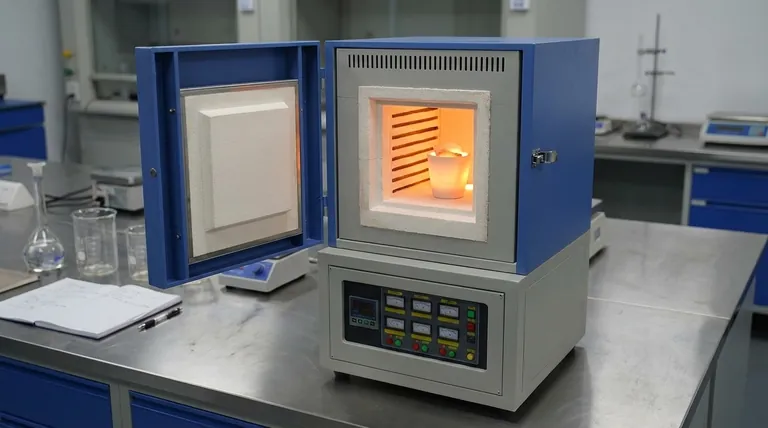
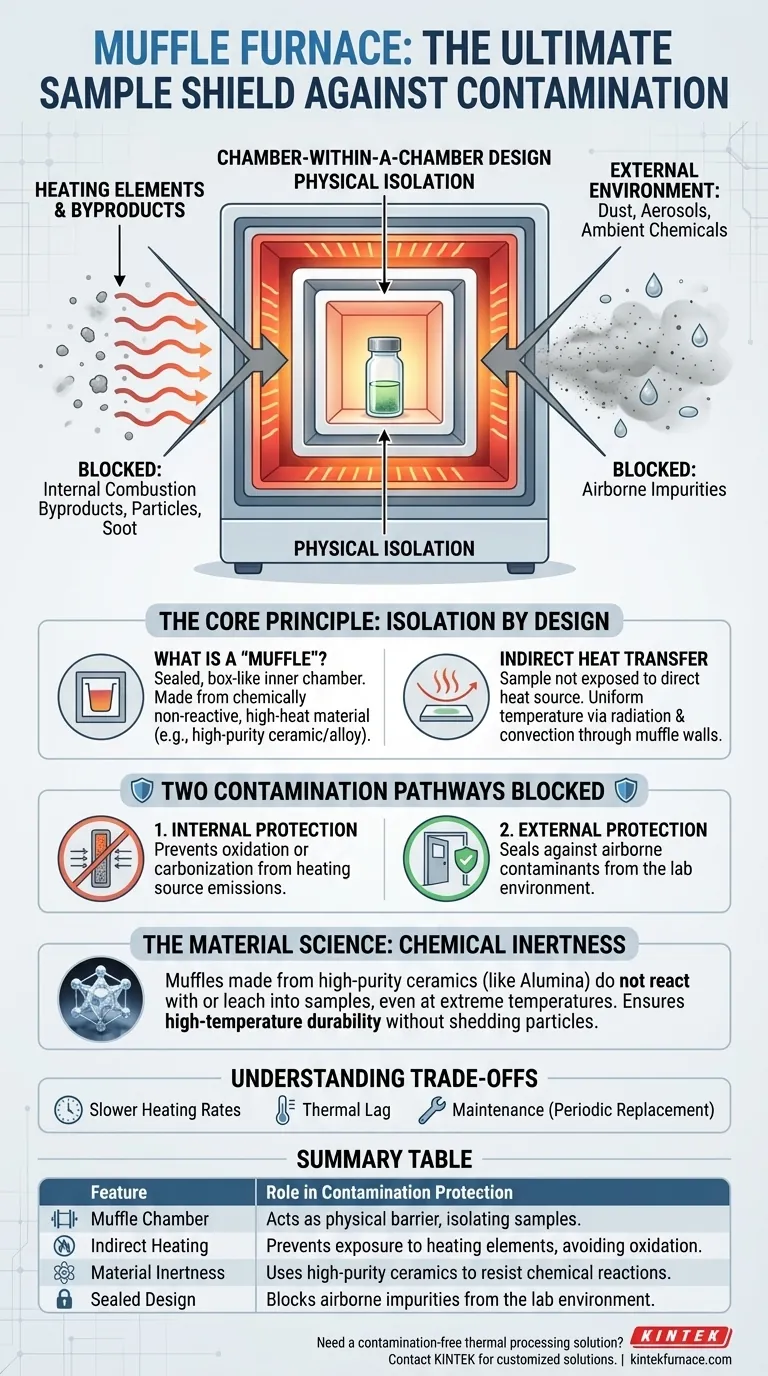
At its core, a muffle furnace protects samples from contamination by using a design principle of physical isolation. It places the sample inside an inner chamber, the "muffle," which acts as a complete barrier, separating it from both the external environment and the furnace's own heating elements or combustion byproducts.
The furnace's protective power comes from its "chamber-within-a-chamber" design. The inner muffle shields the sample from airborne impurities and, critically, from reactive gases generated by the heating source itself, ensuring a chemically pure processing environment.

The Core Principle: Isolation by Design
A muffle furnace is fundamentally different from a simple oven. Its unique construction is engineered specifically to prevent unwanted chemical interactions.
What is a "Muffle"?
The "muffle" is the central component—a sealed, box-like inner chamber where the sample is placed. It is made from a heat-resistant and chemically non-reactive material, such as a high-purity ceramic or a special metal alloy.
Separating Heat Source from Sample
This muffle is then placed inside the larger, insulated furnace, which contains the heating elements or, in fuel-fired models, the flame. This design ensures the sample is never directly exposed to the heat source.
Heat transfers indirectly through the walls of the muffle via radiation and convection, providing uniform temperature without physical contact or exposure to combustion gases.
Two Contamination Pathways Blocked
This isolation strategy effectively blocks the two main routes through which a sample can become contaminated during thermal processing.
1. Protection from Internal Byproducts
In many furnaces, the process of generating heat creates chemical byproducts. For example, gas-fired furnaces produce exhaust, and even electric elements can shed microscopic particles.
The muffle acts as an impermeable barrier, preventing these combustion byproducts, soot, or element particles from reaching the sample. This is critical for preventing unwanted oxidation or carbonization of sensitive materials.
2. Protection from the External Environment
The enclosed nature of the entire furnace assembly seals the muffle and the sample from the outside lab environment.
This prevents airborne contaminants like dust, aerosols, or other ambient chemicals from entering the chamber and compromising the purity of the sample.
The Material Science of the Muffle
The choice of material for the muffle itself is a critical part of the contamination control strategy.
Chemical Inertness
Muffles are typically constructed from materials like alumina or other high-purity ceramics. These materials are chosen for their chemical inertness, meaning they will not react with or leach into the sample, even at extreme temperatures.
High-Temperature Durability
The materials must also withstand severe and repeated thermal cycling without cracking, degrading, or shedding particles. This ensures the muffle itself does not become a source of contamination over its operational lifetime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the muffle furnace design does involve certain compromises that are important to recognize.
Slower Heating Rates
Because heat is transferred indirectly to the sample through the muffle walls, the overall heating process can be slower compared to a furnace where the sample is exposed directly to the heating elements.
Thermal Lag
The muffle itself has thermal mass, meaning it will heat up and cool down more slowly. This can introduce a slight delay in temperature response, which may be a factor in processes requiring rapid temperature changes.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Over time and many cycles, the muffle can degrade, especially if exposed to aggressive vapors from the samples. It must be inspected and replaced periodically to prevent it from becoming a contamination source itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding these principles allows you to leverage the muffle furnace for optimal results based on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or chemical reactions: The muffle's separation from combustion gases and its ability to hold a controlled atmosphere are the most critical features.
- If your primary focus is maintaining high purity for trace analysis: The physical barrier against airborne dust and the chemical inertness of the ceramic muffle material are your key safeguards.
- If your primary focus is processing fragile materials: The indirect, uniform heating method prevents thermal shock and damage that can be caused by direct exposure to heating elements.
By mastering its design, you ensure the integrity of your process and the reliability of your results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Contamination Protection |
|---|---|
| Muffle Chamber | Acts as a physical barrier, isolating samples from external and internal contaminants. |
| Indirect Heating | Prevents exposure to heating elements and combustion byproducts, avoiding oxidation. |
| Material Inertness | Uses high-purity ceramics like alumina to resist chemical reactions with samples. |
| Sealed Design | Blocks airborne impurities such as dust and aerosols from the lab environment. |
Need a contamination-free thermal processing solution? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnaces with advanced isolation designs to protect your samples. Our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems are backed by deep customization to meet your unique lab needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your experimental purity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















