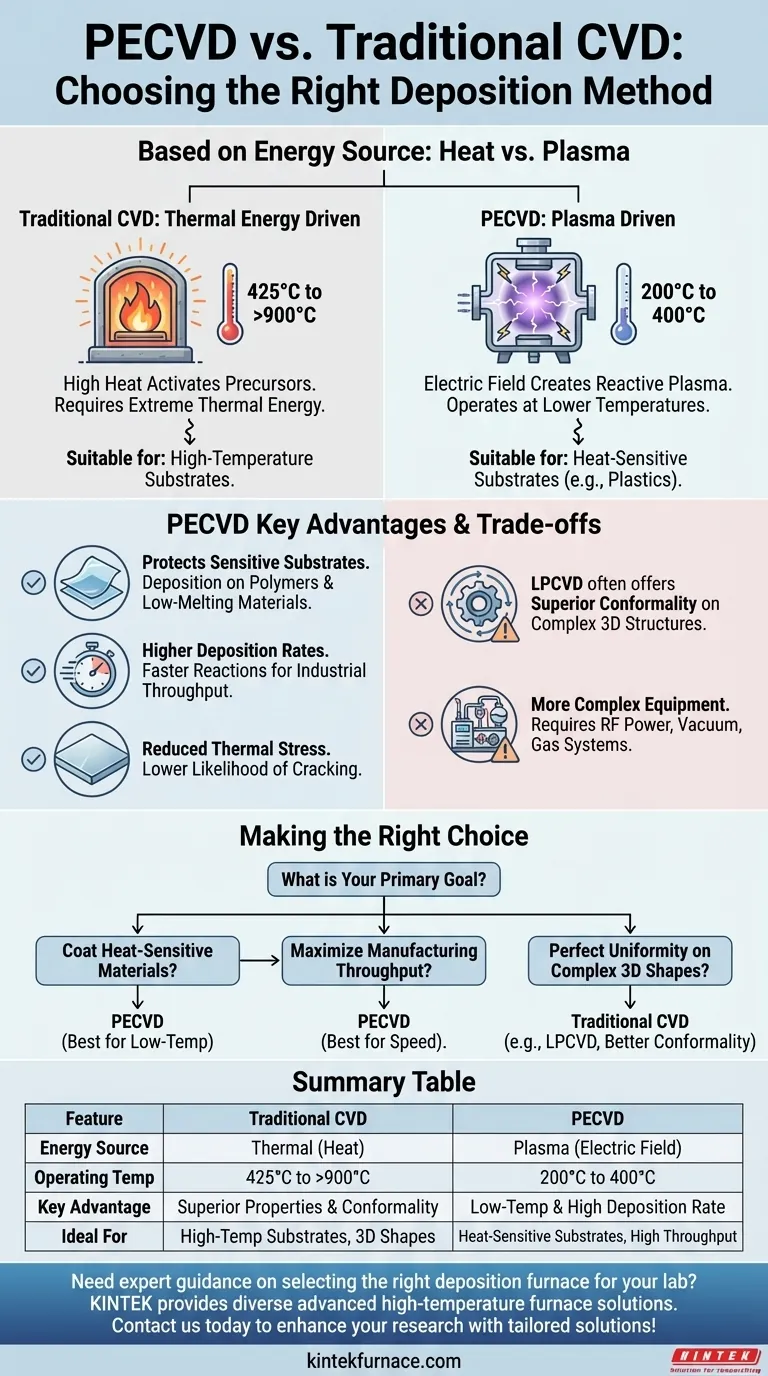
The fundamental difference between Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) and traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the energy source used to drive the reaction. While traditional CVD relies purely on high thermal energy (heat) to break down precursor gases, PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma, allowing the deposition process to occur at significantly lower temperatures.
The choice between PECVD and traditional CVD is not about which is universally "better," but which is appropriate for your specific application. PECVD's primary advantage is its low-temperature operation, which expands the range of usable substrates, but this comes with distinct trade-offs in film properties and process complexity.

The Core Distinction: Heat vs. Plasma
The energy source dictates the operating conditions and, consequently, the suitable applications for each method. Understanding this difference is key to choosing the right process.
Traditional CVD: Driven by Thermal Energy
Traditional CVD processes, such as Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), require high temperatures, typically ranging from 425°C to over 900°C.
This intense heat provides the necessary activation energy for precursor gases to react and form a solid film on the substrate's surface. The high temperature is both a requirement and a major limitation.
PECVD: Driven by Plasma
PECVD operates at much lower temperatures, usually between 200°C and 400°C.
Instead of heat, it uses an electric or magnetic field to excite the precursor gases into a plasma—a highly reactive state of matter containing ions and free radicals. This plasma provides the energy for the chemical reaction, bypassing the need for extreme heat.
Key Advantages of the PECVD Approach
The use of plasma instead of high heat gives PECVD several distinct operational advantages, making it the preferred method for many modern applications.
Protecting Temperature-Sensitive Substrates
This is the most significant benefit of PECVD. The low operating temperature allows for the deposition of high-quality films on materials that cannot withstand the heat of traditional CVD.
This includes substrates like plastics, polymers, and other low-melting-point materials, dramatically expanding its use in fields like flexible electronics and medical devices.
Achieving Higher Deposition Rates
The highly reactive nature of the plasma often results in a faster chemical reaction compared to thermally-driven processes.
This translates to higher deposition rates, which is a critical factor for industrial-scale manufacturing where throughput and efficiency are paramount.
Reducing Thermal Stress and Cracking
Because the substrate is not subjected to extreme temperatures or large temperature fluctuations, the resulting films often exhibit lower internal stress.
This significantly reduces the likelihood of the film cracking, leading to more robust and reliable coatings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PECVD offers powerful advantages, it is not a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its limitations compared to traditional methods like LPCVD.
Film Properties and Conformality
While PECVD produces high-quality films, their specific properties can differ from those made with high-temperature CVD. For example, films from an LPCVD process may offer greater flexibility or different crystalline structures.
Furthermore, traditional CVD methods can sometimes offer superior conformality, meaning the ability to coat complex, three-dimensional structures with a perfectly uniform thickness.
Equipment Complexity
A PECVD system is inherently more complex than a standard thermal CVD furnace. It requires a vacuum chamber, a gas delivery system, and a radio-frequency (RF) power source to generate and sustain the plasma.
This added complexity can translate to higher initial equipment costs and more intricate maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your project's non-negotiable requirements, primarily your substrate material and desired film characteristics.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials (like polymers): PECVD is the clear and often only choice due to its low-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing manufacturing throughput: PECVD is generally superior due to its higher deposition rates.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific film properties like high flexibility or perfect uniformity on complex 3D shapes: A traditional CVD method like LPCVD might be the more suitable technology.
Ultimately, selecting the correct deposition technology requires a clear understanding of your substrate's limitations and the final properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional CVD | PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal energy (heat) | Plasma (electric field) |
| Operating Temperature | 425°C to over 900°C | 200°C to 400°C |
| Key Advantage | Superior film properties and conformality | Low-temperature operation and higher deposition rates |
| Ideal For | High-temperature substrates, complex 3D structures | Heat-sensitive substrates (e.g., plastics), high-throughput manufacturing |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right deposition furnace for your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your research with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of PECVD tube furnaces compared to CVD tube furnaces? Lower Temp, Faster Deposition, and More
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the difference between PVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Coating Technology
- What is the role of temperature in PECVD? Optimize Film Quality and Substrate Protection
- What forms of energy can be applied in CVD to initiate chemical reactions? Explore Heat, Plasma, and Light for Optimal Thin Films



















