Fundamentally, electromagnetic stirring improves melt quality by using inherent physical forces to vigorously and automatically agitate the molten metal. This constant motion ensures the entire melt achieves a uniform temperature and chemical composition. The stirring action actively forces impurities and gases to the surface for removal, resulting in a cleaner, more homogeneous liquid metal.
The true value of electromagnetic stirring is its ability to transform a simple melt into a highly refined and uniform liquid. By actively managing temperature, alloy distribution, and purity, it directly prevents common casting defects and elevates the quality of the final product.
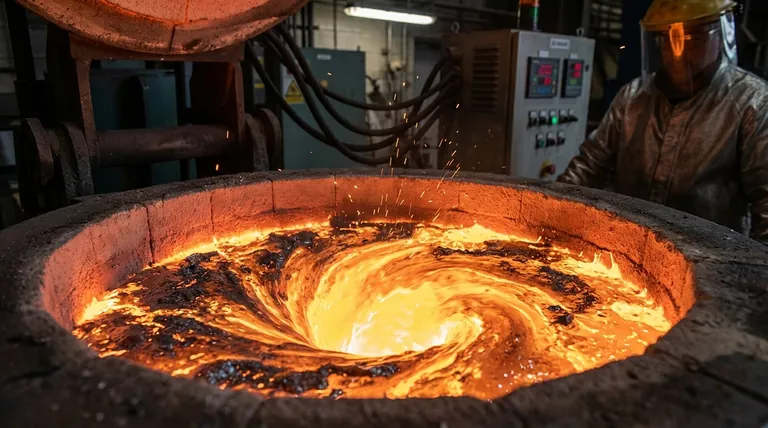

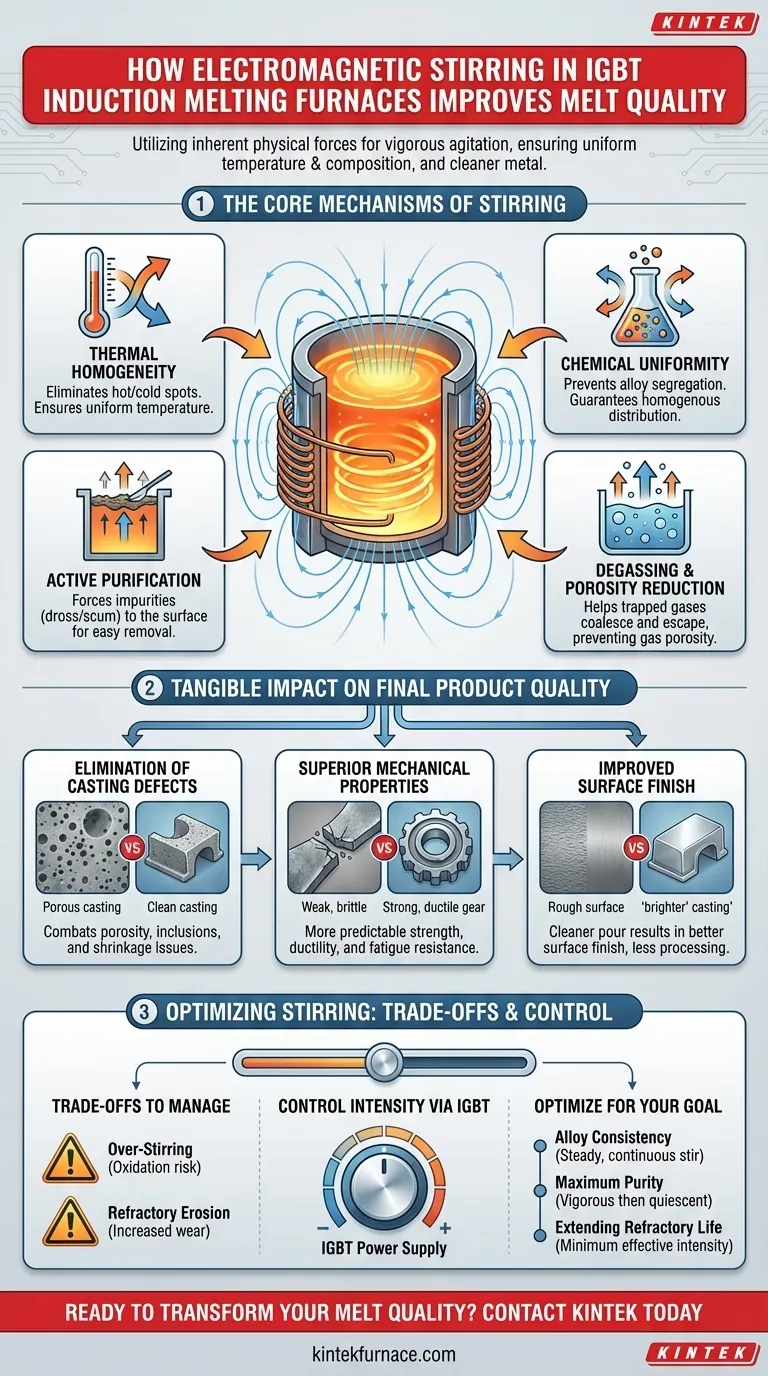
The Core Mechanisms of Electromagnetic Stirring
The benefits of electromagnetic stirring are not a single effect but a combination of several simultaneous physical processes. Understanding these mechanisms reveals why this feature is critical for modern metallurgy.
Achieving Thermal Homogeneity
In any heating process, hot and cold spots can develop. Electromagnetic stirring constantly circulates the molten metal, eliminating these thermal gradients.
This ensures the entire batch reaches and maintains the target temperature uniformly. A consistent temperature is critical for predictable material properties and prevents thermal stress within the melt.
Ensuring Chemical Uniformity
When creating alloys, different elements have different densities and melting points, which can lead to segregation. The stirring force physically blends these elements together.
This action guarantees a homogenous distribution of all alloying agents, from steel and copper to aluminum alloys. The result is a final casting with consistent chemical composition throughout, which is essential for meeting material specifications.
The Process of Active Purification
The rotational flow within the furnace crucible creates a vortex. This motion draws lighter, non-metallic inclusions, slag, and other impurities (known as dross or scum) toward the center and up to the surface.
Once collected on the surface, this dross can be easily skimmed off before pouring. This is an active, self-cleaning process that significantly reduces impurities in the final casting.
Degassing and Porosity Reduction
The same stirring action that moves solid impurities also helps trapped gases coalesce and escape the melt.
By reducing the amount of dissolved gas, such as hydrogen in aluminum, you directly prevent the formation of gas porosity—tiny bubbles that weaken the final cast product. This leads to denser, stronger castings.
The Tangible Impact on Final Product Quality
The refined state of the molten metal directly translates into measurable improvements in the finished product.
Elimination of Casting Defects
A clean, gas-free, and homogeneous melt is the foundation for a defect-free casting. Electromagnetic stirring directly combats common defects like porosity (from trapped gas) and inclusions (from impurities). It also contributes to reducing shrinkage issues by ensuring a uniform cooling process.
Superior Mechanical Properties
Because the alloy composition is perfectly uniform and the material is free from internal voids and impurities, the final product exhibits more reliable and superior mechanical properties. The material's strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance become more predictable and consistent.
Improved Surface Finish
The removal of surface scum and impurities results in a cleaner pour. This leads to what the industry often refers to as "brighter" castings, which have a better surface finish and require less secondary processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, electromagnetic stirring is a process parameter that must be managed correctly to avoid negative consequences.
Over-Stirring and Oxidation
An overly vigorous stir can break the protective layer of slag on the melt's surface. This exposes the molten metal directly to the atmosphere, which can increase gas pickup and oxidation, partially negating the benefits.
Refractory Erosion
The constant, high-velocity flow of molten metal against the furnace walls can accelerate the erosion of the refractory lining. The intensity of the stir must be balanced against the cost and downtime associated with more frequent furnace relining.
Matching Stir to the Alloy
Different metals require different stirring intensities. A light metal like aluminum requires a gentler stir than a dense metal like steel. Using the wrong parameters can be ineffective or, worse, detrimental to the melt quality.
Optimizing Stirring for Your Application
The ability to control stirring intensity via the IGBT power supply is a key advantage. Use this control to match the process to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is alloy consistency: Prioritize a steady, continuous stir throughout the holding phase to ensure all elements remain in a uniform solution before pouring.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Use a vigorous stir during the initial melting and superheating phases to bring impurities to the surface for removal, then reduce the intensity to allow the melt to become quiescent before pouring.
- If your primary focus is extending refractory life: Use the minimum effective stirring intensity required for your specific alloy to achieve homogeneity without causing excessive erosion on the furnace lining.
Ultimately, mastering electromagnetic stirring gives you direct control over the final metallurgical quality of your product.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Outcome |
|---|---|
| Thermal Homogeneity | Eliminates hot/cold spots for uniform temperature |
| Chemical Uniformity | Prevents alloy segregation for consistent composition |
| Active Purification | Forces impurities to the surface for easy removal |
| Degassing | Reduces gas porosity for stronger, denser castings |
Ready to transform your melt quality with advanced electromagnetic stirring?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse foundries and metallurgical labs with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. We can help you optimize your melting process to achieve superior metal purity, homogeneity, and final product quality.
Contact us today to discuss how our IGBT induction melting furnaces can enhance your production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















