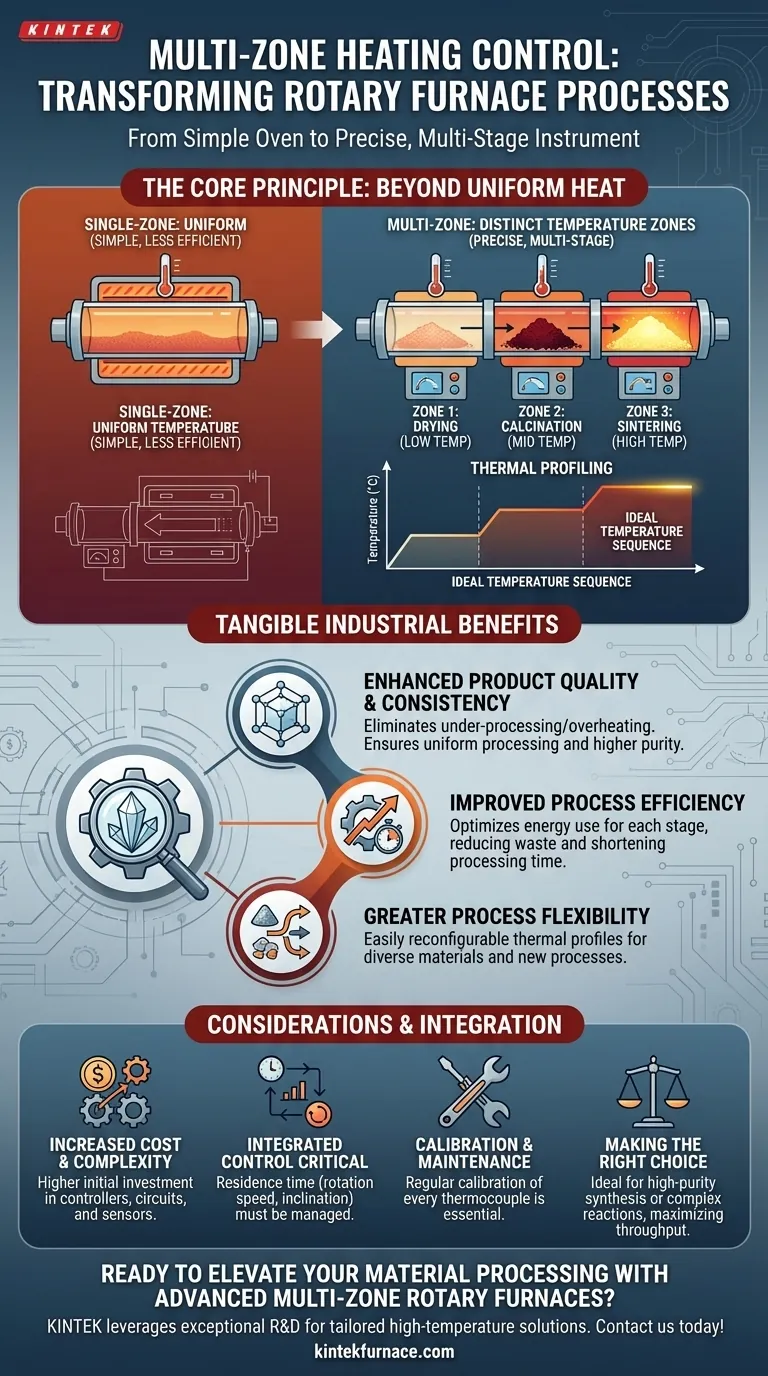
In short, multi-zone heating control transforms a rotary furnace from a simple oven into a precise, multi-stage processing instrument. By creating distinct temperature zones along the length of the furnace tube, it allows you to execute a specific thermal profile—exposing material to different temperatures as it travels—which is critical for improving product quality, consistency, and overall process efficiency.
The core benefit is not just better heating, but the ability to perform a complex, sequential thermal process within a single, continuous operation. This moves beyond simple uniform heating to enable precise material transformation at each stage of its journey through the furnace.
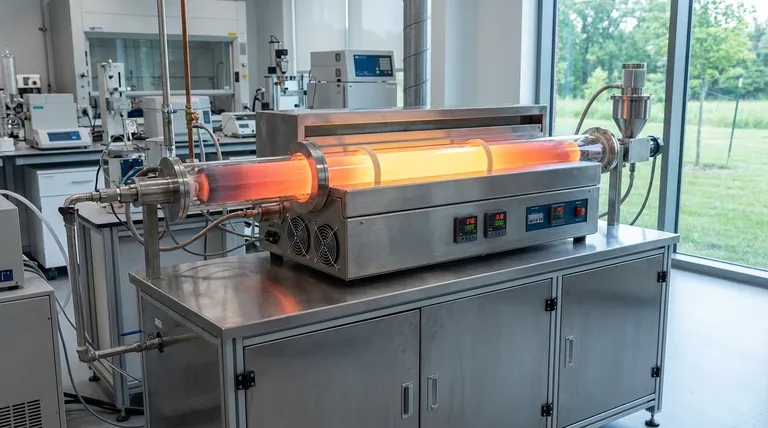

Beyond Uniform Heat: The Principle of Thermal Profiling
A traditional single-zone furnace is effective at one thing: bringing a batch of material to a single, uniform temperature. Multi-zone control introduces a fundamentally more sophisticated capability.
What is Multi-Zone Control?
A multi-zone rotary furnace is divided into several independent heating sections along its length. Each zone has its own temperature controller and sensor (thermocouple), allowing it to maintain a temperature setpoint that is completely different from its neighboring zones.
The Goal: A Precise Thermal Profile
Many advanced material processes are not monolithic; they require a sequence of steps at varying temperatures. For example, a process might need a low-temperature drying stage, a mid-temperature calcination stage, and a high-temperature sintering stage.
Multi-zone control allows you to map this ideal temperature sequence, or thermal profile, directly onto the furnace. As material rotates and moves down the tube, it passes through each zone, undergoing the precise thermal treatment required at that specific stage.
The Production Line Analogy
Think of a single-zone furnace as a large workshop where every tool is set to the same specification. It's functional, but inefficient for a multi-step project.
A multi-zone furnace, by contrast, is like a modern assembly line. Each station (zone) is perfectly calibrated for a specific task, ensuring the product is built correctly and efficiently as it moves from one end to the other.
Tangible Benefits in Industrial Applications
Applying a precise thermal profile directly translates to measurable improvements in process outcomes.
Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency
By ensuring every particle of material experiences the correct temperature at the correct time, you eliminate issues of under-processing or overheating.
In calcining, for instance, an initial cooler zone can gently drive off moisture without flash-boiling, while subsequent hotter zones can achieve the target chemical reaction. This results in a final product with higher purity and greater uniformity.
Improved Process Efficiency
Optimizing the temperature for each stage reduces wasted energy and shortens the overall processing time. You aren't expending high-temperature energy on a low-temperature drying phase.
This focused application of energy at each step ensures the entire process runs at peak thermal efficiency, maximizing throughput and reducing operational costs.
Greater Process Flexibility
A single multi-zone furnace can be reconfigured to run entirely different thermal profiles with simple programming changes. This allows you to process a wide variety of materials or develop new processes without needing to invest in new, dedicated hardware.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, multi-zone control is not a universal solution. It comes with its own set of complexities that must be managed.
Increased Cost and Complexity
Naturally, a system with multiple controllers, power circuits, and thermocouples has a higher initial capital cost than a single-zone furnace. The control system is also inherently more complex to program and operate.
The Importance of Integrated Control
The true power of multi-zone heating is unlocked when it is integrated with other process variables. The residence time—how long the material spends in each temperature zone—is just as critical as the temperature itself.
This residence time is governed by the furnace's rotation speed and inclination angle. An effective system must provide integrated control over all these variables to execute a thermal profile successfully.
Calibration and Maintenance
Each heating zone is a potential point of failure. Maintaining the accuracy of every thermocouple through regular calibration is critical. A deviation in just one zone can compromise the entire process and negate the benefits of the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a multi-zone furnace should be driven by the specific requirements of your material and process goals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis or complex reactions: Multi-zone control is almost certainly necessary to create the precise thermal ramps and soaks required for targeted chemical and physical transformations.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput and efficiency for bulk materials: Multi-zone control allows you to optimize each stage of the process (e.g., drying, calcining, cooling) to reduce energy consumption and processing time.
- If your process requires only a single, uniform heating temperature: A simpler and more cost-effective single-zone furnace is likely the more appropriate choice.
Ultimately, adopting multi-zone control elevates your rotary furnace from a simple heater into a dynamic and precise material processing instrument.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Product Quality | Ensures uniform processing and higher purity by exposing materials to specific temperatures at each stage. |
| Improved Process Efficiency | Reduces energy waste and shortens processing time by optimizing temperature for each step. |
| Greater Process Flexibility | Allows easy reconfiguration for different thermal profiles, supporting diverse materials and processes. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with advanced multi-zone rotary furnaces? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















