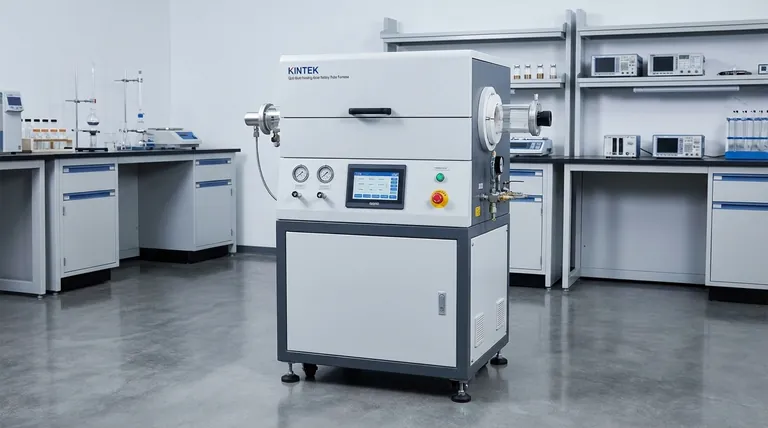
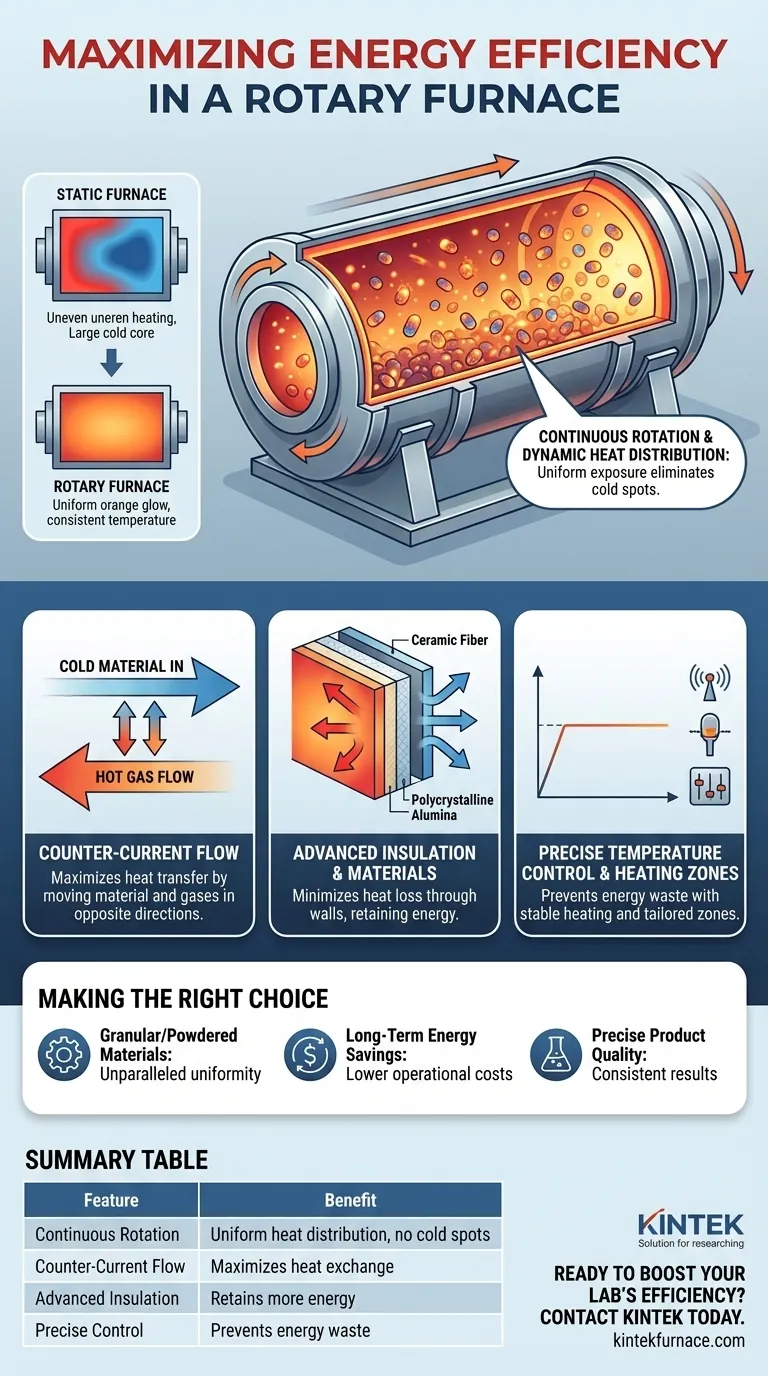
At its core, a rotary furnace maximizes energy efficiency through its defining feature: continuous rotation. This dynamic process ensures every particle of the material being processed is uniformly exposed to the heat source, eliminating the hot and cold spots common in stationary furnaces and dramatically improving the transfer of energy.
The efficiency of a rotary furnace is not the result of a single feature, but a combination of its dynamic heat distribution, intelligent system design like counter-current flow, and the use of advanced materials that minimize heat loss at every stage.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Heat Distribution
The primary advantage of a rotary furnace over a static one is its ability to actively mix the material load. This fundamentally changes how heat is absorbed.
Overcoming the Static Furnace Problem
In a stationary furnace, the material at the bottom and center of the load is insulated by the material on top. This leads to uneven heating, requiring more energy and longer cycle times to ensure the entire batch reaches the target temperature.
The Role of Continuous Rotation
The gentle tumbling action of a rotary furnace constantly brings cooler material from the core of the load to the surface. This exposes new surface area directly to the heat source, whether it's a flame or an electric element.
This constant mixing creates a highly uniform temperature throughout the material batch. No single particle is over- or under-heated, leading to a more consistent and predictable final product.
The Impact on Energy Consumption
Because the heat is transferred so effectively, the furnace can reach and maintain its target temperature with less energy input. The system doesn't need to be "over-fired" to compensate for cold spots, directly reducing fuel or electricity consumption.
Key Design Elements for Maximum Efficiency
Beyond the rotation itself, several key design features work together to prevent energy from being wasted.
Counter-Current Flow for Heat Transfer
Many rotary furnaces employ a counter-current flow design. The solid material moves in one direction through the tube, while the hot combustion gases flow in the opposite direction.
This is exceptionally efficient because it ensures the hottest gases encounter the coldest, incoming material, maximizing the temperature differential and heat transfer. By the time the gases exit the furnace, they have transferred the maximum possible amount of their thermal energy to the load.
Advanced Insulation and Materials
Modern rotary furnaces are built with high-quality insulation, such as ceramic or alumina polycrystalline fibers. These materials have extremely low thermal conductivity, which minimizes the amount of heat that escapes through the furnace walls.
Containing this heat within the chamber means more energy is directed toward the process itself, not lost to the surrounding environment.
High-Performance Heating and Control
Efficiency is also driven by the use of advanced heating elements and precise temperature control systems. These systems allow for rapid temperature ramping and stable maintenance, ensuring no energy is wasted by overshooting the target temperature.
Some designs also feature multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the furnace, allowing for a highly tailored and efficient heating profile for specific applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, the rotary furnace design introduces factors that require careful consideration.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism—including the drive motor, seals, and support system—adds mechanical complexity compared to a stationary furnace. This requires a robust maintenance schedule to ensure long-term reliability.
Material Suitability
The tumbling action that makes a rotary furnace so effective also means it is not suitable for all materials. Materials that are very sticky, prone to breaking, or could be damaged by abrasion may require a different heating solution.
Initial Cost vs. Operational Savings
Rotary furnaces often have a higher initial capital cost than simpler stationary models. However, their significant reduction in energy consumption typically results in lower operational costs, providing a strong return on investment over the lifetime of the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace depends on balancing efficiency goals with process requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing granular or powdered materials: A rotary furnace is ideal, as its dynamic mixing provides unparalleled heating uniformity for these material types.
- If your primary focus is maximizing long-term energy savings: The combined effect of uniform heating, counter-current flow, and superior insulation makes the rotary furnace a leading choice for reducing operational costs.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise, repeatable product quality: The exceptional temperature control and consistency delivered by a rotary furnace minimize process variability and improve final product outcomes.
Ultimately, a rotary furnace represents a sophisticated approach to thermal processing, engineered to convert more of your energy input directly into valuable work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Rotation | Ensures uniform heat distribution, eliminating cold spots and improving energy transfer |
| Counter-Current Flow | Maximizes heat exchange by moving materials and gases in opposite directions |
| Advanced Insulation | Minimizes heat loss through walls, retaining more energy for the process |
| Precise Temperature Control | Prevents energy waste by maintaining stable heating without overshooting |
| Multiple Heating Zones | Allows tailored heating profiles for specific applications, enhancing efficiency |
Ready to boost your lab's energy efficiency and cut costs? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discover how our rotary furnaces can deliver superior performance and long-term savings for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















