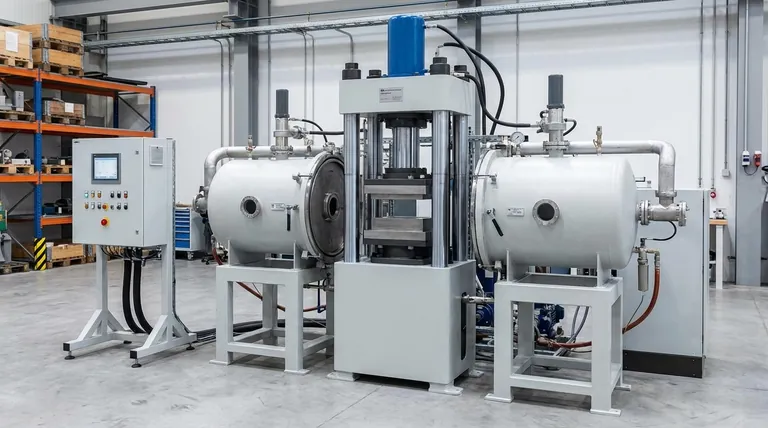
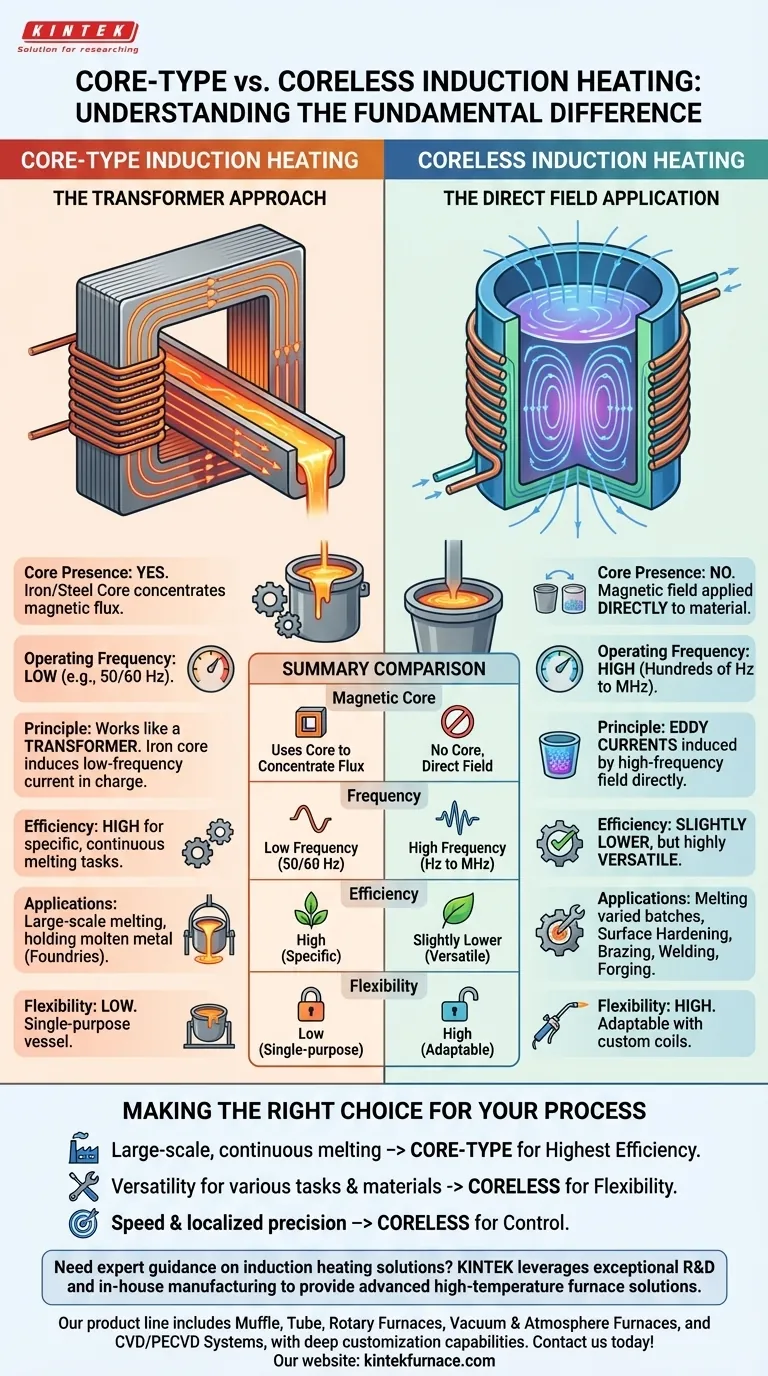
The fundamental difference between core-type and coreless induction heating lies in the presence or absence of a magnetic core. A core-type system uses an iron or steel core to concentrate and guide the magnetic field, operating much like a transformer. A coreless system omits this core, applying the magnetic field directly to the material and compensating for the lower magnetic flux by using a much higher operating frequency.
The choice between core-type and coreless induction heating is a trade-off between efficiency and versatility. Core-type systems are highly efficient for specific, continuous melting tasks, while coreless systems offer unmatched flexibility for a wide range of heating applications.

The Role of the Magnetic Core
At the heart of this technology is the method of energy transfer. The presence or absence of a core fundamentally changes the system's design, operating principle, and ideal use case.
How Core-Type Induction Works
A core-type induction furnace operates on the principle of a transformer. The primary coil is wound around an iron core, and the conductive material to be heated (the "charge") forms a closed loop, acting as the secondary winding.
When AC current flows through the primary coil, the iron core concentrates the magnetic flux and efficiently induces a powerful, low-frequency current in the charge, causing it to heat up. This design is highly efficient for its specific purpose.
The Coreless Approach
Coreless induction heating works by placing the conductive material directly inside a water-cooled copper coil. There is no iron core to guide the magnetic field.
The AC flowing through the coil generates a magnetic field that interacts directly with the workpiece. This induces eddy currents within the material itself, generating precise and rapid heat due to the material's own electrical resistance.
Why Frequency is the Key Differentiator
The absence of a core means the magnetic field in a coreless system is less concentrated, a state known as low flux density.
To generate the same amount of heat, the system must compensate. It does this by operating at a much higher frequency—from hundreds of Hz to several MHz—compared to the low (line) frequencies used in core-type systems. This high frequency is what enables rapid and localized heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right induction method requires an objective look at the advantages and limitations inherent to each design. Your application's needs will determine which set of trade-offs is acceptable.
Efficiency vs. Flexibility
Core-type furnaces are extremely energy-efficient for their designated task, typically large-scale melting and holding of molten metal. However, they are highly inflexible and function essentially as a single-purpose melting vessel.
Coreless systems are the champions of versatility. By simply changing the coil design, you can heat parts of various shapes and sizes for vastly different processes, including surface hardening, brazing, welding, and forging. This flexibility comes at the cost of slightly lower electrical efficiency compared to an optimized core-type system.
Application Scope
Core-type systems, often called channel furnaces, excel at maintaining large volumes of molten metal at a constant temperature. They are a mainstay in foundries for continuous operation.
Coreless systems, or crucible furnaces, are ideal for melting smaller, varied batches of metal and for the precision surface treatments mentioned earlier. Their ability to deliver localized heat makes them incredibly accurate and controllable.
System Complexity and Cost
While both systems require specialized engineering, their complexities differ. Core-type systems are simpler from an electrical standpoint, often running at standard line frequencies (50/60 Hz).
Coreless systems require sophisticated high-frequency power supplies, which can add to the initial cost and complexity of the equipment. Furthermore, the design of the induction coil is critical and often custom-made for the application, which can be a significant engineering expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the primary goal of your industrial process.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous melting of a single metal: A core-type furnace offers the highest efficiency and is purpose-built for this task.
- If your primary focus is versatility for tasks like surface hardening, brazing, or melting varied batches: A coreless system provides the essential flexibility to handle different materials, shapes, and processes.
- If your primary focus is speed and localized heating for precision work: Coreless induction is the superior choice due to its direct field application and excellent controllability.
By understanding this fundamental relationship between the core, operating frequency, and application, you can confidently select the induction technology that best serves your operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Core-Type Induction Heating | Coreless Induction Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Core | Uses iron/steel core to concentrate flux | No magnetic core; field applied directly |
| Operating Frequency | Low frequency (e.g., 50/60 Hz) | High frequency (hundreds of Hz to MHz) |
| Efficiency | Highly efficient for specific tasks | Slightly lower efficiency but versatile |
| Applications | Large-scale continuous melting (e.g., foundries) | Versatile: melting, hardening, brazing, forging |
| Flexibility | Low; single-purpose | High; adaptable with custom coils |
Need expert guidance on induction heating solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in large-scale melting or precision heating, we can help optimize your process. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- What role does Vacuum Hot Press technology play in the automotive industry? Boost EV Batteries, Safety, and Efficiency



















