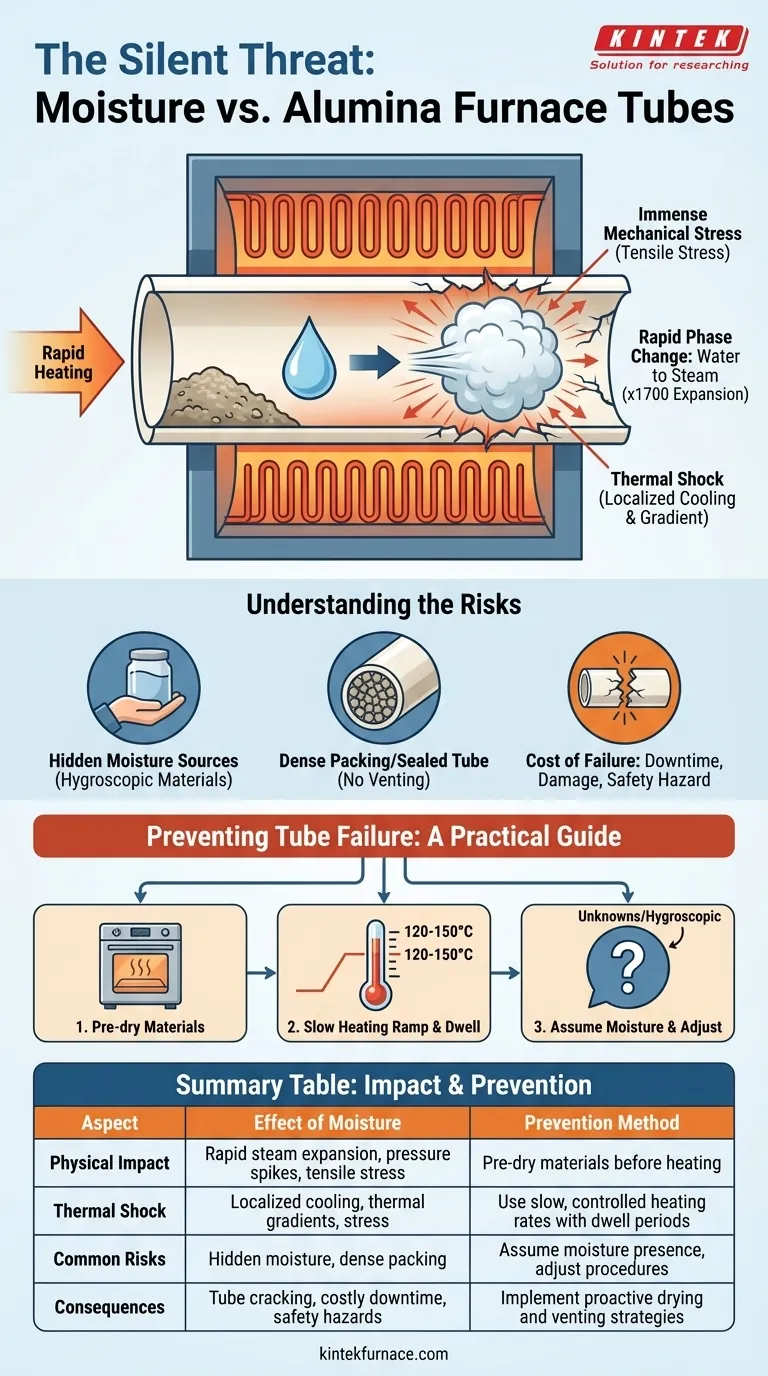
In short, moisture in your heating material is a critical threat to the integrity of an alumina furnace tube. When a moist material is heated rapidly, the trapped water violently turns to steam, creating a sudden and powerful pressure spike inside the tube. This event, often combined with thermal shock, can easily lead to cracks, fractures, and catastrophic failure of the ceramic.
The primary danger of moisture is not chemical but physical. The rapid expansion of water into steam inside a constricted environment generates immense mechanical stress that alumina, despite its high-temperature resilience, cannot withstand. Therefore, proper material drying and controlled heating rates are non-negotiable safety protocols.
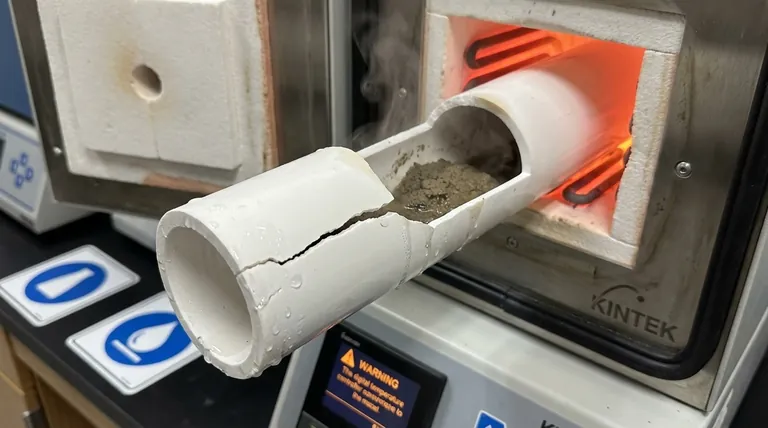

The Physics of Moisture-Induced Failure
To prevent failure, you must first understand the forces at play. The damage happens in a fraction of a second, but it's the result of a powerful physical process.
The Problem: Rapid Phase Change
Water undergoes a massive volume expansion—a factor of approximately 1,700—when it converts from a liquid to a gas (steam) at atmospheric pressure.
If this phase change occurs within a porous material or a confined space inside the furnace tube, this expansion acts like a small explosion.
How Pressure Creates Mechanical Stress
The generated steam exerts immense outward pressure on the inner walls of the alumina tube.
Ceramics like alumina are very strong under compression but are notoriously brittle and weak under tension. The internal pressure from the steam places the tube wall under tensile stress, which is its most vulnerable state.
The Compounding Effect of Thermal Shock
Simultaneously, the rapid vaporization of water causes localized cooling on the inner surface of the tube.
This creates a sharp temperature difference, or thermal gradient, between the cooler inner wall and the hot outer wall. This gradient induces its own stress, a phenomenon known as thermal shock, which further weakens the tube and exacerbates the stress from the pressure spike.
Understanding the Risks and Common Pitfalls
Simply being aware of the danger isn't enough. Many operators fall into common traps that lead to equipment damage.
Hidden Moisture Sources
The risk isn't limited to visibly wet samples. Moisture can be introduced from less obvious sources.
Hygroscopic materials, for example, are powders or salts that actively absorb ambient moisture from the air. A material that was dry yesterday may be hazardous today after sitting out in a humid lab.
The Myth of "Slow Heating" as a Cure-All
While a slow heating rate is crucial, it is not a guaranteed solution if the steam has no path to escape.
If the tube is sealed or the material is packed too densely, pressure will build regardless of the heating rate. The goal of a slow ramp is to allow steam to form gradually and vent safely.
The Cost of Failure
A tube failure is more than just an inconvenience. It results in costly downtime, the high price of a replacement tube, and potential damage to the furnace's heating elements. Most importantly, a violent fracture can create a significant safety hazard.
A Practical Guide to Preventing Tube Failure
To protect your equipment and ensure reliable results, your operational procedure must proactively account for the risk of moisture. Base your approach on your specific process and materials.
- If your primary focus is process safety and equipment longevity: Always pre-dry your materials in a separate, lower-temperature drying oven before placing them in the alumina tube furnace.
- If pre-drying is not an option: Implement a very slow, multi-stage heating ramp with a dwell period just above the boiling point of water (e.g., 120-150°C) to allow steam to vent slowly and completely.
- If you are working with unknown or hygroscopic materials: Assume they contain moisture and incorporate a pre-drying or slow-ramp-with-dwell step into your standard procedure without exception.
Proactively managing moisture is the single most effective way to guarantee the long-term performance and safety of your high-temperature furnace system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Effect of Moisture | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Impact | Rapid steam expansion causes pressure spikes and tensile stress | Pre-dry materials before heating |
| Thermal Shock | Localized cooling creates thermal gradients and stress | Use slow, controlled heating rates with dwell periods |
| Common Risks | Hidden moisture in hygroscopic materials or dense packing | Assume moisture presence and adjust procedures accordingly |
| Consequences | Tube cracking, costly downtime, safety hazards | Implement proactive drying and venting strategies |
Protect your lab's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you avoid moisture-related failures and enhance efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and ensure long-term equipment performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















