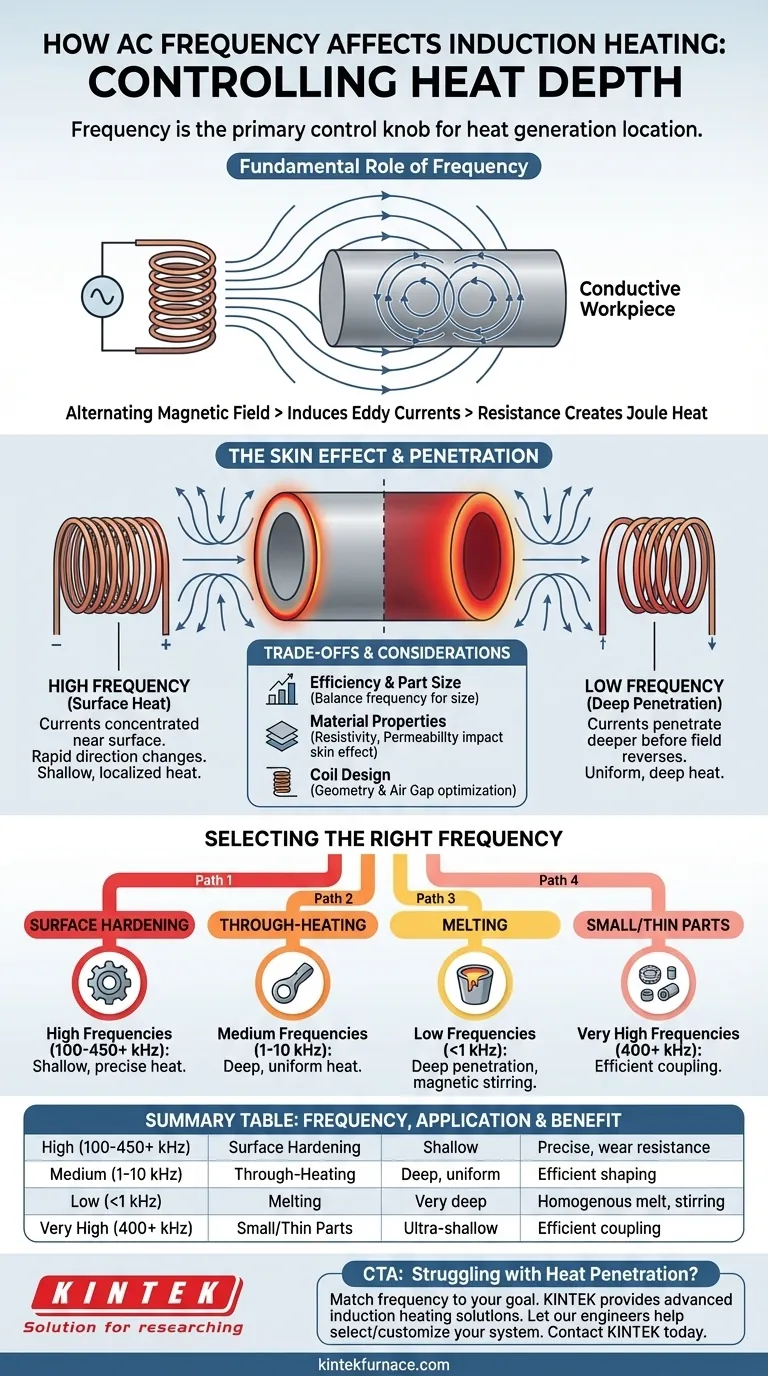
In induction heating, frequency is the primary control knob for determining where heat is generated within a material. The frequency of the alternating current (AC) directly dictates the depth of heat penetration. High frequencies create shallow, surface-level heat, while low frequencies penetrate deeper into the part.
Choosing the right frequency is not about making something "hotter," but about precisely controlling where that heat is generated. The entire efficiency and success of an induction process—from surface hardening a gear to melting a crucible of metal—hinges on matching the frequency to the material and the desired outcome.

The Fundamental Role of Frequency
To understand how frequency controls heat, we must first look at the core mechanism of induction. This process relies on creating a changing magnetic field to generate heat without any physical contact.
The Source: The Alternating Magnetic Field
An induction heating system begins with a coil connected to an alternating current power supply. As AC flows through this coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around it.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a conductive workpiece, such as a piece of steel, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the part. These circulating currents are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
The material of the workpiece has natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance creates friction for the electrons, resulting in intense and localized heat, a principle known as Joule heating.
How Frequency Governs Heat Penetration: The Skin Effect
The frequency of the AC is not just a background detail; it is the critical factor that dictates the behavior of the eddy currents due to a phenomenon called the skin effect.
What is the Skin Effect?
The skin effect is the tendency of alternating current to concentrate near the surface of a conductor. The induced eddy currents are strongest on the workpiece's outer surface and their density diminishes exponentially toward the center.
High Frequencies: Concentrating Heat on the Surface
Higher frequencies cause the magnetic field to change direction more rapidly. This forces the induced eddy currents to flow in a very thin layer at the material's surface, as they don't have time to penetrate deeper before the field reverses.
The result is rapid, concentrated heating in a shallow zone. This is ideal for applications like case hardening, where you need a hard, wear-resistant surface while leaving the core of the part tough and ductile.
Low Frequencies: Driving Heat Deeper
Lower frequencies create a slower-reversing magnetic field. This allows the eddy currents more time to overcome the material's impedance and penetrate further into the part before diminishing.
This produces deeper, more uniform heat distribution. It is the preferred method for through-heating applications like forging, forming, or pre-heating parts for welding. It is also used for melting large volumes of metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Selecting a frequency is a balancing act that involves more than just the desired heat depth. Efficiency and material properties are equally important.
Efficiency and Part Size
For energy to transfer efficiently from the coil to the workpiece, the frequency must be appropriate for the part's size. A frequency that is too low for a very small part will "couple" poorly, leading to inefficient heating as the magnetic field passes through it with little interaction.
Conversely, using a very high frequency on a massive part intended for through-heating is highly inefficient. You will waste energy super-heating the surface while the core remains cold.
Material Properties
The material's electrical resistivity and magnetic permeability also influence the skin effect. Highly conductive materials like copper require different frequency considerations than less conductive materials like steel to achieve the same heating depth.
Coil Design and Coupling
The design of the induction coil itself is inextricably linked to the frequency. The coil's geometry and its distance from the workpiece (the "air gap") must be optimized to create a strong, consistent magnetic field for the chosen frequency and application.
Selecting the Right Frequency for Your Application
Your choice of frequency should be driven entirely by the goal of your heating process. Systems can range from low-frequency (50/60 Hz line frequency) to medium (1-10 kHz) and high-frequency (over 100 kHz into the MHz range).
- If your primary focus is surface hardening or case hardening: Use high frequencies (typically 100 kHz to 450 kHz+) to create a shallow, precise heat zone.
- If your primary focus is through-heating for forging or forming: Use low to medium frequencies (typically 1 kHz to 10 kHz) to drive heat deep into the part uniformly.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of metal: Use very low frequencies (below 1 kHz) to ensure deep penetration and create a magnetic stirring effect for a homogenous melt.
- If your primary focus is heating very small or thin parts: Use very high frequencies (400 kHz and above) to ensure the energy couples efficiently with the small mass.
Mastering frequency control is the key to unlocking the precision, speed, and efficiency of induction heating.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Range | Primary Application | Heat Penetration | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| High (100 kHz - 450 kHz+) | Surface/Case Hardening | Shallow, surface-level | Precise, localized heat for wear resistance |
| Medium (1 kHz - 10 kHz) | Through-Heating (Forging, Forming) | Deep, uniform | Efficient core heating for shaping |
| Low (Below 1 kHz) | Melting Large Volumes | Very deep | Homogenous melt with stirring effect |
| Very High (400 kHz+) | Heating Small/Thin Parts | Ultra-shallow | Efficient coupling with small mass |
Struggling to achieve the right heat penetration for your process? The key to efficient and precise induction heating lies in matching the frequency to your specific material and application goal. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced induction heating solutions. Whether you need a system for surface hardening, deep through-heating, or melting, our expertise ensures optimal frequency control for your unique requirements.
Let our engineers help you select or customize the perfect system. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















